Feature Description
A grid map is essentially a spatial aggregation method that visualizes the distribution and statistical characteristics of spatial data. Its fundamental principle involves partitioning spatial regions into regularly shaped grid cells using grid aggregation algorithms. Each grid cell can be subdivided into multiple hierarchical levels, where higher-level cells are divided into smaller lower-level units, with each containing statistical information.
SuperMap supports constructing grid aggregation maps from spatial point data, offering two grid shapes for aggregation display: rectangular grids and hexagonal meshes. The process involves dividing map point features using grids, then calculating the count of point features within each grid cell as statistical values. Weighted values of points within cells can also be incorporated. Finally, grid cells are color-filled using color ramps based on sorted statistical values.
A complete grid aggregation map consists of the following elements:
- Grid: Uniform-sized grid cells (quadrilateral or hexagonal) maintain fixed dimensions regardless of map scale changes. Grids tally point records falling within each cell.
- Label: Each grid center displays a label showing statistical values, which can be either point counts or weighted values within the cell.
- Grid Rendering Style: Fill colors indicate statistical value distribution trends, transitioning from dark to light tones representing high to low values. Grid border styles can also be customized.
Feature Entry
Select the point data layer in Layer Manager:
- In the Thematic Map tab -> Aggregation Map group -> Click Grid Map button.
- Right-click and select Create Thematic Map... from the context menu. In the dialog, choose Aggregation Map -> Grid Map.
Steps
- A grid map thematic layer will be generated in Layer Manager.
- Right-click the grid map layer and select Modify Thematic Map to open the Layer Properties panel.
- Adjust display effects through parameter settings, including general properties like display controls and dataset changes:
- Display Control: Configure layer visibility, layer name, caption, transparency, and visible scale ranges.
- Visibility: Toggle Visible checkbox to control all layers in the group.
- Layer Name: Displays the unique identifier of the selected layer group (non-editable).
- Layer Caption: Editable display name shown in Layer Manager.
- Transparency: Set opacity (0=opaque, 100=transparent) via input box or slider.
- Minimum Visible Scale: Set the smallest scale at which layers become visible using predefined or custom values.
- Maximum Visible Scale: Define the largest scale for layer visibility.
- Change Dataset: Select new datasets/data sources via Datasource and Dataset dropdowns. See: Change Dataset.
- Parameters: Configure grid fields, grid type, colors, and border styles:
- Grid Field: Optional numeric field for weighted statistics. Default uses point counts.
- Display Precision: Adjust numerical display precision for labels (e.g., 178.3129 → 178.3 at 0.1 precision).
- Aggregate: Choose aggregation method (Average, Count, Max, Min, Sum) when grid field is specified.
- Grid Type: Select quadrilateral or hexagonal grids.
- Edge Length: Set grid edge length in pixels.
- Color Ramp: Select color schemes for value visualization.
- Min Color Transparency: Opacity for cells with minimum values.
- Max Color Transparency: Opacity for cells with maximum values.
- Color Mode: Choose between HSB and RGB color models.
- Original Point Visible Scale: Set visibility scale range for source point data:
- System Default Scale: Auto-calculated threshold scale.
- Set to Current Scale: Use current map scale as visibility threshold.
- Grid Label: Customize label display:
- Show Label: Toggle label visibility and configure font/color styles (font size cannot be modified).
- Border Style: Configure grid border lines (none/solid/dashed), width, color, and transparency.
- Complete grid map creation by finalizing parameters.
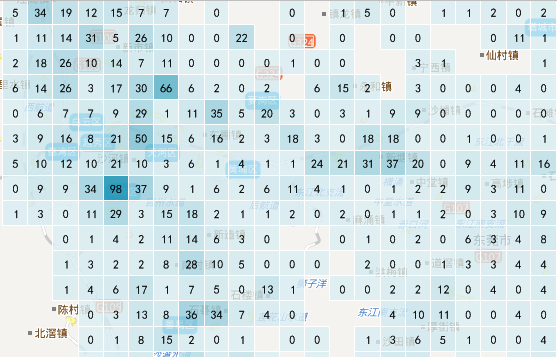 |
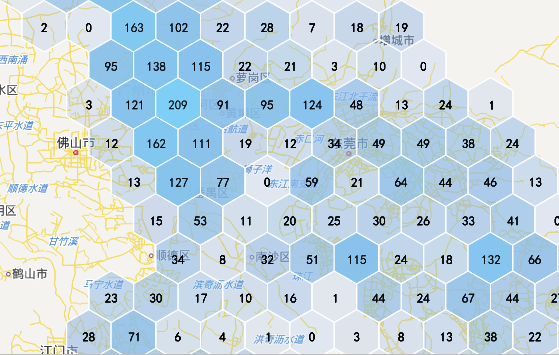 |
| Figure: Quadrilateral Grid | Figure: Hexagonal Grid |
 |
Application Example
Grid maps excel in quantifying spatial distributions compared to heatmaps. The example below demonstrates tourism attraction distribution in Zhejiang Province using grid mapping.
Data Path: SuperMap Sample Data -> SampleData -> AggregationMap -> GridAggregationMap
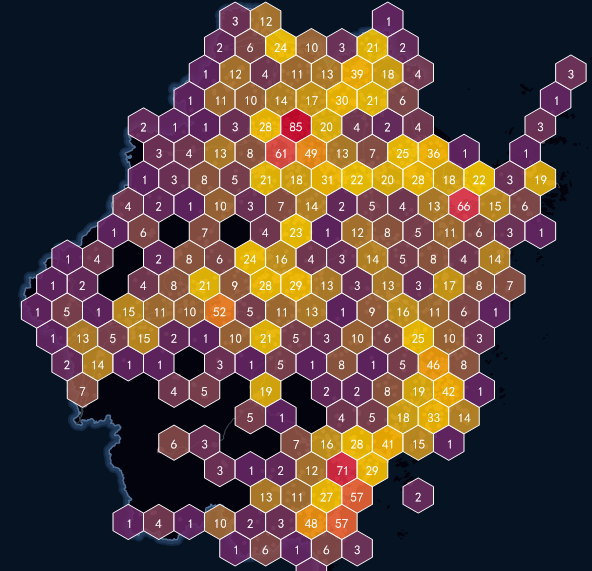 |
| Figure: Grid Map of Tourist Attractions Distribution in Zhejiang Province |



