After the Oracle Database software is installed, you need to run the Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA) to configure the Oracle database.
Find the Database Configuration Assistant tool under the Oracle configuration and migration tool directory in the Start menu, and double-click to run the configuration tool to open the interface as shown in the following figure:
Click Next to enter the configuration of the Oracle database, which consists of 12 steps.
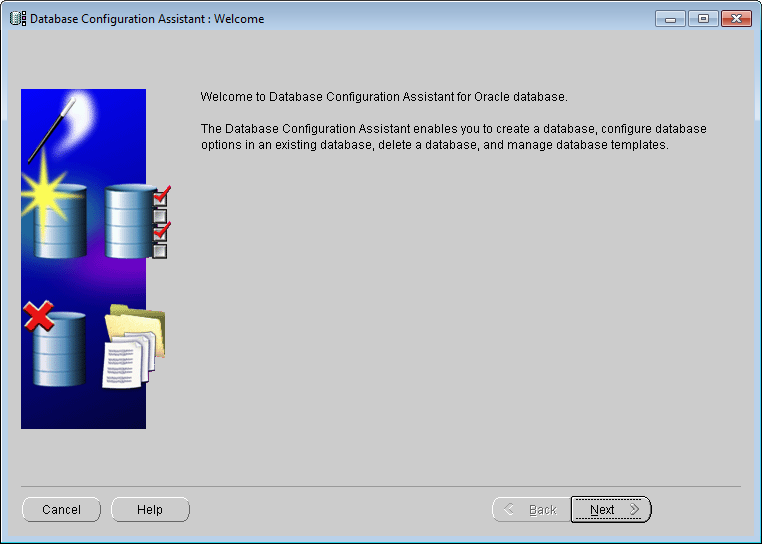 |
| Figure: Database Configuration Assistant Welcome Screen |
- Create the database
Select the "Create Database" operation and click the "Next" button to enter step 2.
Action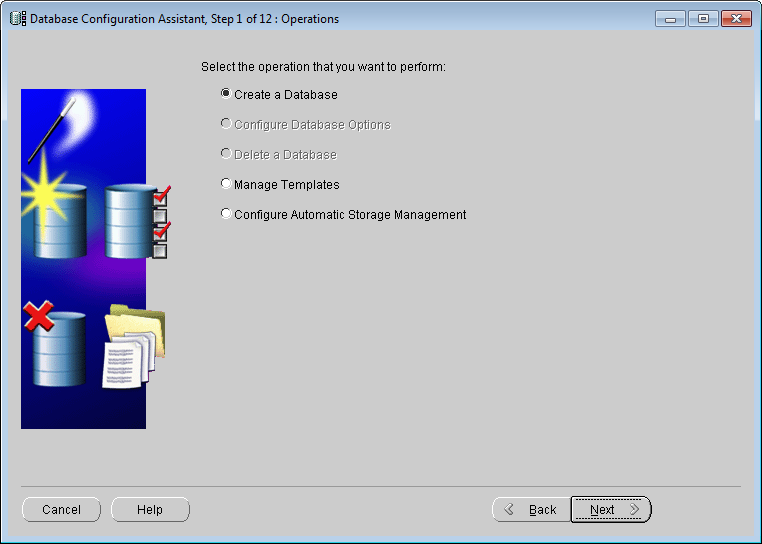
Figure: Database Configuration Assistant Select - Select Data Library template
Select the Custom Database item. We want to build an Oracle database suitable for SuperMap SDX +, so we choose "Custom Database" here. Click the Next button to proceed to step 3.
Database Template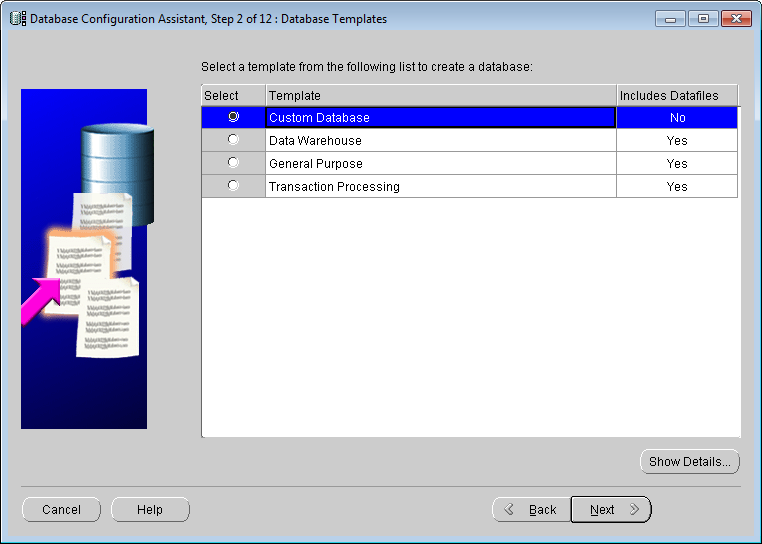
Figure: Database Configuration Assistant - Database identification Name
the global database and identify the Oracle database Unique identifier, as shown in the following figure. Click the Next button to proceed to step 4.
