In SuperMap, data coordinate systems are classified into three categories: planar coordinate system, geographic coordinate system, and projected coordinate system.
Planar Coordinate System
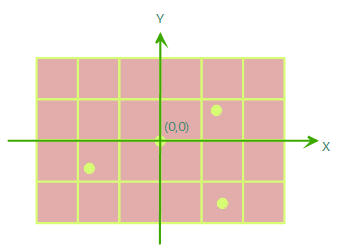
Generally used as the coordinate reference for data unrelated to geographical locations, and also serves as the default coordinate reference for newly created data, such as CAD designs, scanned paper maps, or schematic diagrams without geographical significance. A planar coordinate system is a two-dimensional system with origin coordinates (0,0), where each point's position is determined by its distance from the horizontal X-axis and vertical Y-axis.
Geographic Coordinate System
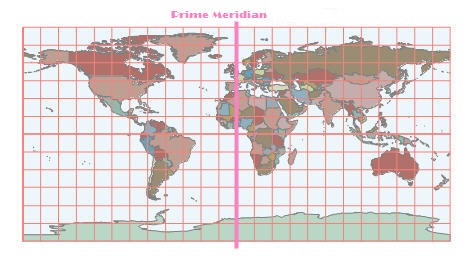
Uses latitude and longitude coordinates to represent any point on an ellipsoid. A geographic coordinate system typically includes definitions of horizontal datum, prime meridian, and angular units. Commonly used systems include WGS 1984, Beijing 1954, and Clarke 1866. For example, KML data in Google Earth and GPS-collected data use WGS 1984 coordinate system, while geodetic control points in China may use Xi'an 80 or Beijing 1954. The image shows a world map in WGS 1984 coordinate system.
Projected Coordinate System
Projects any point on an ellipsoid to a plane through specific projection methods. Uses two-dimensional planar coordinates (X,Y) to represent spatial features. A projected coordinate system typically contains definitions of geographic coordinate system, map projection, parameters, and distance units. Common systems include Gauss-Kruger, Albers, Lambert, and Robinson. Projected geographic data enables map measurements, spatial analysis, and cartographic representation. For instance:
- Chinese basic-scale topographic maps: 1:1,000,000 scale uses Lambert projection, while most others use Gauss-Kruger 6° or 3° zonal projections
- Urban planning large-scale maps (1:500, 1:1000) for road construction and architectural designs often use planar coordinate systems
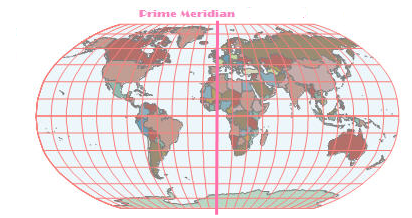
The image shows a Robinson projection of the original WGS 1984 world map.
Related Topics
Reference System Conversion Methods



