When Oracle is installed, run Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA) in the start menu to configure Oracle.
In the start menu, click All Programs > Oracle > Configuration and Migration Tools > Database Configuration Assistant, the interface is as the following.
Click Next for the configuration of Oracle, there are 12 steps.
 |
| Database Configuration Assistant: Welcome |
- Create database
Select Create a Database, click Next.
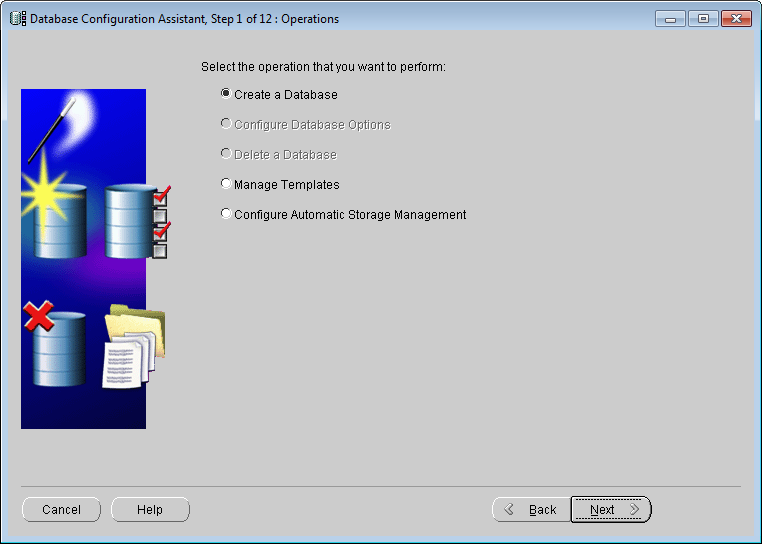
Database Configuration Assistant: Select operation - Select database templates
Select Custom Database because we need the Oracle database for SuperMap SDX+. Click Next.
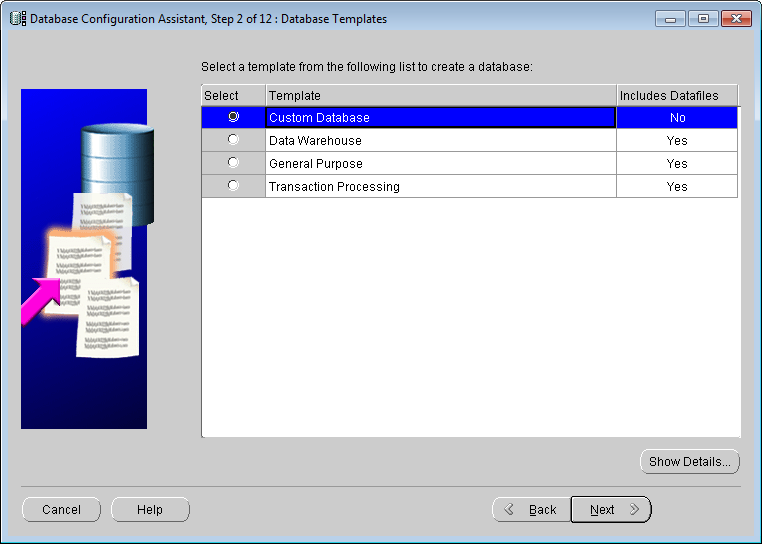
Database Configuration Assistant: Database templates - Database Identification
Name the Global Database and the SID, as shown below. Click Next.
