Instructions for Use
A map series is a collection of map pages generated by applying a single layout and traversing a set of map bounds. For example, using a regular polygon grid layer as the index layer, a map series can easily create a set of pages covering a town area with equal area, as shown in the following figure:
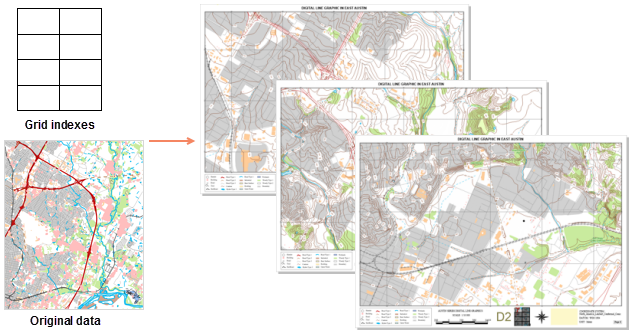 |
Before starting a map series, you need to insert a map in the layout. The layout size of the map frame defines the display scale of the map in the series layout pages. The visible bounds of the map in each page of the series will be centered on the center of the index feature and support setting various different map visible bounds.
If users need to output layout pages strictly according to the grid size, please adjust the layout size of the map frame appropriately. For details on inserting a map frame and selecting a fill map, please refer to Drawing Maps.
Through the above operations, the "Map Series Settings" panel will pop up. Check the Enable checkbox to enable the map series. Deselecting this checkbox will disable the map series function.
Function Entry
- Features Tab -> Series -> Map Series Settings.
Parameter Description
- Map Index:
- Index Map: To create a map series, you will need to select a map from the index map drop-down menu. This drop-down menu displays all map frames in the layout. Only one map can be selected at a time. The map bounds of the map frame will change accordingly for each page in the series. These map bounds are driven by the spatial range of features within the index layer.
- Index Layer: Defines the geographic range of the map frame for each page in the series. The index polygon objects in the index layer are used to control or define each page in the series.
The Create Grid Index function can help you create an index layer. The first layer in the map is selected by default. If you do not wish to use this layer as the index layer, you can select another layer from the drop-down menu.
The index layer can be grid data or other polygon layers in the map. When a polygon layer is selected, the index bounds are based on the spatial envelope rectangle of the objects. For example, you can use an administrative boundary polygon layer to create a "series of pages," where a corresponding page will be created for each administrative division.
- Index Field: The map series traverses the polygon objects in the index layer, and after each page is defined, the attribute value from the index field is used as the page name. Page names accept null and duplicate values, but to avoid confusion when processing series pages, it is recommended to use a name field where all values are unique for the index field settings.
This drop-down menu displays a list of available fields in the index layer, including short integer, long integer, and text fields. The default field is the first field that uses the text "name." If there is no field using "name," the system will default to the first available valid field. You can choose to use another field from the drop-down menu.
- Current Page: By default, the first field page name in the index field is displayed. You can select a page from the drop-down list to navigate to the corresponding page.
- Map Bounds: Provides three methods to set the visible bounds of the map in each page: optimal range, center and fix scale, and use field scale.