Database Identification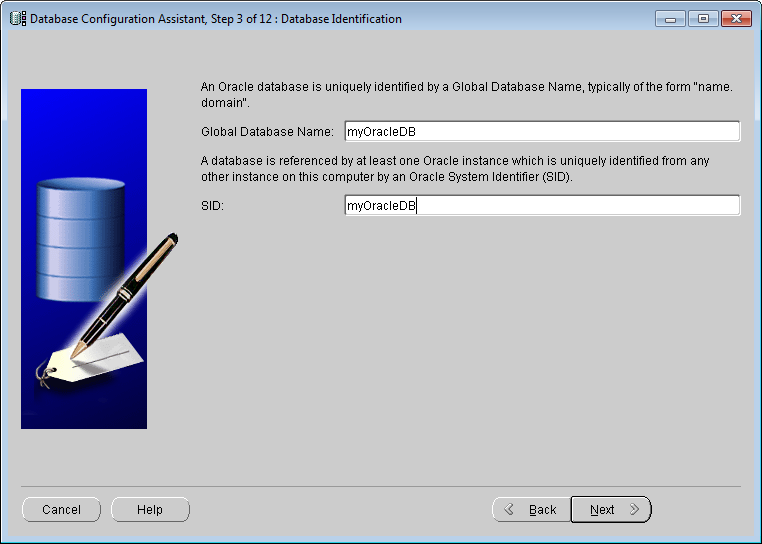
Figure: Database Configuration Assistant - Manage options Set the
Use Enterprise Manager to configure the database check box to deselected, as shown in the following figure. Click the Next button to proceed to step 5.
Administration Option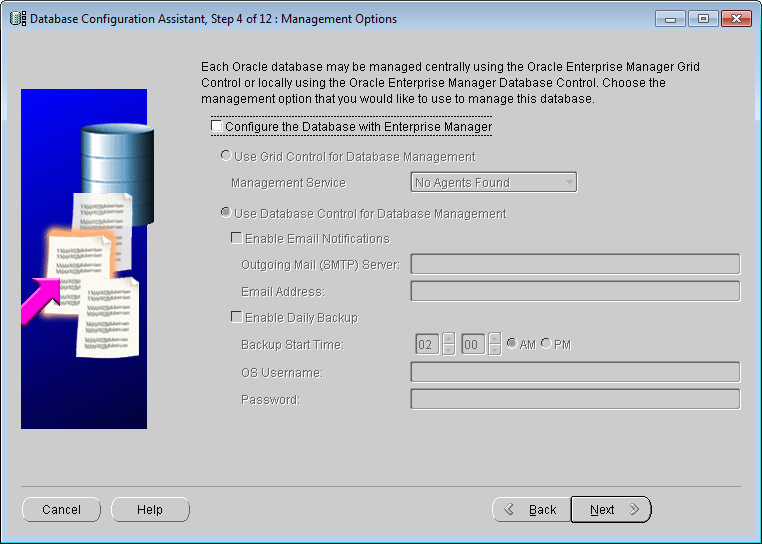
Figure: Database Configuration Assistant - Database credentials
In the Password text box, Input Data: The password for the library account. Here, you can select "All users use the same password" or "Use different passwords" according to your own needs, as shown in the following figure. Click the Next button to proceed to step 6.
