Commonly used coordinate systems in China include: Beijing Geodetic Coordinate
System l954, Xi’an Geodetic Coordinate System 1980, World Geodetic System-1984
Coordinate System and China Geodetic Coordinate System 2000. Following table
list relative parameters:
| Coordinate system | Reference ellipsoid | Semi-major axis | Flattening |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing Geodetic Coordinate System l954 | Krasovsky | 6378245 | 1: 298.3 |
| Xi’an Geodetic Coordinate System 1980 | IAG-75 ellipsoid | 6378140 | 1: 298.257 |
| WGS 84 | WGS 84 | 6378137 | 1: 298.257223563 |
| China Geodetic Coordinate System 2000 | CGCS2000 | 6378137 | 1: 298.257222101 |
Because of all coordinate systems are based on different reference ellipsoids or different geodetic datums, a point on the Earth has different coordinate values on different coordinate system. When converting or transforming from one coordinate system to another, you must to know about whether a conversion will be happened among the same reference ellipsoid or a transformation will be done from one reference ellipsoid to another. For example, both Geodetic Coordinate of Beijing Coordinate System l954 and Plane Rectangular Coordinate of Beijing Coordinate System l954 are based on the same reference ellipsoid, hence the conversion between them is rigorous. However, Beijing Coordinate System l954 and China Geodetic Coordinate System 2000 are based on different reference ellipsoids, the translation between them is imprecise without a set of certain parameters being used. So, the transformation models are necessary, and you need to get the transformation parameters through transforming datums, and then perform the coordinate conversion based on the same datum.
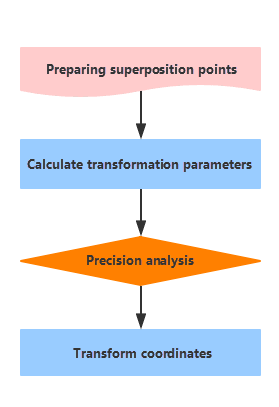
Technology Process of Coordinate Conversion
- Preparation : Gather and organize all data for converting or transforming, and then pick up the superposition points which should be reliable, high-precision, and even-distributed to cover all areas.
- Transformation parameters : According to the obtained superposition points and transformation conditions, determine the transformation model. For the redundant coincident points, take the least square method as the constraint condition.
- Precision Analysis : According to the transformation parameters, calculate target coordinates of superposition points and then analyze the transformation residuals which are the differences between the calculated coordinates and the actually given coordinates. With the transformation residuals, calculate errors thereby assess the coordinate transformation precision. Based on the error tolerance (3 times of error) determine which superposition points can not be adopted and should be abandoned.
- Coordinate system transformation : Calculate target coordinates of other features according to the final qualified parameters.
Note : Maybe you want to know following questions before performing the transformation.
- How to select superposition points?
- [How to select the transformation model?](TransformationModel)