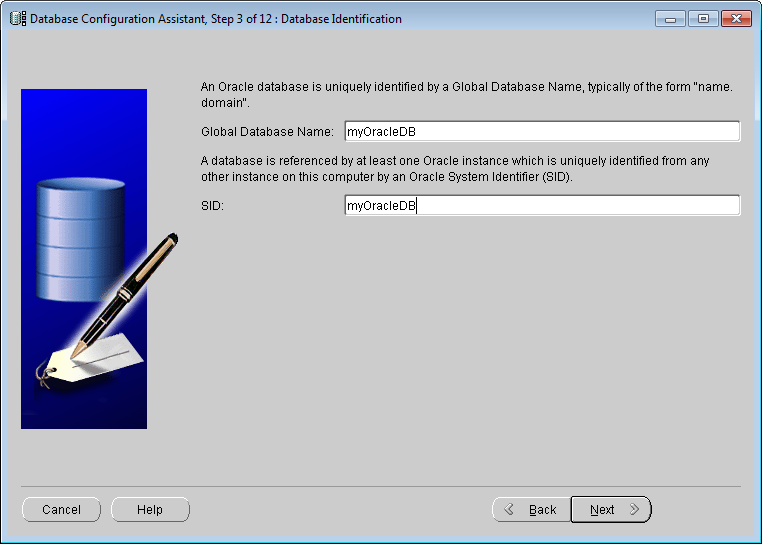
Database Configuration Assistant: Database Identification - Management Options
Uncheck Configure the database with Enterprise Manager, as shown below. Click Next.
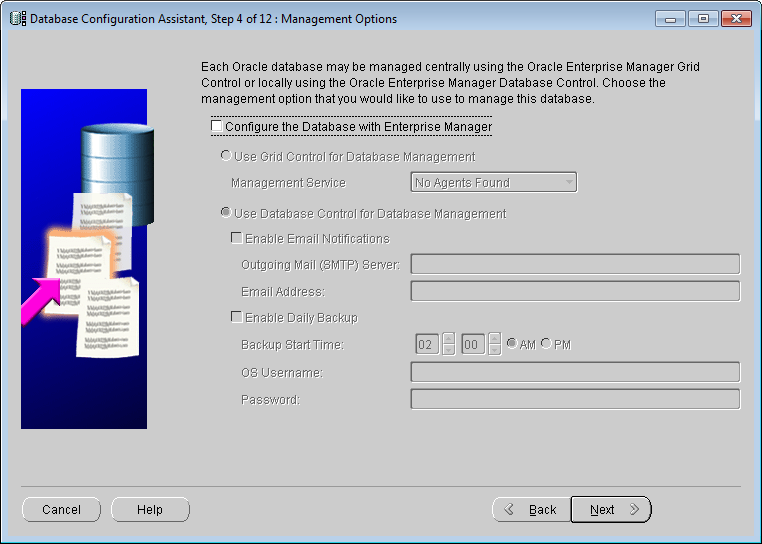
Database Configuration Assistant: Management Options - Database Credentials
Input the password for the database account in the Password text box. You can use different passwords, as shown below. Click Next.
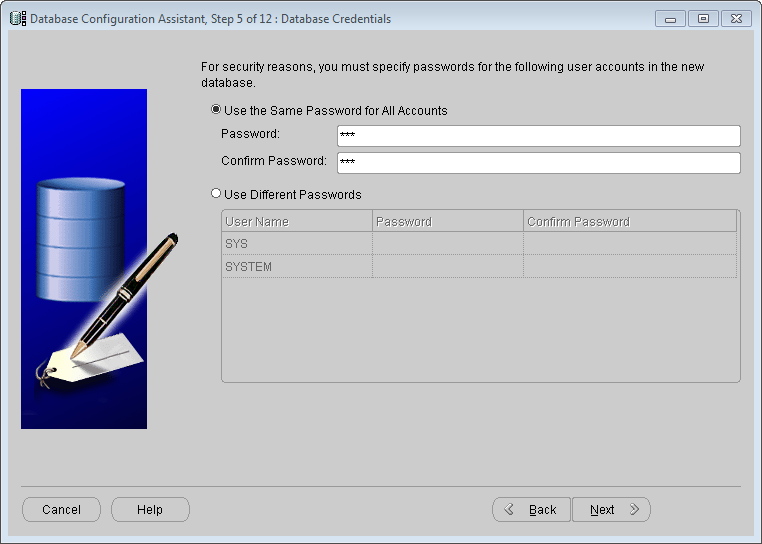
Database Configuration Assistant: Database Credentials - Storage Options
The system provides three database mechanisms, in which Automatic Storage Management (ASM) and RAW Devices are used for advanced server, for normal PCs, just select File System.
- File System: Save and maintain single instance database file in the current file system directory.
- Automatic Storage Management (ASM): With ASM, the database just need to manage a few disk packs and there is no need to manage numerous database files, if you select this option, it is needed to specify a group of disk packs to create a ASM disk packs or specify an existing ASM disk packs.