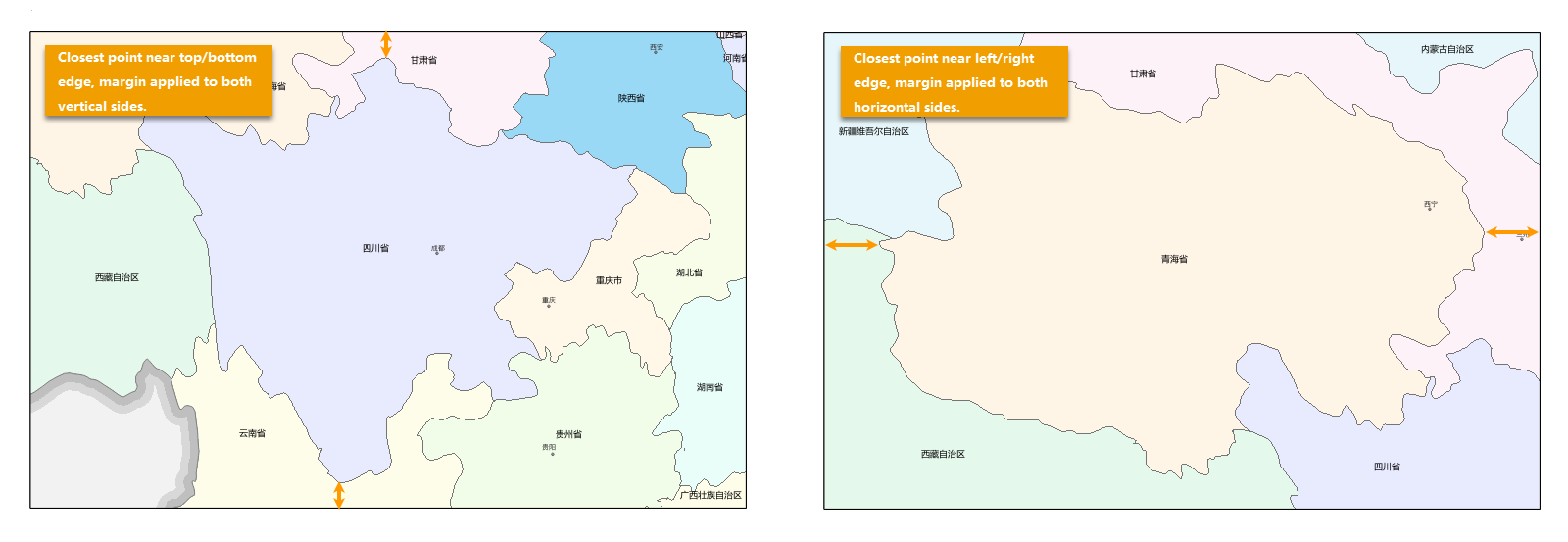
- Optimal Range: The optimal range option is used to set the margin between the map frame edge and the point of the index object closest to that edge. If the closest point is nearest to the left or right side of the map frame, the margin will be set along the horizontal axis. If the closest point is nearest to the top or bottom edge of the map frame, the margin will be set along the vertical axis. Three margin units are provided: percentage, page units, and map units.
- Percent: The percentage is relative to the longest side of the minimum bounds of the index object. A margin size value of 0% means no margin, so the top and bottom or left and right edges of the object will align with the map frame, depending on the position of the closest point. A value of 100% means the margin is half the length of the longest side of the object's bounds; when the margins on both sides are added together, the result will equal the distance of the longest side of the object's bounds. The default setting is 10%.
- Map Unit: Provides five common map units: meters, kilometers, yards, feet, and miles. The set value will be applied to each side of the horizontal or vertical axis, depending on the position of the closest point.
- Page Units: Provides four common page units: points, inches, millimeters, and centimeters. The set value will be applied to each side of the horizontal or vertical axis, depending on the position of the closest point.
- Center and Fix Scale: Selecting this option means the map frame for each page in the series will be centered on the index object, maintaining a constant map scale. You can input another scale, or use the drop-down button to select the map's fixed scale or system scale, or choose Custom from the drop-down menu to pop up the custom scale dialog to set a new scale.
- Use Field Scale: Specifies a field in the index data set as the denominator value of the scale bar. Centered on the center point of the index object, the map box is scaled for each page in the map series based on the field value of each object. Only numeric fields can be selected. If the field value is negative, the system will automatically take its absolute value; if the field value is 0 or null, the field value of the previous object will be used automatically.
- Optimal Range: The optimal range option is used to set the margin between the map frame edge and the point of the index object closest to that edge. If the closest point is nearest to the left or right side of the map frame, the margin will be set along the horizontal axis. If the closest point is nearest to the top or bottom edge of the map frame, the margin will be set along the vertical axis. Three margin units are provided: percentage, page units, and map units.
- Map Locator: When a map expresses details of a small range, its spatial location is often difficult to determine. Providing a map locator offers a reference for map users, i.e., a method to display the range of another map frame within a map frame. The range displayed by the locator map is larger than that of the main map, enabling map browsers to quickly locate and identify the spatial position of the current map within a larger area. For example, the locator map might show the position of a province (main map bounds) within a country (locator map bounds). For details, please refer to the Drawing Map Locator document.
- Locator Map: The locator map is based on the index map. By copying the index layer, two new layers are created to form a new map. The two layers created and edited for it are: the mask layer and the marker layer.
- Marker Layer: Used to highlight features in the locator map that are located in the current map page.
- Mask Layer: Used to dim map features in the locator map that are not intended to be highlighted. These are features not in the current page.
Next, you can add operations such as Dynamic Text and Drawing Map Locator to the series layout.
Related Topics



