Select a vector layer as the current layer in the Layer Manager, and the Layer Properties interface will display vector parameter settings, including functional controls for property settings such as Show Full Line, Intersection, Scale with Map, Minimum Object Size, and Display Filter.
Show Full Line
Show Full Line ensures that the line symbol of a line object is displayed completely, helping users optimize the display effects of line symbols.
If the length of a line object is shorter than the periodic length of the line symbol, or if the line object's length is not an integer multiple of the symbol's periodic length, the part of the line shorter than a full symbol period cannot be fully displayed. Using the Show Full Line command recalculates the line symbol length to find a value very close to the object's length for rendering.
For example, with a line marker style like 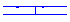 , when the line object's length is less than one symbol period, the schematic diagrams with and without Show Full Line are as follows:
, when the line object's length is less than one symbol period, the schematic diagrams with and without Show Full Line are as follows:
 |
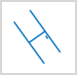 |
| Without Show Full Line | With Show Full Line |
Therefore, the Show Full Line command provides better display effects for line layers with shorter lengths or many polylines, achieving the goal of map beautification.
Intersection
For line layers, it is common for multiple line objects to intersect, such as in water systems or roads. If left unprocessed and displayed normally, it may not only be aesthetically unpleasing but also inconsistent with reality, failing to correctly express the connectivity between intersecting line objects. Optimization is often needed for intersecting lines, removing overlapping parts at "intersection" points to achieve realistic crossroad display effects.
As shown below, we often need to optimize intersecting lines by removing overlapping parts at "intersection" points, ultimately achieving realistic crossroad display effects.
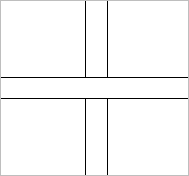 |
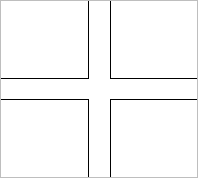 |
| Without Intersection | With Intersection |
- The Intersection function applies to ordinary line layers and network data line layers but not to CAD data line layers or route data.
- The Intersection function only works on line objects with a double-line layer style, such as
 , and does not apply to some line symbol types, like single-line symbols, e.g.,
, and does not apply to some line symbol types, like single-line symbols, e.g.,  .
.
Enable Intersection
Check the Intersection checkbox to enable the crossroad function for line objects in the current layer. Checking this box applies the intersection effect to the layer's lines; otherwise, the effect is not applied.
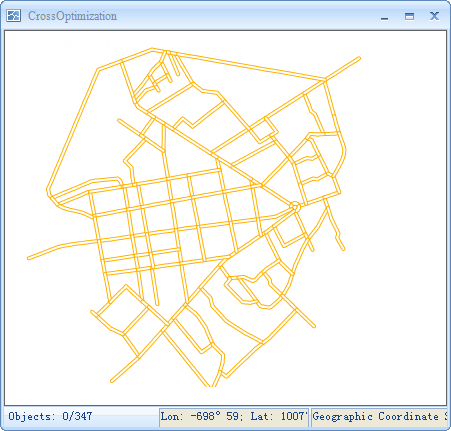 |
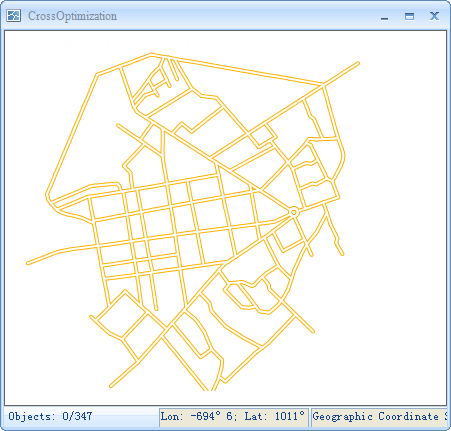 |
| Before Using Intersection | After Using Intersection |
Scale with Map
Used to set whether map symbol objects in the layer scale up or down during map zoom-in or zoom-out operations. The Scale with Map checkbox can be applied to point symbols, line symbols, area symbols, and their borders.
After checking the Scale with Map checkbox, map symbols in the current layer will scale with the map. Each time the user performs a zoom-in or zoom-out operation, the degree of scaling for symbol objects in the current layer is determined by both the scaling base scale and the map scale after zooming.
Scaling Base Scale
Each time the user performs a map zoom-in or zoom-out operation, the degree of scaling for symbol objects in the current layer is determined by both the scaling base scale and the map scale after zooming. If the current map scale is larger than the scaling base scale, map symbols will scale up by the same magnification ratio; conversely, they will scale down by the same reduction ratio. For example, if the symbol scaling base scale is 1:500,000 and the symbol size is 30, then when the map scale is 1:100,000 (i.e., the map is magnified five times), the symbol size will also magnify five times, becoming 150.
After checking the Scale with Map checkbox, the Scaling Base Scale combo box becomes available. Users can click its drop-down button and select Set to Current Scale from the list to set the current map scale as the scaling base scale. Users can also select Clear from the drop-down list to cancel the scaling base scale setting. At this point, the Scaling Base Scale combo box displays empty, indicating that symbols do not scale with the map.
