Instructions for use
A heat map is a map representation that intuitively displays data (such as crowd distribution, density, change trends, etc.) through color distribution, suitable for showing data that is difficult to understand or express, such as density, frequency, temperature, etc.
Only point datasets are supported for creating heat maps. By establishing buffers for each discrete point and filling them with a progressive grayscale band (0~255) from the inside out and light to dark, overlapping buffer areas accumulate grayscale values, where higher values indicate "hotter" regions. Using the accumulated grayscale value as an index, colors are mapped from a 256-color band (e.g., rainbow colors) and recolored, typically using cool to warm colors to represent point density from low to high. Alpha Channel must be enabled during rendering.
Heat maps not only reflect the relative density of point features but can also express density distribution more accurately through attribute weighting (e.g., point weights). Additionally, heat maps are dynamic raster surfaces that update with map zooming, such as a national tourist attraction heat map displaying provincial or local passenger flow distribution when zoomed in.
Function Entries
Select the point data layer for creating a heat map in the layer manager:
- On the Thematic Map tab -> Aggregation Map group -> click the Heat Map button.
- Right-click and select Create Thematic Map ... from the context menu. In the Create Thematic Map dialog, choose Aggregation Map->Heat Map.
Operation Steps
- A heat map thematic layer is generated in the layer manager.
- Select the heat map layer, right-click the Modify Thematic Map command. The Layer Properties panel appears on the right side of the map, displaying current heat map settings.
- Modify basic functions like display control and change dataset in the Layer Properties panel.
- Display Control: View and set layer visibility, layer name, layer caption, transparency, and maximum/minimum visible scales.
- Visibility: In the layer properties panel, uniformly set visibility for all layers in a layer group. Check the Visible checkbox to make all layers visible; uncheck to hide all layers.
- Layer Name: Displays the name of the selected layer group. Group names cannot be modified and serve as unique identifiers in the map.
- Layer Caption: The text box on the right shows the caption of the selected layer group. Modify the caption to change the display name in the layer manager without altering the group name.
- Transparency: Use the numeric adjustment box and spinner to set the current layer's transparency. Input values directly or use the spinner to adjust transparency in real time. Default is 0 (fully opaque); higher values increase transparency up to 100 (fully transparent). Values range from 0 to 100.
- Minimum Visible Scale: Set the minimum visible scale for all layers in the group. If the map scale is smaller than this value, all layers become invisible. Enter a scale value (e.g., 1:500000) in the adjustment box, set the current map scale, or use the dropdown to select from default scales (1:5000 to 1:1000000) or fixed scales if set.
- Maximum Visible Scale: Set the maximum visible scale for all layers in the group. If the map scale exceeds this value, all layers become invisible. Input a scale value, set the current map scale, or use the dropdown for predefined scales.
- Change Dataset: Click the dropdown arrows next to Datasource and Dataset to select the referenced dataset and its datasource. For details, see: Change Dataset.
- Display Control: View and set layer visibility, layer name, layer caption, transparency, and maximum/minimum visible scales.
- Parameters: Set parameters for the heat map layer, including kernel radius, weight field, color, color gradient blur, maximum color weight, and extremum values. These determine the display effects.
- Kernel radius: Sets the influence radius for discrete points.
- A buffer is created for each point based on the kernel radius value, measured in screen coordinates.
- Each buffer is filled with a progressive grayscale band (0~255), light inside to dark outside.
- Grayscale values accumulate in overlapping buffer areas (higher values indicate "hotter" regions; any ARGB channel can be used for accumulation).
- The accumulated grayscale value indexes a 256-color band (e.g., rainbow), recoloring the image to form the heat map.
- Weight Field: Determines a point's influence on density. A weight value scales the buffer's impact (e.g., weight=10 changes influence coefficient from 1 to 10).
With weights, a new accumulated grayscale index is created and colored using the specified band.
Note: The weight field must be numeric.
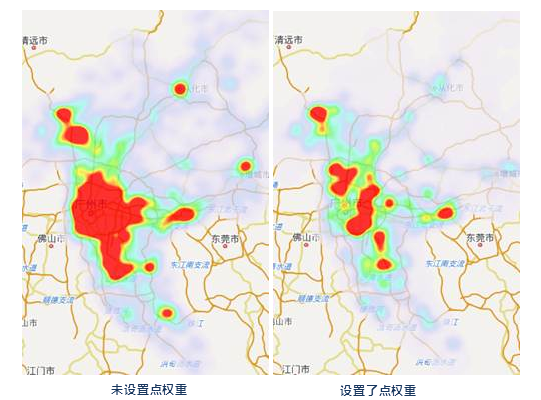
- Aggregate: When a weight field is specified, choose the aggregation method for points: average, count, maximum, minimum, or sum.
- Set color: Select a color scheme from the dropdown list; styles are automatically assigned based on the chosen color.
- Minimum color transparency: The first color box shows the transparent display state of the minimum color. Adjust transparency via the numeric box (default 100, fully transparent).
- Maximum color transparency: The first color box shows the transparent display state of the maximum color. Adjust transparency via the numeric box (default 10).
- Vertex Color: Choose vertex color display mode: HSB or RGB.