Credentials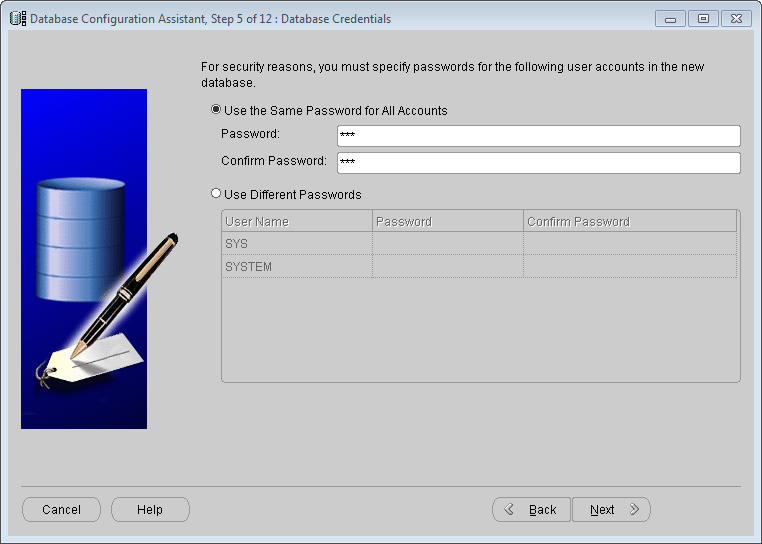
Figure: Database Configuration Assistant Database - Storage options
The product provides three database storage mechanisms, which users can choose according to their actual needs. Among them, "Automatic Storage Management (ASM)" and "Raw Device" are suitable for advanced servers, and "File System" can be selected for ordinary PCs. The storage mechanisms of the three databases are described as follows:
- File System: Saves and maintains the single-instance database files in a directory on the current file system.
- Automatic Storage Management (ASM): ASM is used to manage a small number of disk groups instead of a large number of database files. You must specify a set of disk groups to create an ASM disk group or specify an existing ASM disk group.
- Raw device: a disk or disk partition that is not managed by a file system. Use this option only if your site has at least as many raw disk partitions as Oracle datafiles.
setting the Storage Options, click the Next button to proceed to step 7.
Storage Option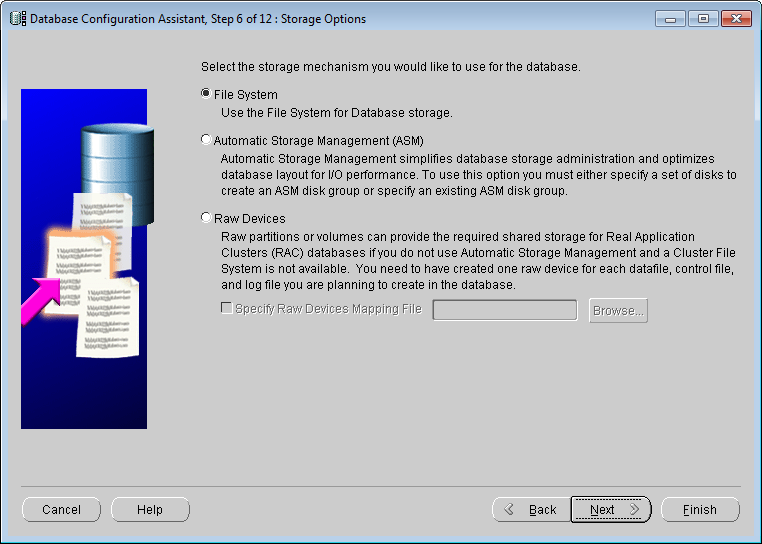
Figure: Database Configuration Assistant - Database file location Use
this step to specify where and how to store the database files. Here, we follow the default, which is the database File Position "entry in the Use Template. Click Next to proceed to step 8.
Location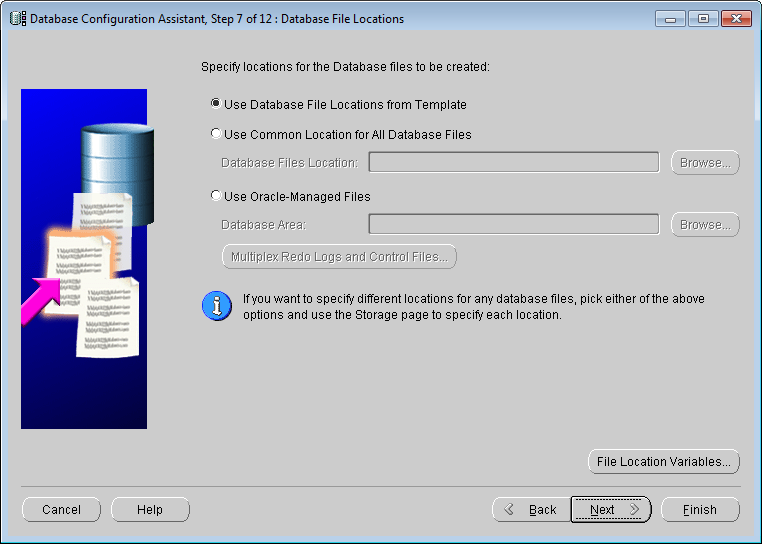
Figure: Database Configuration Assistant Database File - Restore the configuration
In this step, you specify a flash recovery area and enable archiving to recover your data in the event of a system failure.
