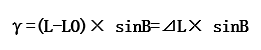Function description
Three norths are usually considered in surveying: True North, Grid North, and Magnetic North. In some medium scale maps and small scale maps, all of three norths are required.
Grid North
Grid north refers to the direction northward along the grid lines of a map projection. In the transverse Mercator projection, grid north points the direction that the vertical axis points.
True North
True north is the direction along the Earth’s surface towards to the north pole. In terms of a map, true north is the north direction of the central meridian.
In the transverse Mercator projection, except the central meridian, other meridians are projected to curves. The angle between a meridian and the corresponding vertical axis is the convergence of meridian.
The convergence of meridian
The convergence of the meridians at any point of the earth ellipsoid is the angle between the tangent to the meridian at the point and the central meridian in the projected zone. That is the angle between grid north and true north in the Gauss plane coordinate system. The convergence angles are positive when points locate in the East of Central Meridian while negative when points locate in the West of Central Meridian.
The convergence of the meridians can be obtained through a formula or a table. iDesktop can calculate out the convergence angles with the coordinates of a map center.
Formula
Given the geographic coordinates of a point (B, L). iDesktop can calculate the convergence angle using the formula which is from the book Principles and Methods of Digital Mapping published by China University of Mining and Technology Press.
L: longitude. LO: the longitude of the central meridian. ΔL: the longitude difference that is the difference between the longitude of a point and the prime meridian. B: latitude.
For instance, a central point P of a map has coordinates B=18°18’32.82820” and L=109°18’36.94903”. the convergence angle is LO=6°19-3°=111° y=(109°18’-111°) sin18°18’32.82820”=-0°31’50.59”.
Magnetic North
Magnetic North is the direction that compass needle points to. The magnetic north pole and south pole are near rather than coincident with the true north pole and south pole.
The North Magnetic Pole is the wandering point on the surface of Earth’s Northern Hemisphere at which the planet’s magnetic field points vertically downwards. It is distinct from Geographic North Pole. The North Magnetic Pole moves at the speed of 20.5 meters per day.
Magnetic declination
Magnetic declination is the angle on the horizontal plane between magnetic north and true north. The magnetic declination is positive if magnetic north is east of true north and negative when it is the west of true north.
The magnetic declination can be measured by some instruments.
In general, cartographers need to add the magnetic declination in their maps. iDesktop asks you to enter the measured declination and then it can label magnetic north automatically.
You can get the declination according to data provided by The World Magnetic Model. But you need to enter time, longitude, and latitude. Models provided in The World Magnetic Model are updated per five years. The models now will expire on December 31, 2019. For more specific information, please consult The World Magnetic Model.
Basic steps
- In your map layout select the map which is required to add a compass.
- Click Object Operations > Drawing group > North Arrow > Three North Arrow.
- Click and drag your mouse at an appropriate position to draw three norths. iDesktop will calculate the convergence and label the truth north but the declination which needs specifying.
Note : iDesktop can’t draw three norths on a plane coordinate system map.
- Double click on three norths to open the North Arrow Properties panel where you can set each parameter to a valid value.
- Meridian Convergence: its value is calculated by iDesktop automatically and not editable. If there are no central meridians on the current map, the convergence value is 0. True north is coincident with north of the map.
- Magnet Angle: 0 is by default and unit is degree. You need to set it to a correct value. iDesktop will draw magnetic north according to it and true north.
- You can change the size of the three-north compass by setting its rotation, width, and height. For more details about parameters, please refer to Draw Compass.