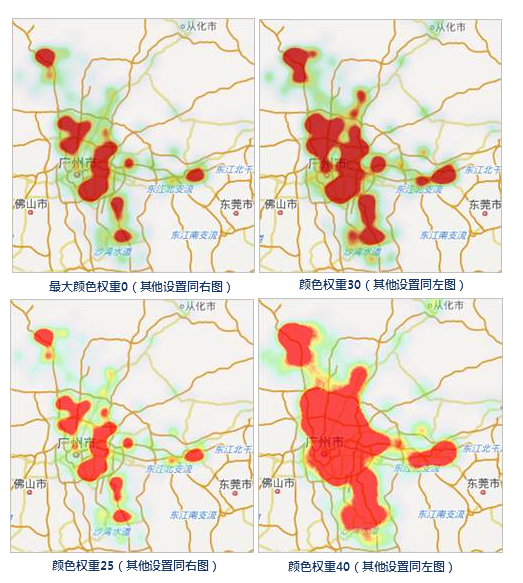
- Color gradient blur: Adjusts the blur level of color gradients to refine band rendering.
- Maximum color weight: Sets the proportion of the maximum color in the gradient band; higher values increase its dominance.
- Original point visible scale: Sets the visible scale range for the point dataset layer. Use the dropdown to select from 10 scales (e.g., 1:5000, current scale, system default) or input custom values.
- System default scale: Computes a scale where points are visible above this scale.
- Set to current scale: Uses the current map scale; points are visible above it.
- Extremum value settings: Sets maximum and minimum values for rendering. Values above maximum use the maximum color; below minimum use the minimum color.
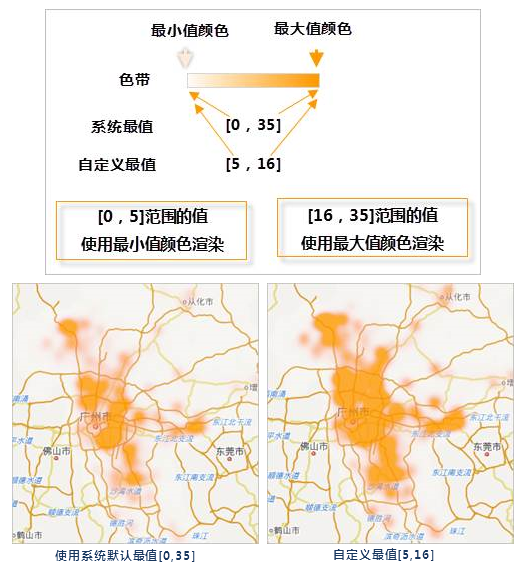
- The extremum value of the view: Uses the current view's max/min to build the color band (changes with zoom).
- The system extremum value: Default max/min based on map scale (changes with scale).
- Custom extremum values: Manually set max/min to define the color band.
- Display filter: Filters points using custom SQL expressions. Click "..." to open the SQL Expression dialog (see SQL Expression). Improves performance for large datasets.
- Kernel radius: Sets the influence radius for discrete points.
- After setting parameters, the heat map based on the point dataset is complete.
Application Example
Case Description
Using national cultural and educational institution distribution data, create a heat map to reflect their distribution across China.
Data Description
- Point data of national cultural/educational institutions (names and types) for the heat map layer.
- Chinese administrative region polygons, national boundaries, and world country polygons for the base map.
- Chinese highway line data to highlight distribution patterns relative to the heat map.
Data for this case is located in SuperMapsample data SampleData\AggregationMap\HeatMap. Requires a separate installation package; details at Get sample data package.
Main Operation Steps
- Open workspace: Sample Data\AnalyticalMap\HeatMap\HeatMap.smwu.
- Add Chinese administrative, boundary, and world country data to the map. Set styles and create a single symbol label thematic map for administrative regions using "Name" as the label expression.
- Add cultural/educational institution point data to the base map. Right-click the layer in the layer manager and select create thematic map.
- In the dialog, choose Aggregation Map -> Heat Map. Click OK to generate a default heat map.
- Adjust parameters: kernel radius, weight field, color, gradient blur, maximum color weight, and extremum values. Complete the national education institution heat map.
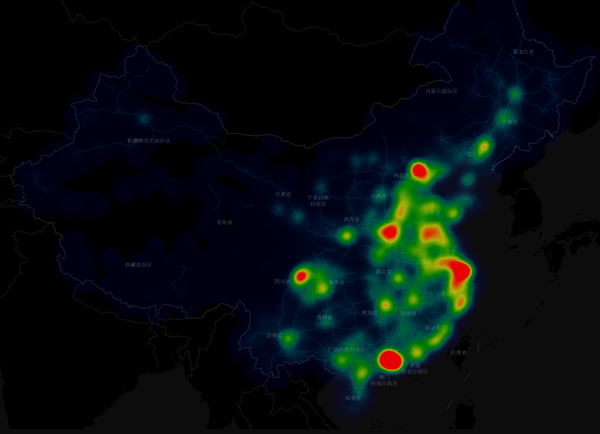 |
| Figure: Heat Map of National Education Institution Distribution |
Related Topics