If the "Designated Fast Recovery Area" option is selected, the data security can be ensured, but the Oracle performance will be affected. The user can select according to the actual needs. The recovery configuration interface is shown in the following figure. Click the Next button to proceed to step 9.
Restore Configuration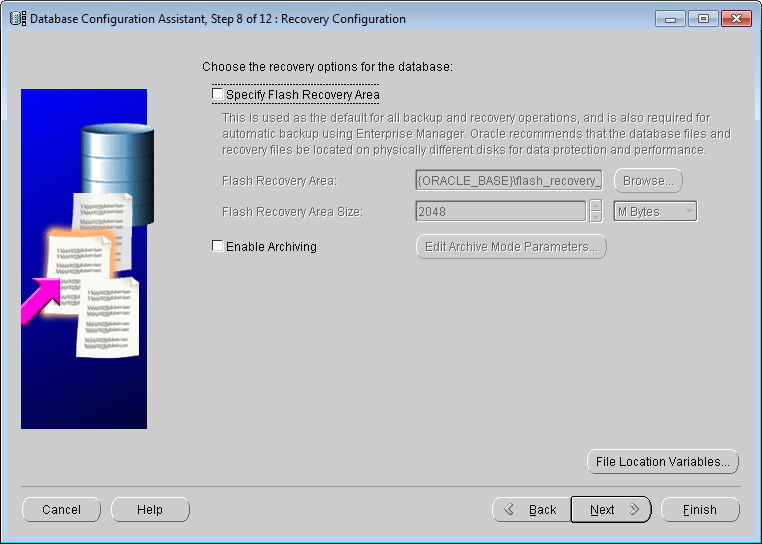
Figure: Database Configuration Assistant - Database contents
In this step, make the check boxes for Oracle Data Mining ", Oracle Spatial", and Enterprise Manager Repository unchecked. Click Standard Database Components.. to display the Standard Database Components dialog box. Uncheck the Oracle JVM "and Oracle XML Database check boxes, and then click OK. Finally, click the Next button to proceed to step 10.
Database Content
Figure: Database Configuration Assistant - Initialization parameters
The initialization parameter is step 10 of the Oracle configuration. The parameter setting in this step has a great impact on the performance of the Oracle database. Attention should be paid to the following five aspects of parameter configuration.
- All initialization parameters
In the pop-up initialization parameter interface, click All Initialization Parameters to pop up the All Initialization Parameters interface, and then click Display Advanced Parameters, as shown in the following figure. Most of the initialization parameters can be optimized to improve the database performance. It is recommended to modify the parameters CPU _ count and db _ file _ multiblock _ read _ count.
The CPU _ count is the number of CPUs allocated to the Oracle database. The default value is 1. If your machine is a multi-core CPU, you can increase this value. For example, for a machine with a dual-core CPU, the value of CPU _ count can be set to 2. This increases the speed at which Oracle runs.
db _ file _ multiblock _ read _ count affects the number of blocks Oracle reads at one time when performing a full table scan. The default is 16. The maximum value supported by Oracle cannot exceed 128. You can make changes based on your System Environment. This value is affected by the maximum I/O capability of the system: Max (db _ file _ multiblock _ read _ count) = Max (system I/O)/db _ block _ size, which can typically be changed to 32 or more.