 Note:
Note:When the scaling base scale and the current map scale are inconsistent, unchecking symbol scaling (i.e., disabling Scale with Map) may cause the marker size in the current map to change. At this time, symbol display will scale from the scaling base scale size to the current map scale size.
Anti-Alias
Anti-aliasing: When drawing non-horizontal and non-vertical lines or polygon boundaries on a raster graphics display, they more or less exhibit a jagged or stair-step appearance. This is because lines, polygons, color boundaries, etc., are continuous, while rasters are composed of discrete points. Representing lines, polygons, etc., on a raster display device requires sampling at discrete positions. The information distortion caused by insufficient sampling during reconstruction is called "aliasing." Techniques used to reduce or eliminate this effect are called anti-aliasing.
The Anti-alias checkbox is used to reduce or eliminate layer information distortion, optimizing layer display effects. Anti-aliasing requires both map anti-aliasing and layer anti-aliasing to be enabled. For map anti-aliasing operations, please refer to: Map Display Optimization.
Show Overlap
Used to control whether to display objects that cause overlapping phenomena. If this checkbox is checked, all objects with overlapping phenomena will be displayed. The layer Show Overlap effect only takes effect when the Show Overlap checkbox in the Map Properties panel is also checked. Detailed settings can also be configured in Overlap Settings. For specific content, please refer to Overlap Settings in map properties.
Show Full Label
Used to control whether the layer displays labels completely. The complete label display effect for the layer only takes effect after Show Full Label is enabled for the map. It is only effective for labels and point symbols.
Minimum Object Size
The text box to the right of the label is used to set the minimum display size for objects in the current layer. When the current map is zoomed in or out, if the larger value between the width and height of the minimum bounds of any geometry in the layer is less than the minimum display size set here, the geometry becomes invisible. You can enter a specific value in the text box to the right of the label to set the minimum display size for objects in the current layer. The unit is millimeters.
Rarefy Display
When there are too many nodes on a line object or the boundary line of a region object, Rarefy Display can be applied. By setting a threshold, nodes within the specified tolerance pixels are thinned out to improve map display performance. Note: Rarefy Display settings are only supported for line datasets and region datasets.
- Tolerance (Pixels): Set a tolerance value. Within this range, if the number of nodes for line objects and region objects exceeds the set threshold, they are thinned out. The tolerance unit is px. The default tolerance is 0.5, meaning within 0.5 pixels, if there are more than the default threshold of 500 nodes, the object undergoes Rarefy Display.
- Threshold (Count): By setting a threshold, within the specified tolerance range, if the number of nodes exceeds this threshold, the object is thinned out; otherwise, it is not.
When applying Rarefy Display to a region dataset, if the set tolerance is too large or the threshold is too small, connections between objects on the map may appear disconnected. This is because Rarefy Display only controls the display of data within the visible screen range and does not involve the topology between objects.
Filter Small Overlapping Objects
Supports setting Filter Small Overlapping Objects, specifying that within a tolerance area, only one object is drawn for all small objects smaller than the set size. This reduces the time consumption when displaying a large number of small objects at small scales, improving browsing performance.
Overlapping Small Objects: If both the length and width of an object's Bounds are smaller than the overlapping small object threshold, the object is considered a small object. Overlapping small objects refer to multiple small objects within a specified unit pixel area (a square area with side length equal to the Minimum Object Size attribute value). If the center point of a small object's Bounds falls within this square area, the small object is considered to be within the area.
Filter Small Overlapping Objects: Means that when displaying small objects in a layer, a unit pixel area is only drawn once. Therefore, only one small object will be displayed in that area, and other overlapping small objects will not be displayed.
Filter Small Overlapping Objects requires setting two parameters: Tolerance and Minimum Object Size. The parameter descriptions are as follows:
- Tolerance: This attribute sets the size of the unit pixel area. The valid range for this tolerance value is no less than 1 and no more than 10, in pixels.
- Minimum Object Size: This attribute sets the size threshold for objects participating in the filtering. The valid range for Minimum Object Size is no less than 1 and no more than 10, in pixels.
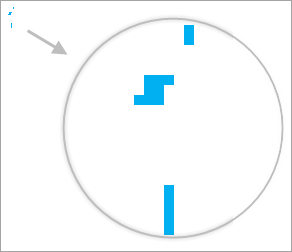
The following schematic diagram can help you understand the Filter Small Overlapping Objects function. Figure 1 shows the display without filtering at large and small scales. Figure 2 shows the display after setting Tolerance to 8 pixels and Minimum Object Size to 8 pixels.
 |
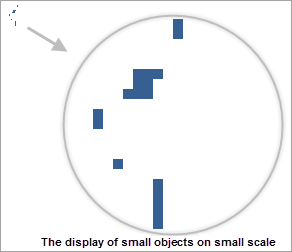 |
| Figure 1: Without Filter Small Overlapping Objects |
If the overlapping small object tolerance setting is 8 pixels, objects whose Bounds length and width are both less than 8 pixels participate in filtering. The specified unit pixel area is a square area with a side length of 8 pixels. The starting point of the unit pixel area is the upper-left corner of the map window. As shown in Figure 3, based on the set unit pixel area, the map is divided into a regular grid. Taking the object in the 2nd row, 2nd column area of the drawing as an example, assume the object marked with a purple arrow is drawn before the object marked with a red arrow. When drawing the object pointed to by the purple arrow, it is identified as a small object with its center point within the square area. Since no other small object has been drawn in this square area, this small object remains displayed, and the area is marked as having a drawn small object. When drawing the object pointed to by the red arrow, it is also a small object with its center point in the square area. However, since the area is already marked with a small object, this object is not displayed.
