Single Feature Spatial Query
Spatial query is a query mode that builds filters through spatial relationships between geometries. For example, it can find spatial objects contained within polygons, separated from or adjacent to other spatial objects.
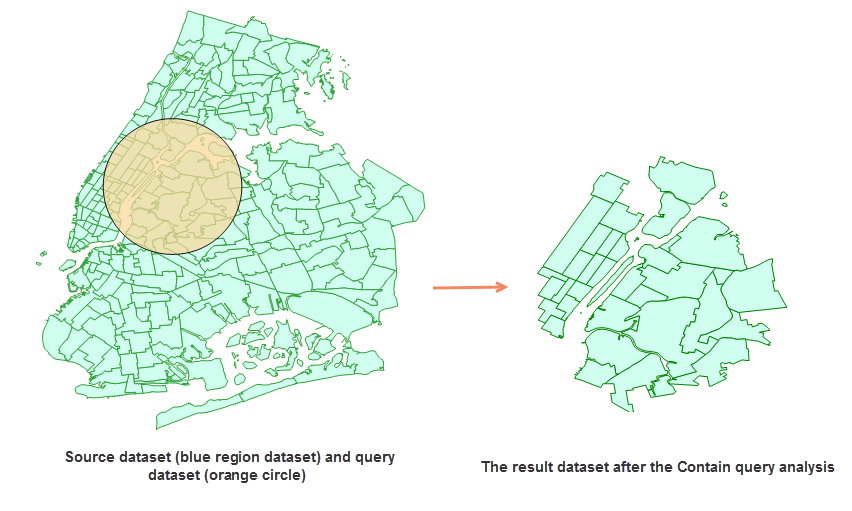
The application currently supports 8 types of spatial query relationships: Intersect, Contain, Cross, Disjoint, Coincide, Overlap, Adjacent, and Within. For detailed descriptions, please refer to the Spatial Query Tool page.
The Single Feature Spatial Query in online analysis only supports querying with a single feature from the query object dataset. If the query object dataset contains multiple features, the feature with the smallest SmID will be used for spatial query against the queried dataset by default.
Feature Entry
- Online Tab -> Analysis Group -> Single Feature Spatial Query.
Steps
- iServer Address: Select the iServer address and log in with your account via the dropdown options. For details, see the Data Input page.
- Source Dataset: (Required) Specifies the dataset to be queried. Select vector datasets for analysis by choosing Input Method and clicking the dropdown button. Available datasets will be automatically filtered. For details, see Data Input.
- Query Data: (Required) The dataset containing the query object. Only single-feature queries are supported. If multiple features exist, the feature with the smallest SmID will be used.
- Analysis Parameters: Configure Spatial Query Mode. Different modes require specific dataset types:
- Coincide, Disjoint, Contain, Intersect, Adjacent, Within: Accept point/line/polygon for both source and query datasets.
- Cross: Source dataset must be line type; Query dataset must be line or polygon type.
- Overlap: Both datasets must be line/line or polygon/polygon combinations.
- After configuring parameters, execute the spatial query. Successful analysis will automatically display results on the map and show the output workspace path in the message window. Note: Directly opening result data may fail due to server-side locking. Copy the data to another location for editing.
Related Topics