- RAW Devices: The disk or disk partition not managed by file system. You can select this option when you site have at least the same raw disk partitions with Oracle data file.
Click Next.

Database Configuration Assistant: Storage Options - Database File Locations
Specify locations for the Database files to be created, for more details, please refer to the help of Oracle. Here, we used the default option, that is Use Database File Locations from Template, click Next.

Database Configuration Assistant: Database File Locations - Recovery Configuration
Specify flash recovery area and enable archiving.
Check Specify Flash Recovery Area can ensure the security of the data, but it will degrade the performance. Click Next.
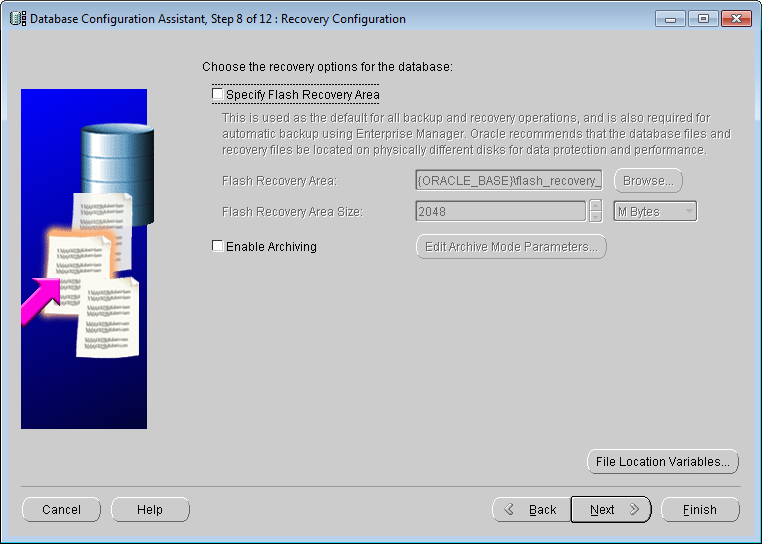
Database Configuration Assistant: Recovery Configuration - Database Content
Uncheck Oracle Data Mining, Oracle Spatial and Enterprise Manager Repository. Click Standard Database Components..., uncheck Oracle JVM and Oracle XML DB in the dialog box appears, click OK. Click Next.
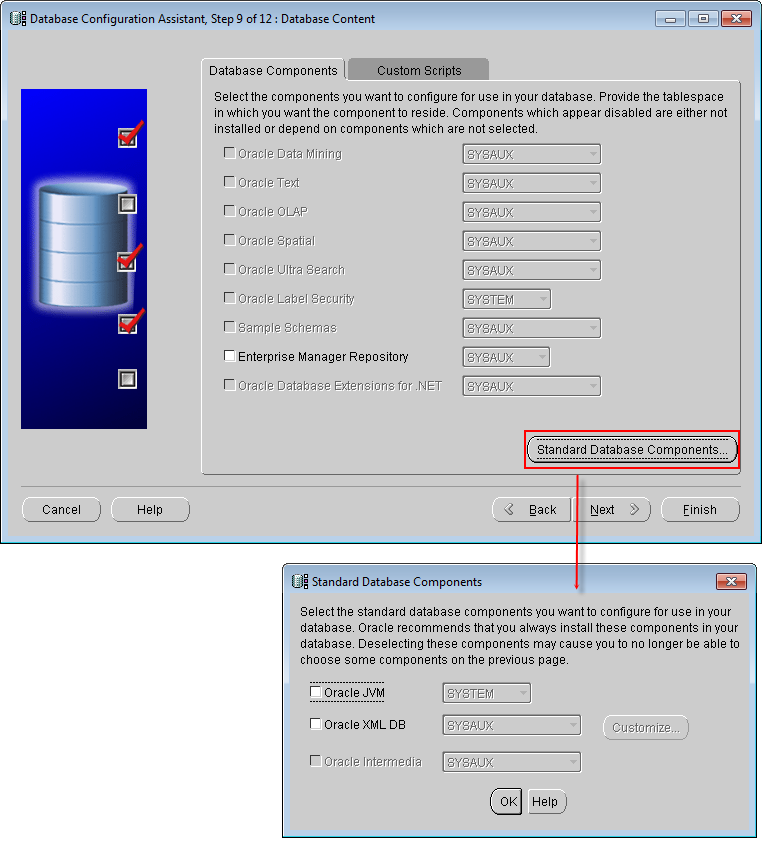
Database Configuration Assistant: Database Content - Initialization Parameters
The parameter settings in this step will affect the performance of the database tremendously. Note the settings of the 5 aspects.