For the default object display order, please refer to Object Display Order Field.
 |
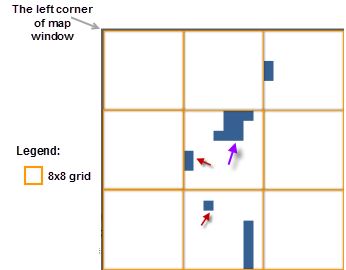 |
| Figure 2: Filter Small Overlapping Objects, Tolerance 8 pixels, Minimum Object Size 8 pixels | Figure 3: Schematic Diagram of Filter Small Overlapping Objects Process |
Filter Small Overlapping Objects can reduce the display time consumption for a large number of small objects at small scales. The difference between Filter Small Overlapping Objects and filtering small objects by Minimum Object Size is: after setting the minimum display size for objects, all objects smaller than this minimum size will not be displayed, which may result in large areas with concentrated small objects having no objects displayed on the map. Filter Small Overlapping Objects ensures that at least one small object is displayed in a unit pixel area, avoiding the problem of large areas with concentrated small objects having no display.
Display Filter: The spatial combo box is used to set the display filter for the current layer, filtering which objects in the layer are displayed and which are not, making it easier for users to display features of interest and filter out features temporarily not needed. For specific operation steps, please refer to: Display Filter.
Object Display Order Field
The draw order of objects affects their display order on the map. Objects on the map are displayed according to the order of values in the set field. Supports setting Multi-Field Display Sorting. Click the button to the right of the Object Display Order display box to pop up the Display Order Field Settings dialog. In this dialog, you can add one or more sort fields and perform operations such as editing and deleting the order of added fields. When multiple fields are added, sorting is first done according to the first field in the list box, then based on the first sort, sorting is done according to the second field value, and so on. The order of multiple fields can be adjusted using Bring to Front, Bring to Back, Up, and Down in the lower right corner of the dialog.
If there is no sort field, the engine's default display order is used, i.e., the draw order. Generally, it follows the rule of taking the SmID field with ascending order for identical displays. Currently, only single vector layers or single thematic map layer settings support the Object Display Order field. As shown below, Object 1 has SmID 1, Object 2 has SmID 2. Sorting by the SmID field in ascending and descending order yields the following results:
|
Field
|
Sort
|
Diagram
|
|
SmID
|
Ascending
|
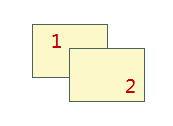 |
|
SmID
|
Descending
|
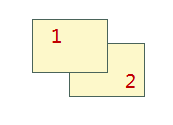 |
As shown below: Adjust the display order of three objects A, B, C. First, perform an initial ascending sort by the ID field, then a secondary descending sort by the Name field, resulting in the outcome shown in the figure.
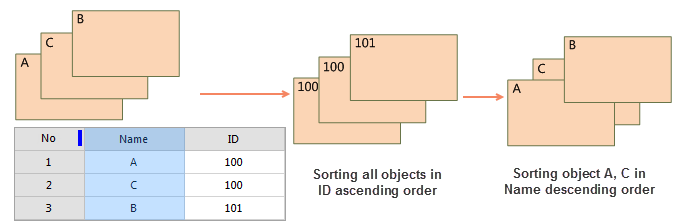 |
 Note:
Note:- After setting the object display order, Intersection will become ineffective.
- If multiple sort fields need to be set, individual field settings can be separated by a comma ",", e.g., field1 asc, field2 desc.
- Setting the display order is saved to the current map and workspace, avoiding repeated user settings and improving mapping efficiency.
Set Layer Join Attribute Table
Click the Join Attribute Table... button to set the associated field and connect an external table, thereby filtering the content displayed in the layer by constructing a filter involving fields from the external table. For specific operation steps, please refer to: Filter Display Objects in the Map.
Set Output Fields
Used to set whether output fields for generating vector tiles from the layer or fields published as a WebMap service are displayed. Click the Settings Output Fields button to pop up the Set Output Fields dialog. The toolbar provides Top/Bottom, Move Up/Move Down buttons to set the display order of fields. After the tile publish service, the field display order will match the order set here.
- Output: Used to set whether this field is included when outputting to vector tiles. Selected: The vector tile result will include this field. Not selected: The vector tile result will remove this field, effectively reducing data volume and improving transmission and loading performance.
- Service Visible: Used to set whether the field is visible after publishing the map service. Selected: After publishing the service, this field is visible. Not selected: After publishing the service, this field will be hidden.
Related Topics



