In terms of data management, since data is generally stored and managed based on a certain data model, and data models usually include many specific sub-data models, such as points, lines, polygons, networks, mosaic datasets, etc. Therefore, the first step of data migration is to replace other data models with the data models provided by SuperMap. Additionally, these data are stored in personal, file, or database formats, so it is necessary to convert these storage media from other platforms to the corresponding databases provided by SuperMap for storage.
Therefore, data migration is divided into Data Model Migration and Geodatabase Migration.
Data Models
ArcGIS Data Models
Geodatabase is a data model that uses standard relational database technology and an object-oriented approach to represent geographic information. It supports storing and managing geographic information in standard database management system (DBMS) tables, organizing geographic data according to a hierarchical data object structure, including object classes, feature classes, and feature datasets, etc. Geodatabase can be seen as a data management model that integrates the storage and management of vector, raster, address, network, projection, and other data, and its representation of geographic spatial features is close to human cognition of the real world.
SuperMap Data Models
In SuperMap GIS, datasets are used to store spatial objects of the same type and are one of the basic organizational units of spatial data. Currently, various types are supported, including point datasets, line datasets, region datasets, tabular datasets, network datasets, CAD, text datasets, route datasets, images, raster datasets, etc. For a detailed description of SuperMap data models, please refer to SuperMap SDX+ Spatial Data Model.
Supported Data Types for Migration
| ArcGIS Data Model | SuperMap Data Model | Support Status |
| Point (Feature Class) | Point Dataset | √ |
| Line (Feature Class) | Line Dataset | √ |
| Polygon (Feature Class) Donut Polygon | Region Dataset | √ |
| Annotation | Text Dataset | √ |
| Mosaic Dataset | Mosaic Dataset | √ |
| Geometric Network | Network Dataset | √ |
| Network Dataset | Network Dataset | √ |
| Raster Image | Raster Dataset | √ |
| Table | Tabular Dataset | √ |
| Relationship Class | Relation Dataset | √ |
Supported Data Attributes for Migration
In ArcGIS, if data such as feature classes, attribute tables, or feature classes in feature datasets have configured domain and subtype information, these domain and subtype information will be automatically retained and synchronously migrated when migrating to SuperMap.
| ArcGIS Data Attribute | SuperMap Data Attribute | Support Status |
| Attribute Domain | Range | √ |
| Subtype | Subtype | √ |
| M Value | M |
√ (Only supported for GDB and SHP data) |
As shown in the figure below, when migrating a coastline land class management data, the domain information in the data is migrated together.
