Class SymbolGroups
- java.lang.Object
-
- com.supermap.data.SymbolGroups
-
public class SymbolGroups extends java.lang.ObjectThe SymbolGroups class.The objects of the class is the set of {
SymbolGroup}. It's used to manage the subgroup of the Symbolgroup. It is used to create or remove the subgroup.Below is the illustration for the structure of marker, line, and fill symbol libraries.
The structure of symbol libraries is similar to the structure of Windows explorer. In the root of the disk, there can be 0 or more folders or files, with each of the folders containing 0 or more folders or files. The root group, symbol groups, and symbols of the symbol library are similar to the root of the disk, folders, and files respectively. The root group can contain 0 or more symbol groups or symbols, with each of the symbol groups containing 0 or more symbols groups and symbols.
As shown below, the red dashed rectangle indicates the root group of the symbol library. The root group is a symbol group with the highest level in the symbol library. Each symbol group, including the root group, can contain 0 or more symbol groups or symbols. All symbol groups in a group compose a object and each symbol group can have only one object at most. The object is used to manage (create or delete) all symbol groups in it. We can see that the yellow rectangle indicates a symbol group, corresponding to a , that contains multiple symbol groups and symbols, which compose a object. The symbol group in the yellow rectangle is the parent group of the three symbol groups in the pink rectangle. The three symbol groups in the pink rectangle are the child groups of the symbol group in the yellow rectangle.
Note: Groups and child groups are used to store symbols logically in a tree hierarchy, which would bring convenience for symbol management and usage.
In summary, a contains a unique
SymbolLibraryobject, which can contain at most 1SymbolGroupobject and 0 or several Symbol objects. TheSymbolGroupobject is the collection ofSymbolGroupsobjects, which contributes to the tree hierarchical management of symbols.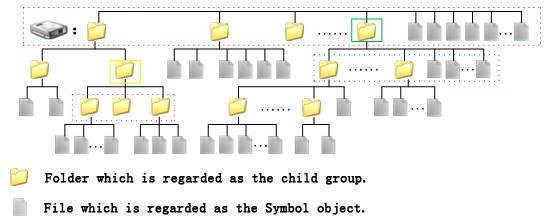
-
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors Constructor and Description SymbolGroups()
-
Method Summary
All Methods Instance Methods Concrete Methods Modifier and Type Method and Description booleancontains(java.lang.String name)Tests whether the given name has existed in the SymbolGroups object or not.SymbolGroupcreate(java.lang.String name)Creates a new SymbolGroup object in the SymbolGroups object as the child group.SymbolGroupget(int index)Returns theSymbolGroupobject with the specified index in the SymbolGroups object.SymbolGroupget(java.lang.String name)Returns theSymbolGroupobject with the specified name in the SymbolGroups object.intgetCount()SymbolGroupsReturns the count of the SymbolGroup objects contained by the SymbolGroups object.intindexOf(java.lang.String name)Returns the index of the SymbolGroup object with the specified name in the SymbolGroups object.booleanremove(java.lang.String name)Removes the specified group.booleanremove(java.lang.String name, boolean bMove)Removes the SymbolGroup object with the specified name in the collection.
-
-
-
Method Detail
-
get
public SymbolGroup get(int index)
Returns theSymbolGroupobject with the specified index in the SymbolGroups object. For more information about the structure of the SymbolGroups object, please refer to the remarks in the SymbolGroups class.- Parameters:
index- the specified index- Returns:
- The SymbolGroup with the specified index in the SymbolGroups.
-
get
public SymbolGroup get(java.lang.String name)
Returns theSymbolGroupobject with the specified name in the SymbolGroups object. For more information about the structure of the SymbolGroups object, please refer to the remarks in the SymbolGroups class.- Parameters:
name- given point name.- Returns:
- the SymbolGroup with the specified name in the SymbolGroups.
-
getCount
public int getCount()
SymbolGroupsReturns the count of the SymbolGroup objects contained by the SymbolGroups object. For more information about the structure of the SymbolGroups object, please refer to the remarks in the {} class.- Returns:
- the count of SymbolGroup in the SymbolGroups object.
