Data Registration Overview
Remote sensing image data contains various geometric distortions during imaging process, requiring coordinate correction through registration operations. Paper maps may undergo deformation during preservation, and scanned drawings are prone to distortion errors. Scanned paper maps lack spatial positioning, necessitating data registration to align them with geographic coordinate systems or projected coordinate systems. This process also corrects geometric distortions and deformation errors, achieving coordinate unification for different datasets in the same area. Another scenario is when analyzing multiple datasets (e.g., image mosaics, vector data merging, or overlay analysis), all participating datasets must share the same coordinate system, which requires data registration.
Supports registration of single or multiple datasets, and enables rapid registration through registration files (*.drfu).
Principles of Data Registration
Data registration is the process of spatial correction and transformation for registration datasets (layers) using reference datasets (layers). Through specified registration algorithms and control point information, the registration dataset is adjusted to produce result datasets spatially aligned with the reference dataset (layer).
When specifying a reference layer, appropriate registration points should be selected in the registration layer while corresponding control points are identified on the reference layer. The registration process transforms the positions of registration points in the registration layer to match the spatial positions of the reference layer using specific algorithms. Without a reference layer, users should select registration points in the registration layer and input corresponding control point coordinates in the Input Control Points dialog.
Data Registration Workflow
Step 1: New Registration: Select one or multiple registration datasets to establish registration relationships between registration layers and reference layers.
Step 2: Select Control Points: The critical step of point matching involves selecting homologous feature points at identical spatial positions in both registration and reference layers. Existing control point registration files (*.drfu) can also be imported for registration.
Step 3: Calculate Error: Select registration algorithm to compute registration errors. The application calculates X-residual, Y-residual, RMSE, and total root mean square error for all control points to verify selection accuracy.
Step 4: Perform Registration: Execute registration when calculated errors meet precision requirements. Supports exporting registration files.
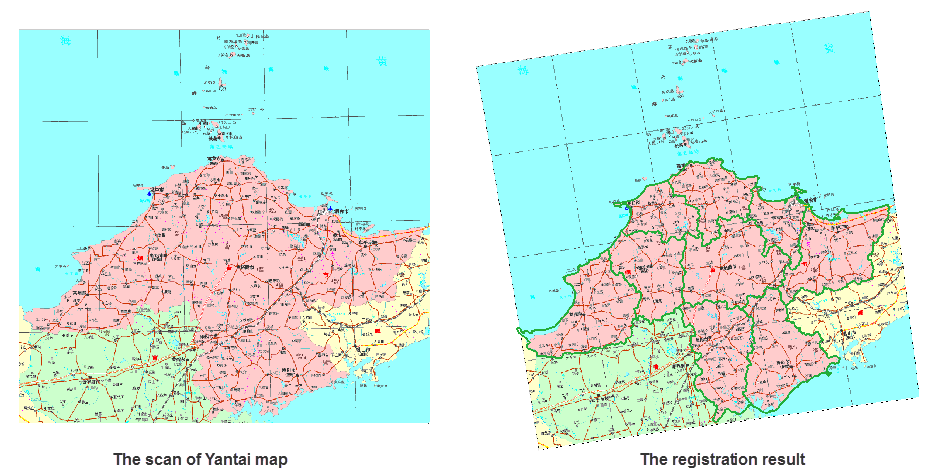
Application Example:
Registering scanned maps of Yantai City to align coordinate systems with vector region dataset (reference layer). The registration results show good alignment with reference data. The basemap displays registered scanned images, with green lines representing the transparently displayed YantaiR region dataset (reference dataset).
 |