Initialization Parameter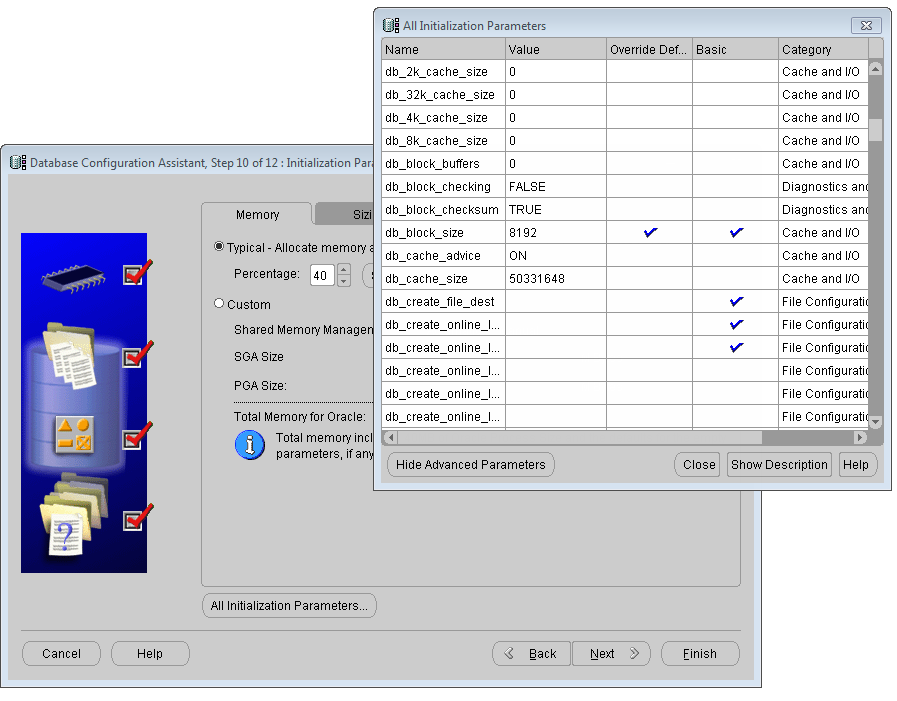
Figure: Database Configuration Assistant All - Memory The total amount of memory
allocated to Oracle directly affects the performance of Oracle. It is allocated according to the System Environment of the machine. The larger the memory, the better. When the memory value reaches a certain upper limit, the performance will not be significantly improved by continuing to increase the amount of memory. Generally, 1G-2G servers are enough. For 1G of memory, it is recommended that no more than 60% of the memory be allocated to Oracle.
SGA: System Global Area
PGA: Program Global Area
Memory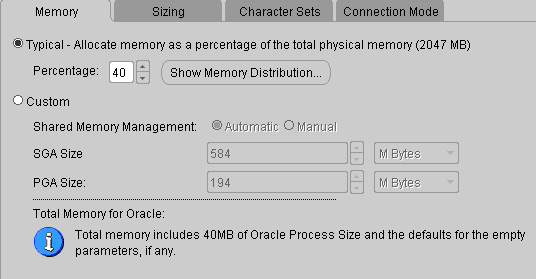
Figure: Database Configuration Assistant Initialization Parameter - Resize
Block size: Default. The Oracle Database Data Save is in these blocks. A data block corresponds to a specific number of bytes of physical database space on disk.
Processes: Specifies the maximum number of operating system user processes that can simultaneously connect to Oracle. If there are a lot of concurrent users, this value can be set to a larger value.
resizing
Figure: Database Configuration Assistant initialization parameter - Character set Select Use Default
for the character set.
Database Configuration Assistant Initialization Parameter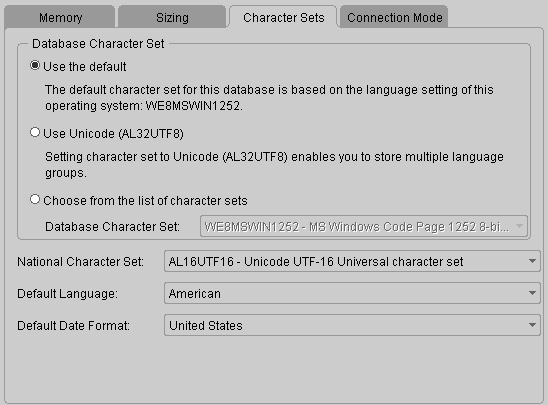
Figure: Character Set of -
Connection mode
The Oracle database configuration provides two connection modes, dedicated server mode and shared server mode.
