Feature Description
SuperMap supports calculating parameter values for commonly used four-parameter and seven-parameter transformations through operations such as control point selection, coordinate transformation models, and accuracy evaluation. Users can utilize these parameters for coordinate system conversion of spatial data.
Preparation
- Case Description: A user possesses vector data of a region in the Xi'an 1980 coordinate system and wishes to convert it to the China Geodetic Coordinate System 2000. Control points measured within the survey area contain both Xi'an 1980 and CGCS 2000 coordinates. This example provides detailed steps for this data conversion process.
- Preparation Work: Select control points with both Xi'an 1980 and CGCS 2000 coordinates as matching point files.
- Control Point selection is crucial for transformation parameter calculation. Users must choose control points with coordinate values in both coordinate systems.
- Basic Principles for Selecting Control Points: High-grade, high-accuracy, evenly distributed coverage of the entire conversion area, and minimal local deformation.
- Quantity Requirements: Generally, no fewer than 6 control points for conversion to CGCS 2000 system, with at least 6 external verification points, all evenly distributed across the conversion area. Additional backup points should be prepared considering possible outliers. More control points are recommended.
 |
| Figure: Data Control Points |
Feature Entry
- In Start tab -> Data Processing group -> Project drop-down button -> Calculate Transformation Model Parameters.
Steps
 |
| Figure: "Calculate Transformation Model Parameters" Dialog |
- Model Settings: Select transformation model method. Click the drop-down button next to "Model Method" label to access five available models: Position Vector (7-para), Coordinate Frame (7-para), China_3D_7P (7-para), China_2D_7P (7-para) and China_2D_4P (4-para).
Model selection depends on control point coordinates and conversion area. The Technical Specifications for Geodetic Control Point Coordinate Transformation provides applicable scopes for each model. Users should choose models according to source data's coordinate system and conversion area. Refer to Transformation Models for details.
- Set Coordinate System Types for Mutual Conversion (source and target). Supports conversion between geographic coordinate systems, projected coordinate systems, and their combinations:
- Source Coordinate System Settings: Two configuration methods:
- Projection Settings: Select radio button and click Settings... to choose geographic/projected coordinate system matching source data. See Projection Settings for details.
- Import Projection File: Select radio button and click Select to import projection information file.
- Target Coordinate System Settings: Configure destination coordinate system type.
- Source Coordinate System Settings: Two configuration methods:
- Control Point Settings: Input control points with source and target coordinates. Coordinate formats must match specified coordinate systems.
Three methods for adding control points:
- Create Matching Point Pair: When control points exist as datasets, specify source/target datasets and matching fields. Click
 button in toolbar to configure relationships.
button in toolbar to configure relationships. - Import Control Points: Click
 button to import .txt file. File format reference:
button to import .txt file. File format reference:

Figure: Control Points (.txt) File - Manual Input: Click
 button to add new entries in list box for manual coordinate input.
button to add new entries in list box for manual coordinate input.
- Create Matching Point Pair: When control points exist as datasets, specify source/target datasets and matching fields. Click
- After importing, review control point details in list box. Use Apply checkboxes to select points participating in calculation (minimum 6 pairs required).
- Calculate Transformation Parameters: Click "Calculate" to obtain:
① Transformation parameters calculated using least squares method: Offset X, Offset Y, Offset Z (meters); Rotation X, Rotation Y, Rotation Z (arc-seconds); Scale Difference (ppm).
② Calculated control point residuals (Dx, Dy, DH) and mean square errors. Points with residuals exceeding 3×MSE will be marked No in Usable column.
Note: Remove or disable unusable points to improve parameter accuracy.

- Verify Accuracy: Click
 to import external verification points (≥6, not used in calculation). Use internal/external accuracy assessments with residuals ≤3×MSE.
to import external verification points (≥6, not used in calculation). Use internal/external accuracy assessments with residuals ≤3×MSE. - Export Parameters: After passing verification, click
 in parameter panel to export *.ctp file.
in parameter panel to export *.ctp file. - Apply exported Coordinate Transformation Parameters File (*.ctp) to reproject entire dataset. See Reproject Dataset for implementation details.
- Comparison between original and transformed data:
 |
| Figure: Data Comparison Before/After Transformation |
Related Topics
Calculate Transformation Model Parameters




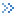 Related Error Calculation Formulas
Related Error Calculation Formulas
