Regardless of the layer type (vector, raster, or image), you can set properties such as transparency, order, visible scale range, and filter display objects for the layer.
Set Layer Transparency
Transparency is a display property of a layer. It can be set in the numeric adjustment box labeled Transparency: in the Layer Properties panel.
The numeric adjustment box for transparency allows you to set the degree of transparency for the current layer. You can also directly input a transparency value to preview the result in real time. The default transparency value is 0, indicating the layer is completely opaque. As the value increases, the layer becomes more transparent; when set to 100, the layer becomes fully transparent. The transparency value must be an integer between 0 and 100.
Adjust Layer Order
The stacking order of layers directly affects the map's display effects. There are two general rules for the stacking order of map layers:
- Based on the map bounds of objects, from top to bottom: small -> medium -> large;
- Based on layer type, from top to bottom: text/point -> line/region.
 Note:
Note:The above stacking order rules are general recommendations. Depending on specific map creation requirements, other layer sorting methods may be used.
The following two maps show the display effects before and after moving a specific layer (RoadLine) to the bottom. These maps clearly illustrate the importance of layer stacking order for map display.
 |
 |
| Map display effects before layer adjustment | Map display effects after layer adjustment |
As can be seen from the figure above, a line layer appears to have "disappeared" from the map. It has not been removed but moved to the very bottom layer for display.
Layer order can be adjusted primarily through the following two methods:
 Note:
Note:Direct dragging requires the layer node to be set as draggable. The Layer Control dropdown menu in the layer manager toolbar -> Layer nodes can be dragged option controls whether the layer order can be changed by dragging.
- Using Layer Control
Operation Steps:
- If there is an open map in the current workspace, open the Layer Control dialog box through one of the following steps:
- In the layer manager, click the layer control button;
- In the layer manager, right-click any layer and select the Layer Control command.
- In the Layer Control dialog box, select one or more layers, then use the toolbar buttons (Bring to Front, Move Up, Move Down, Send to Back, etc.) to adjust the layer order. For detailed information about layer control, please refer to Layer Control.
- If there is an open map in the current workspace, open the Layer Control dialog box through one of the following steps:
- Direct Dragging
Operation Steps:
- In the layer manager, select one or more layers.
- Drag the selected layer(s) to the target position.
- Release the mouse button.
Layer Blend Mode
Blend Mode is used to set the blending method between two layers. It calculates the color of the upper layer with the color of the lower layer to produce different shading effects, depending on the selected mode.
The provided modes are as follows:
| Mode Category | Mode Name | Description |
| Normal Mode | Normal | Does not change the layer color. This is the default blend type. |
| Darken | Darken | Compares the layer color with the color of the layer below and uses the minimum RGB value from both layers as the final rendering color. |
| Multiply | Multiplies the layer color with the color of the layer below, usually resulting in a darker final rendering color. | |
| Color Burn | Darkens the color of the layer below. White remains unchanged. | |
| Linear Burn | Adds the layer color to the color of the layer below and then subtracts the value 1. | |
| Lighten | Lighten | Compares the layer color with the color of the layer below and uses the maximum RGB value from both layers as the final rendering color. |
| Screen | Subtracts the white areas of the layer and the layer below and then multiplies them. | |
| Color Dodge | Reduces the contrast between the layer and the layer below, increasing the brightness of the layer below. Black remains unchanged. | |
| Linear Dodge (Add) | Adds the brightness of the layer to the brightness of the layer below. Black remains unchanged. | |
| Contrast | Overlay | Multiplies areas in the layer below with a color value less than 0.5 with the blend layer, and uses the Screen mode for areas in the blend layer greater than 0.5. |
| Soft Light | Uses the same algorithm as the Overlay mode but reduces the color contrast of the layer. | |
| Hard Light | Multiplies areas in the layer with a color value less than 0.5 with the layer below, and uses the Screen mode for areas greater than 0.5. | |
| Vivid Light | A combination of Color Dodge and Color Burn. | |
| Linear Light | Brightens areas where the brightness of the blend layer color is higher than 0.5, and darkens areas where it is lower than 0.5. | |
| Pin Light | If the current layer color is lighter than 50% gray, pixels darker than the current layer color are replaced. If the current layer color is darker than 50% gray, pixels lighter than the current layer color are replaced. | |
| Difference | Difference | Subtracts the color value of the lower layer from the color value of the upper layer, divides the result by 2, and then adds the color value of the lower layer back. This produces an effect where the color of the upper layer is the inverse of the color of the lower layer. |
| Subtract | Subtracts the color of the upper layer from the color of the lower layer to obtain the resulting color. |
Set Fill Mode
Fill mode is used to control the drawing method of symbols, supporting both Global mode and Object mode, enriching the expression of symbols on the map.
