Color is the general term for all colors, including achromatic series and chromatic series. Black, white, and gray belong to the achromatic series, while red, orange, yellow, green, cyan, blue, and purple belong to the chromatic series.
This section briefly introduces hue, lightness, saturation, and color sensations related to color. For a deeper understanding of other color-related topics, such as color mixing and color modes, please refer to professional books or online resources on color theory.
General Properties of Color
General properties of color refer to the basic variables of color that the human vision can distinguish. The three attributes of color include hue, lightness, and saturation, which are distinct and independent yet interdependent and mutually constraining.
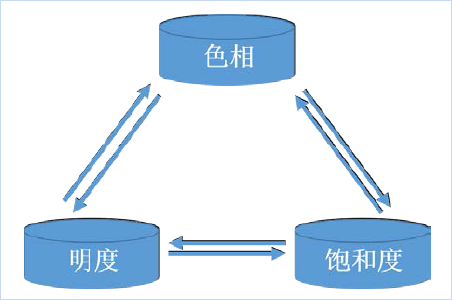 |
| Figure: Three Properties of Color |
- Hue
Hue is the inherent appearance of each color. It represents the "qualitative" difference between colors and is the most fundamental attribute of color. The seven representative hues in the spectrum are red, orange, yellow, green, cyan, blue, and violet.

Figure: Seven Hues in the Spectrum - Lightness
Lightness refers to the brightness or darkness of a color, indicating the degree to which it reflects light. As shown below, in the achromatic series, white has the highest lightness, black has the lowest, and various shades of gray fall in between.
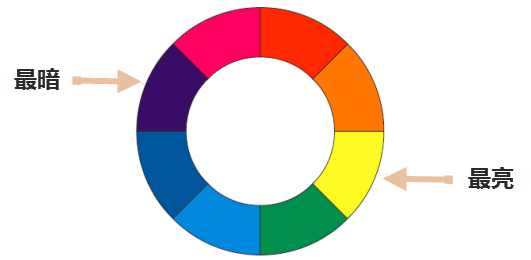
Figure: Lightness of Colors in Chromatic Series 
Figure: Lightness of Colors in Achromatic Series - Saturation
Saturation refers to the purity of a color. Pure colors have the highest saturation, while mixing colors (whether black, white, gray, or chromatic colors) reduces their purity.
It is important to note that "saturation" and "lightness" are distinct concepts. "Lightness" relates to brightness and intensity, while "saturation" pertains to vividness and purity. High lightness does not necessarily imply high saturation.
Color Sensations
Color itself has no soul; it is merely a physical phenomenon. However, people can perceive emotional responses to colors due to long-term exposure to a colorful world, accumulating visual experiences. When perceptual experiences resonate with external color stimuli, certain emotions are evoked psychologically.
- Excitement and Calmness of Colors
The excitement or calmness induced by colors depends on the intensity of visual stimulation. Among the color attributes affecting human emotions, hue has the strongest impact, followed by saturation, and then lightness. For example, warm colors like red, orange, and yellow evoke excitement, while cool colors like cyan and blue induce calmness. Intermediate colors like green and purple are neutral. High-lightness colors tend to be exciting, and low-lightness colors tend to be calming.
- Warm and Cool Sensations of Colors
Warm colors include red, orange, yellow, etc.; cool colors include cyan, blue, etc.; neutral colors include green, purple, etc.
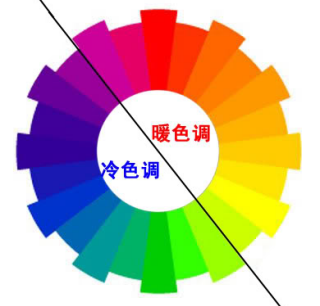
Figure: Contrast of Warm and Cool Colors - Advancement and Recession, Expansion and Contraction of Colors
Warm colors create a protruding effect and are advancing colors; cool colors create a receding effect and are retreating colors. In map design, the sense of distance in colors can be used to form different layers and distinguish primary from secondary content.
- Lightness and Heaviness, Softness and Hardness of Colors
The sense of lightness or heaviness in colors relates to perceptual intensity. Low-lightness, dark colors are stable and feel heavy, while high-lightness, light colors are airy and feel light. Under constant lightness, high-saturation warm colors feel heavy, and low-saturation cool colors feel light. The basic principles of color weight are:
- (Heavy) Black > Low Lightness > Medium Lightness > High Lightness > White (Light)
- (Heavy) High Saturation > Medium Saturation > Low Saturation (Light)
The sense of softness or hardness in colors mainly depends on lightness and saturation. High-lightness, grayish colors feel soft, while low-lightness, pure colors feel hard.
- Gorgeousness and Simplicity of Colors
The sense of gorgeousness or simplicity in colors is most influenced by hue, followed by saturation and lightness. Warm colors like red and yellow, and bright, vivid colors appear gorgeous; cool colors like cyan and blue, and dull, muted colors appear simple. Chromatic colors feel gorgeous, while achromatic colors feel simple. Color combinations also affect this sensation.

Figure: Gorgeousness and Plainness of Colors - Liveliness and Melancholy of Colors
The sense of liveliness or melancholy in colors is primarily related to lightness and saturation. High-lightness, vibrant colors evoke liveliness, while dark, dull colors evoke melancholy. Color schemes with a high-lightness base easily achieve liveliness, whereas low-lightness bases tend to induce melancholy.
In the achromatic series, black and dark gray often cause melancholy, white and light gray evoke liveliness, and medium-lightness gray is neutral.
Color Contrast and Harmony
- Color Contrast
- Lightness Contrast
Contrast formed by differences in lightness among the three color attributes is called lightness contrast. High-lightness colors appear brighter, while low-lightness colors appear darker. For instance, a color of the same lightness may look darker on a white background but brighter on a black background.

Figure: Lightness Contrast - Hue Contrast
Contrast formed mainly by differences in hue among the three attributes is called hue contrast. Hue contrast includes comparisons of similar hues, analogous hues, contrasting hues, and complementary hues.
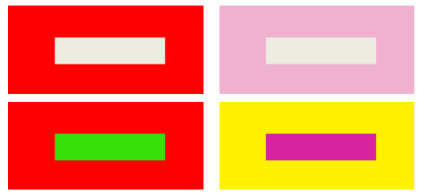
Figure: Hue Contrast - Saturation Contrast
Contrast formed by differences in saturation among the three attributes is called saturation contrast. A color of the same saturation appears more vivid on a low-saturation background and duller on a high-saturation background, assuming similar lightness and hue.

Figure: Saturation Contrast - Warm and Cool Contrast
Contrast formed by differences in warmth and coolness is called warm and cool contrast. The distribution ratio of warm and cool colors in an image determines its overall tone, commonly referred to as warm or cool tones. Using warm and cool contrasts adds depth to the image.

Figure: Contrast of Warm and Cool Colors - Area Contrast
When hues are juxtaposed, the size of their areas affects the viewer's perception. Color schemes utilizing area size relationships are called area contrast. For example, monochromatic schemes can produce different visual effects by changing color areas and positions.

Figure: Area Contrast
- Lightness Contrast
- Color Harmony
Color harmony has two interpretations: one refers to the process of adjusting and combining contrasting colors to form a harmonious whole; the other refers to a harmonious and aesthetically pleasing relationship between distinctly different or contrasting colors, avoiding sharp stimuli, achieved through rhythmic combinations of hue, lightness, and saturation.
There are many methods, techniques, and principles for color harmony, which are not detailed here. It is essential to remember the key principle: color schemes should align with the theme and resonate with the viewer's aesthetic psychology.

Figure: Color Harmony
Related Topics



