Used to measure the distance, area, or angle between points to be measured on a map. For Raster Data, measuring Surface Distance, Surface Area, or Surface Volume is also supported.
When measuring, users can turn on the Capture function to obtain the position of the point to be measured more accurately.
Illegal face does not support Map Measurement.
Function entrance
- Map tab-> Operation group.
Unit
It is recommended to set the unit of measurement and calculation before measurement and calculation. Click the Map tab-> Operation-> Unit button, and set the units of distance, area and angle in the pop-up dialog box.
Provide Automatic Conversion Unit, and the measurement and calculation results will be automatically converted in their respective systems. For example, if the current measurement unit is decimeter, when the measurement result is greater than or equal to 10 decimeter, the result will be displayed in meter; when the measurement result is greater than or equal to 1000 meter, the result will be displayed in kilometer.
Distance Measure
Distance Measure includes straight line, geodesic line and Surface Distance:
- Straight-line Distance refers to the horizontal distance between any two points on the map in a flat two-dimensional space, regardless of the curvature of the earth.
- Geodesic Distance refers to the length of the shortest line between any two points in the map on the surface of the ellipsoid (ellipsoid). For example, it can be used to measure the shortest path distance between two city airports as a flight route. The SmLength field in the properties table and the Length value in the Object Properties also take the geodesic calculation method.
- Surface Distance refers to the distance of the topographical surface measured along the specified line segment or polyline segment on the 3D surface fitted by Raster Data in the map. Surface Distance measures the distance on the surface, which is greater than straight-line distance and geodesic distance.
Take the Straight-line Distance measurement operation as an example to introduce how to complete the Distance Measure:
- Select the Straight-line Distance option from the Map Measurement drop-down list, and the mouse status in the current Map becomes a crosshair.
- Click the left mouse button at the starting point of the Measure Distance to determine the starting point; move the mouse, and a temporary line segment with changing length connecting the current mouse position and the starting point will appear on the screen, with the distance value displayed simultaneously.
- Move the mouse to the location of the second measurement point and click the left mouse button to determine the second point.
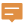 Caution: During measurement:
Caution: During measurement:The map will display two result values simultaneously: the length between the current mouse position and the previous point, and the total length from the starting point to the current mouse position.
- Before clicking the second point, both values are equal;
- After clicking the second point and moving the mouse, the two values become unequal;
- The length between current mouse position and previous point is always less than the total length from starting point.
- Repeat step 3 to add remaining measurement points. After adding the endpoint, complete the measurement with a right mouse click.
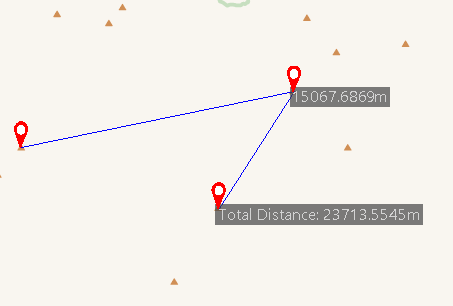
Area Measure
Area Measure includes plane area and Surface Area. Surface Area refers to the surface area measurement on the fitting surface of Raster Data. The following illustrates plane area measurement:
- Select the Area option in the Map Measurement drop-down. The mouse cursor becomes a crosshair.
- Click the left mouse button at the boundary starting point of the area to be measured in the current Map.
- Continue clicking left mouse button along the boundary inflection points to draw polygon vertices.
- Repeat step 3 and right-click to complete polygon drawing.
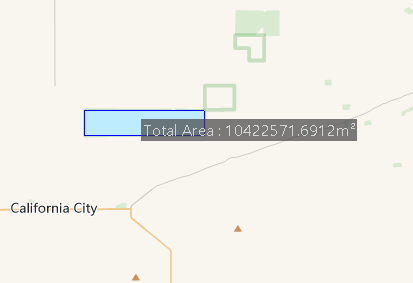
Angle Measure
Used to measure the angle value between continuous line segments.
- Select the Angle option from the Map Measurement drop-down. The mouse cursor becomes a crosshair.
- Click any point on one side of the angle with left mouse button as starting point. A dotted line pointing to true north will appear. Moving the mouse forms a ray from starting point, displaying both the angle between ray and true north direction (azimuth) and the ray's angle value.
- Click left mouse button to select angle vertex, determining the first edge. Moving the mouse draws another ray forming an angle with the first edge, displaying two values: angle between edges and ray's azimuth.
- Click left mouse button on the other side of the angle and right-click to complete measurement. Continuous angle measurements can be performed.
Clear
Click the Clear button in the Operation group to remove temporary polylines/polygons and measurement labels from the current Map. Pressing Esc key also activates this function.
Related topics