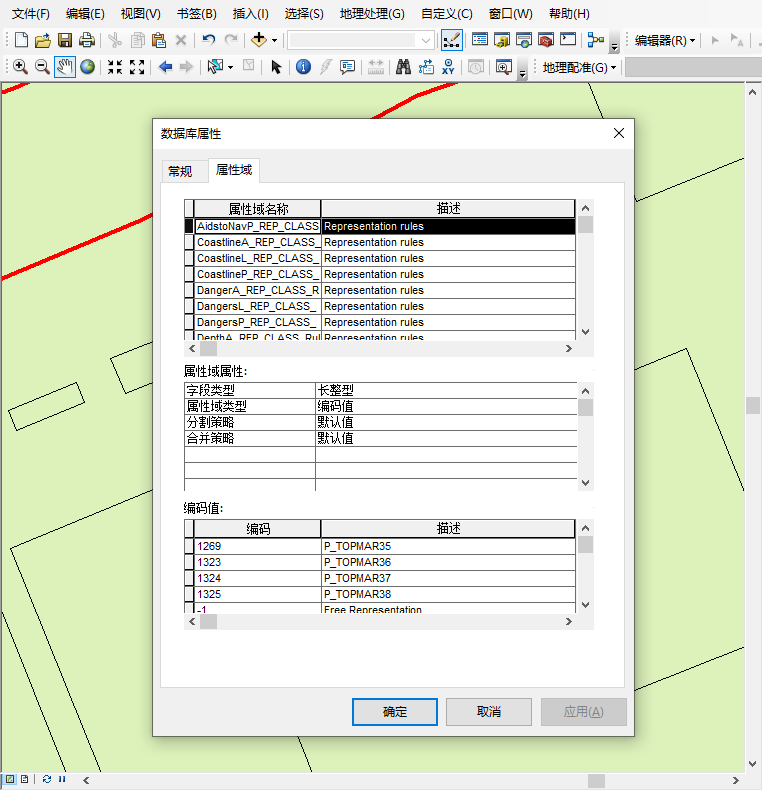 |
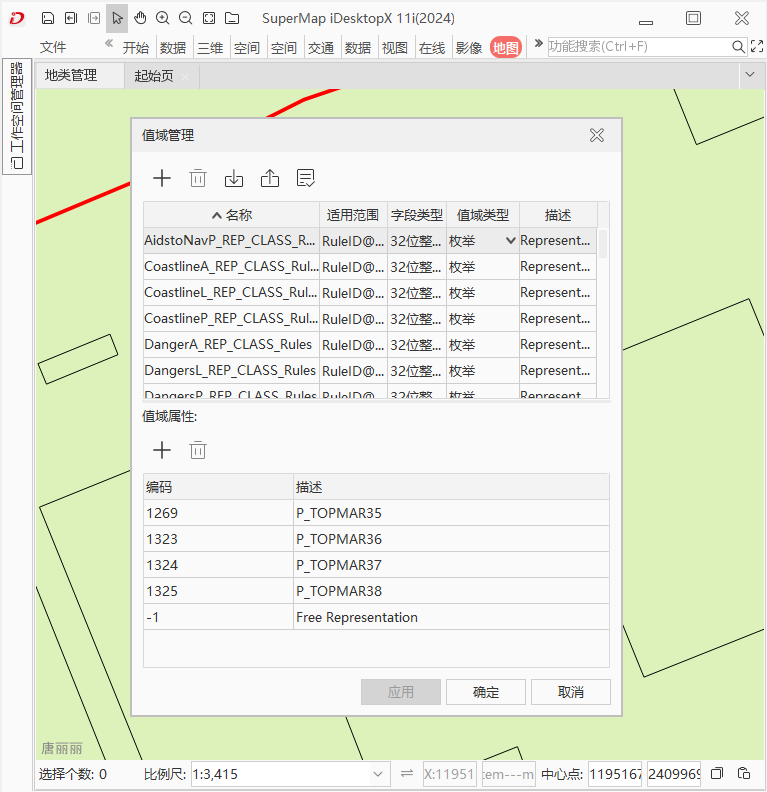 |
| Figure: Domain Information Before Migration | Figure: Domain Information After Migration |
Geodatabase
ArcGIS Geodatabase
ArcGIS geodatabase types include personal geodatabase, file geodatabase, and enterprise geodatabase.
- Personal Geodatabase: It is the source data format of ArcGIS geodatabase stored and managed in Microsoft Access data files. The maximum size of this data file is 2 GB, and it is only applicable to Windows operating systems.
- File Geodatabase: It is a collection of various types of GIS datasets stored in file system folders, with each dataset saved as a file. The file size can be expanded up to 1 TB.
- Enterprise Geodatabase (ArcSDE): It is a collection of various types of GIS datasets stored as tables in relational databases, with no limitations on size and number of users. This type of database uses Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, IBM Informix, or PostgreSQL stored in relational databases.
SuperMap Geodatabase
SuperMap SDX+ is a spatial database engine. It enables the integrated storage of GIS spatial geometry data and attribute data into various relational databases, providing capabilities such as data editing, index management, and spatial queries. For a detailed description of SuperMap SDX+, please refer to SuperMap SDX+ Spatial Data Engine Topic Introduction.
- File-based Engine
The file engines supported by SuperMap SDX+ include: SuperMap's custom UDB/UDBX engine, Shapefile file engine, original image files engine, vector tile file engine, etc. Among them, UDBX is an extension and enhancement of SuperMap's custom UDB engine, offering more stable functionality. The UDB engine is the only file-based spatial data engine in SuperMap Objects' custom format. A UDB engine data project includes two files: a file with the extension UDB stores spatial data using OLE compound document technology, and a file with the extension UDD is the attribute database using SQLite database format. Since UDB/UDBX files use compound document technology, they support both vector data and image data storage.
- Database Engine
The database engines supported by SuperMap SDX+ primarily target relational database management systems such as Oracle, SQL Server, Kingbase, as well as Alibaba POLARDB and Huawei GaussDB databases. It also adapts to support the native spatial engine PostGIS in PostgreSQL.
Supported Database Types for Migration
| ArcGIS Geodatabase | SuperMap Geodatabase | With A License | Without A License | ||
| Personal GDB | File-based/Database | √ | √ | ||
| File GDB | File-based/Database | √ | √ | ||
| ArcSDE | Oracle | ST_Geometry | File-based/Database | √ | × |
| SDO_Geometry | File-based/Database | √ | × | ||
| Oracle Spatial | File-based/Database | √ | × | ||
| PostgreSQL | ST_Geometry | File-based/Database | √ | × | |
| PostGIS | File-based/Database | √ | × | ||
Related Topics