- All Initialization Parameters
Click All Initialization Parameters..., then click Display Advanced Parameters, as shown below. Most of the initialization parameters can be optimized to improve the performance of the database, it is recommended to modify cpu_count and db_file_multiblock_read_count.
cpu_count is the number of CPUs assigned to Oracle database, the default is 1, you can magnify this value if you machine has multi-core CPU, for dual-core CPU machine, the value of cpu_count can be set as 2, this may improve the speed of Oracle.
db_file_multiblock_read_count affects the number of Blocks read at a time when performing full table scan, the default value is 16, the maximum value supported by Oracle is no large than 128. You can change it according to your system environment. This value is affected by the maximum ability of the system I/O: Max(db_file_multiblock_read_count)=Max(System I/O)/db_block_size, usually, it can be changed to 32 or greater.
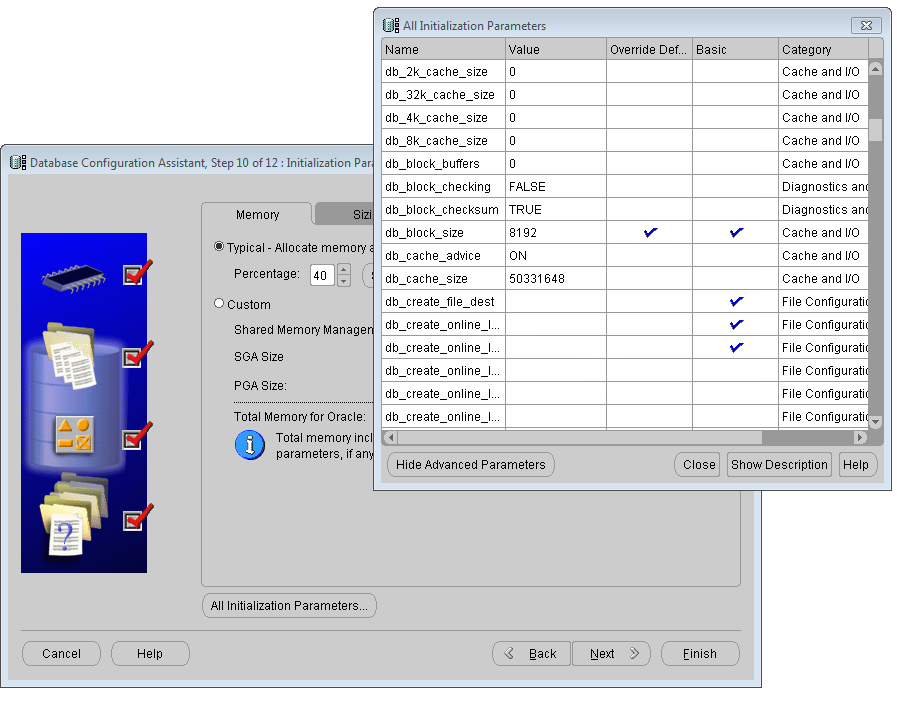
Database Configuration Assistant: All Initialization Parameters - Memory
The memory assigned to Oracle, for normal servers, it can be 1G to 2G, if you memory is no more than 1G, it is recommended the memory assigned to Oracle should not be higher than 60%.
SGA: System Global Area
PGA: Program Global Area
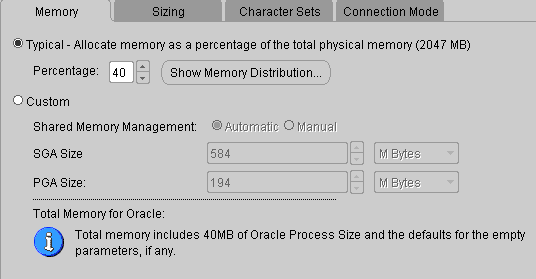
Database Configuration Assistant: Initialization Parameters-Memory - Sizing
Block Size: Use the default value. Oracle database saves the data in these blocks. Each block corresponds to a physical database space with specific bit on the disk.