Application Example
Case Description: Taking the fill mode of all prefecture-level cities in Sichuan Province as an example, you can set the symbol mode for area objects to either Global mode or Object mode to enrich symbol expression.
Data Description: Region dataset.
Main Operation Steps
- Select the area layer in the layer manager that requires symbols. In the Styles tab -> Fill Style group -> Symbols dropdown, choose the desired symbol style.
- Select the area layer in the layer manager for which you want to set the fill mode. Right-click and choose Layer Properties from the context menu.
- In the Layer Properties window, under Display Control -> Fill Mode, you can choose either Global Fill or Object Fill.
- Depending on the selected fill mode, the resulting effect will differ, as shown below:
- Left image: Global Mode: Drawing starts from the top-left corner of the entire layer, filling the symbols across the whole layer.
- Right image: Object Mode: Drawing starts from the top-left corner of each individual object, filling the symbols per object within the layer.

 Note:
Note:For CAD Datasets, which contain point, line, and area objects, the fill mode is only effective for the area objects within them.
Set Layer Visible Scale Range
Filter objects within a layer by setting the visible scale in Layer Properties or by setting a filter.
Minimum Visible Scale
Minimum Visible Scale: The combo box is used to set the minimum visible scale for the current layer. After setting the minimum visible scale for the layer, if the map's scale is smaller (i.e., zoomed out further) than this set minimum visible scale, the layer will not be visible.
Maximum Visible Scale
Maximum Visible Scale: The combo box is used to set the maximum visible scale for the current layer. After setting the maximum visible scale for the layer, if the map's scale is larger (i.e., zoomed in closer) than or equal to this set maximum visible scale, the layer will not be visible.
 Note:
Note:The drop-down button on the right provides different scale options depending on the situation:
- If the current map has fixed scales set, the drop-down button provides those fixed scale options;
- If the current map does not have fixed scales set, the drop-down button provides eight basic scale options from 1:5000 to 1:1000000;
- If you have customized a scale value in the numeric adjustment box next to Max/Min Visible Scale, the drop-down button will remember your custom value (in addition to the options from the previous two cases) for easy reuse;
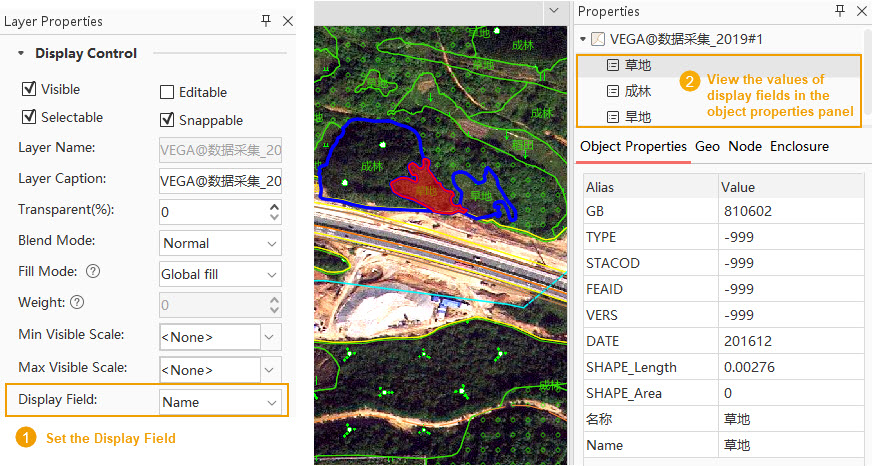
Display Field
Used to set the Display Field for vector objects in the Properties panel. After setting, when a vector object is selected on the map, the attribute value of the specified display field can be viewed directly in the Object Properties panel, making it easier to distinguish object categories intuitively from attributes. By default, the 'name' field in the layer is used. If there is no 'name' field, a text field is used. If there is no text field, the SmID field is used.
- If an invalid expression field is set, it will display as an invalid value "Null" when viewed in the Object Properties panel.
Display Filter
Filter Expression: Used to set the display filter for the current layer, filtering which objects in the layer can be displayed and which cannot. This allows users to display features of interest and filter out features that are temporarily not needed.
Users can input an SQL Expression as a filter in the text box under Display Filter. Press the Enter key to apply the filter to the layer, making objects that meet the filter conditions visible. Users can also click the button to the right of the text box to open the SQL Expression dialog to build the filter expression. After setting, click the OK button to apply the filter to the layer, making objects that meet the filter conditions visible.
Click the Join Attribute Table... button to pop up the "Join Attributes" dialog. Connect an external table through a join field, and then filter the content displayed in the layer by constructing a filter that involves fields from the external table.