Dedicated Server Mode: Oracle Database in this mode requires one dedicated server process per user process and one server process per client. Oracle Net send that address of the existing serv process back to the client. The client then resends the connection request to the provided server address.
The dedicated server mode is recommended forthe following situations:
(1) Using a database in a data warehouse environment.
(2) Only a few clients connect to your database.
(3) The database client will make persistent, long-running requests to the database.
Shared Server Mode: Also known as multi-threaded server mode, an Oracle Database configuration in this mode allows multiple user processes to share very few server processes, thus supporting a larger number of users.
Shared server mode is recommended inthe following situations:
(1) Using a database in an online transaction processing (OLTP) environment. Online transaction processing applications can benefit greatly by using a shared server.
(2) a large number of users need to connect to the database and efficiently use the available system resources.
(3) There is a memory limitation. Compared to dedicated servers, shared server memory usage is relatively low as the number of users increases. In the shared server model, memory usage is roughly proportional to the number of users. A shared server can tune and optimize overall system performance, so if a high degree of control over database tuning is necessary, a shared server is an option.
(4) You want to use Oracle Net features such as connection sharing, connection concentration, and load balancing.
(5) Efficient management and use of system resources are required.
(6) The connection is predictable and fast, such as Web Application.
Database Configuration Assistant Initialization Parameter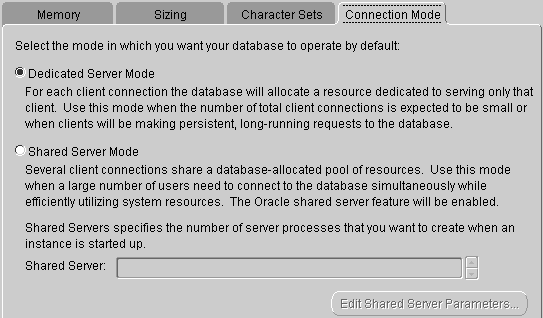
Figure: Connection Mode of
the above parameters are set, click the "Next" button to go to step 11.
- All initialization parameters
- Database storage
In this interface, you can specify the storage parameters of the database. It is recommended to use the default parameters, as shown in the following figure. Directly click the "Next" button to proceed to step 12.
Database Storage
Figure: Database Configuration Assistant - Create options After
clicking the "Finish" button, the parameter Details confirmation window will pop up. After clicking "Confirm", enter the database creation.
Creation Option Database Creation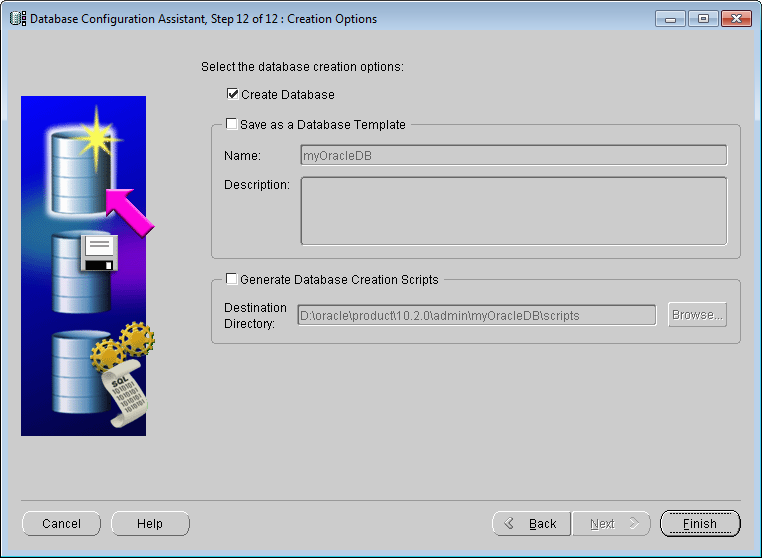
Figure: Database Configuration Assistant 
Figure: Database Configuration Assistant Confirms
 Caution:
Caution: - Installing multiple Oracle instances (that is, databases) on the same server
- is not recommended and will reduce the performance of the database. After the
- Oracle database is created, it will occupy a certain amount of processes and memory. It is recommended that the user change the two Oracle-related services to be started manually. The method is as follows: in the "Control panel & gt;" Systems and Security & > Management Tools & gt; "Service", in the service window, find the two services shown in the following figure, and change the startup mode to "Manual".
 |
| Figure: Changing how |




 Related topics
Related topics