-
indexOf
public int indexOf(java.lang.String name)
Returns the index of the SymbolGroup object with the specified name in the SymbolGroups object.- Parameters:
name- The specified name of the SymbolGroup object.- Returns:
- the index of the SymbolGroup object with the specified name in the SymbolGroups object.
-
create
public SymbolGroup create(java.lang.String name)
Creates a new SymbolGroup object in the SymbolGroups object as the child group.- Parameters:
name- The specified name of the new SymbolGroup object. If the name has existed it will throw exception.- Returns:
- the SymbolGroup object newly created.
-
contains
public boolean contains(java.lang.String name)
Tests whether the given name has existed in the SymbolGroups object or not.- Parameters:
name- The name to be tested.- Returns:
- Returns true if contained; otherwise false.
-
remove
public boolean remove(java.lang.String name, boolean bMove)Removes the SymbolGroup object with the specified name in the collection. Here only the logical structure will be changed, with the subgroups and symbols in the group not changed.Firstly, the logical storage structure of the symbol library is introduced. Then, deleting SymbolGroup objects from the SymbolGroups object is illusrated.
Below is the illustration for the structure of marker, line, and fill symbol libraries.
The structure of symbol libraries is similar to the structure of Windows explorer. In the root of the disk, there can be 0 or more folders or files, with each of the folders containing 0 or more folders or files. The root group, symbol groups, and symbols of the symbol library are similar to the root of the disk, folders, and files respectively. The root group can contain 0 or more symbol groups or symbols, with each of the symbol groups containing 0 or more symbols groups and symbols.
As shown below, the red dashed rectangle indicates the root group of the symbol library. The root group is a symbol group with the highest level in the symbol library. Each symbol group, including the root group, can contain 0 or more symbol groups or symbols. All symbol groups in a group compose a object and each symbol group can have only one object at most. The object is used to manage (create or delete) all symbol groups in it. We can see that the yellow rectangle indicates a symbol group, corresponding to a , that contains multiple symbol groups and symbols, which compose a object. The symbol group in the yellow rectangle is the parent group of the three symbol groups in the pink rectangle. The three symbol groups in the pink rectangle are the child groups of the symbol group in the yellow rectangle.
Note: Groups and child groups are used to store symbols logically in a tree hierarchy, which would bring convenience for symbol management and usage.
In summary, a contains a unique
SymbolLibraryobject, which can contain at most 1SymbolGroupobject and 0 or several Symbol objects. TheSymbolGroupobject is the collection ofSymbolGroupsobjects, which contributes to the tree hierarchical management of symbols.
For example, if you remove the child group in the green rectangle in figure 1, the child groups and symbols in the child group will be physically deleted. The content, as shown in the pink dashed rectangle, will be moved to the father group, as shown in the yellow rectangle, of the child group, with the structure unchanged. Figure 2 shows the result after removing the child group in the green rectangle.
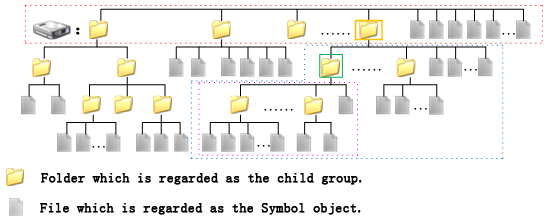
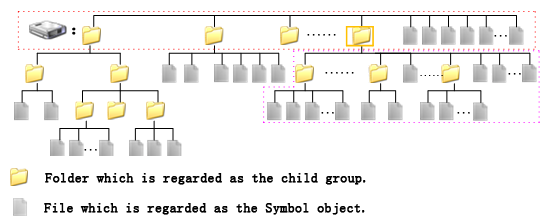
- Parameters:
name- The name of the SymbolGroup object to remove.bMove- Moves the content of the sub group up- Returns:
- True, if successful; Otherwise false.
-
remove
public boolean remove(java.lang.String name)
Removes the specified group.- Parameters:
name- Name- Returns:
- boolean
-
-



