Function Introduction
Vegetation plays an important role in the global ecological system. Using remote-sensing images to acquire vegetation information becomes an important direction to research climate and ecological change.
- NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) can extract vegetation from water and soil. It can reflect the variation of vegetation-covered area. It is the best indicator to growth state and coverage of vegetation. NDVI, acquired by satellite images like SPOT/VEGETATION and MODIS, can be used in vegetation monitoring, land use, vegetation variation detection, Herbage yield assessing, drought monitoring, and so on.
- NDVI is obtained based on the reflectance values of the near-infrared band and red band. The formula is NDVI=(NIR-R)/(NIR+R)**. Among them, NIR is the reflectance value of the near-infrared band, and R is the reflectance value of the red band.
- NDVI ranges from -1 to 1.
- Negative value means surface features are things that has high reflection to visible light like water, snow, and cloud.
- 0 indicates there are rocks or bare soil. NIP is equal to R approximately.
- Positive value denotes there is vegetation. The greater the value, the greater the vegetation coverage.
Data Description
We can calculate vegetation index and water index according to multiple kinds of remote-sensing data. At present, the calculation of NDVI/NDWI based on satellite images like TM, SPOT/VEGETATION, MODIS has applied to many types of research like detecting vegetation changes. This article helps us know about the types of remote-sensing data and distinguish the meaning of each band.
- Each TM satellite image includes 7 bands. Band2 denotes green band, Band3 means red band, and Band4 represents near-infrared band. Then NDVI=(Band4-Band3)/(Band4+Band3); NDWI= (Band2-Band4)/(Band2+Band4).
- For SPOT-5 satellite images, Band1 denotes near-infrared band; Band2 means red band; Band2 means green band. Then: NDVI=(Band1-Band2)/(Band1+Band2), NDWI= (Band3-Band1)/(Band3+Band1).
- Each Landsat 8 OLI image includes 9 bands. Among them, Band3 means green band; Band4 means red band; Band5 denotes near-infrared band. Then: NDVI=(Band5-Band4)/(Band5+Band4), NDWI=(Band3-Band5)/(Band3+Band5).
Operation Instructions
Function Entrance
- Click Data tab > Data Processing > Raster > NDVI.
- Click Toolbox > Data Processing > Raster > NDVI. (iDesktopX)
Parameter Description
- Red band : Select the red band involved in the calculation. You can specify a single-band (red band) dataset or the red band of a multi-band dataset.
- Near-infrared Band : Select the near-infrared band involved in the calculation. You can specify a single-band (near-infrared band) dataset or the near-infrared band of a multi-band dataset.
- Result Data : Specify a datasource to save the resulting dataset. The program will produce a raster dataset as the NDVI expression based on the red band and near-infrared band.
Applications
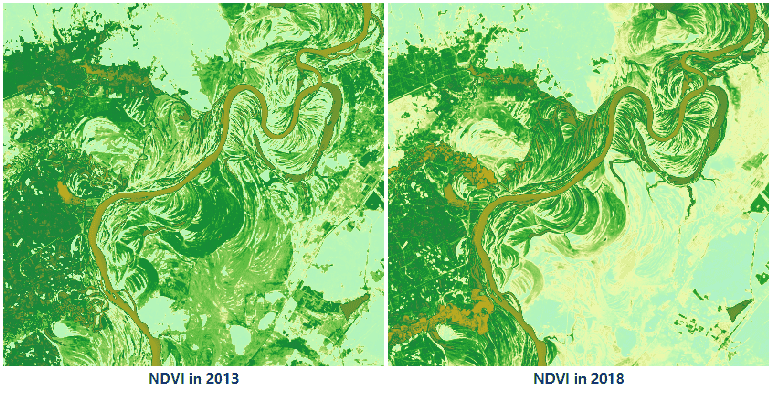
Given two groups of Landsat 8 satellite image data. One is in June of 2013 and another one is in June of 2018. NDVIs of these two years are obtained through calculating. Compared to vegetation-covered variation, we can find vegetation coverage in 2018 is lower than in 2013.