Processes: You can specify the maximum user processes connected to Oracle. You can set a relatively large value if there are many concurrent users.

Database Configuration Assistant: Initialization Parameters-Sizing - Character Sets
Select Use the default.
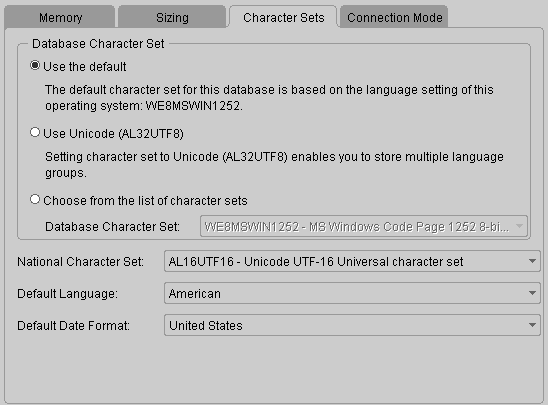
Database Configuration Assistant: Initialization Parameters-Character Sets - Connection Mode
Two connection modes are provided: Dedicated Server Mode and Shared Server Mode.
Dedicated Server Mode: In this mode, Oracle database requires each user process has a dedicated server process, each client has a server process. Oracle Net returns the current server process address to the client. Then the client sent the connecting request to the server address again.
It is recommended to select the dedicated server mode in the following circumstance:
(1) Use database in the data warehouse environment.
(2) There are only a few clients connected to your database.
(3) Database clients will send lasting and long hour running requests.
Shared Server Mode: Also called multi-thread server mode, in this mode, the Oracle database configuration allows multiple user processes to share a few server processes, thus supporting more users.
It is recommended to select the shared server mode in the following circumstance:
(1) When using database in the on-line transaction processing (OLTP) environment, shared server mode can benefit the on-line transaction processing application a lot.
(2) Multiple users need to connect to the database and use the system resources effectively.
(3) Memory limitation. Compared with dedicated server, the use of shared server memory is relatively small when the number of users increases. In shared server mode, the memory used is generally in proportion to the number of users. Shared server can adjust and optimize the whole system performance, so you can choose shared server if it is needed to control the optimization of the database highly.
(4) If you want to use the functionalities of Oracle Net, such as connection sharing, connection concentration and load balancing.
(5) If you need to manage and use system resources efficiently.
(6) connection is predictable with fast speed, for example, Web application.
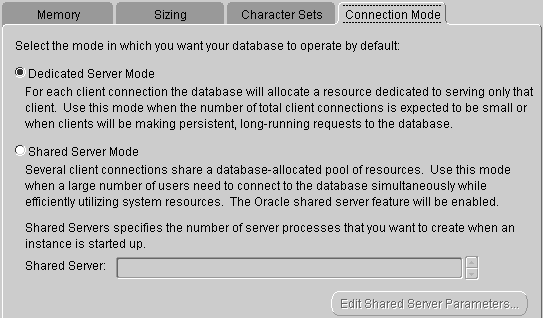
Database Configuration Assistant: Initialization Parameters-Connection Mode
Click Next.
- All Initialization Parameters
- Database Storage
You can specify the storage parameter of the database here, it is recommended to use the default parameter, as shown below. Click next.
Database Configuration Assistant: Database Storage - Creation Options
Click Finish. The Confirmation window appears, click OK.
Database Configuration Assistant: Creation Options 
Database Configuration Assistant: Confirmation
 Note
Note
- It is not recommended to install multiple Oracle instances (databases) on a server, this may lower the performance of the database.
- After the creating of the Oracle database, it may occupy some process and memory, it is recommended to change the two services of Oracle to manual, you can open the service window in Control Panel > System and Security > Administrative Tools > Service, and change the startup type to Manual.
 |
| Change the startup type of the Oracle services |
 Related Topics
Related Topics
 Local Net Service Configuration
Local Net Service Configuration