Generate Tie Points
Instructions for Use
Tie points are corresponding image points that can construct stereo models or establish connection relationships between adjacent models (images). Generating tie points helps improve accuracy during geometric correction to ensure spatial consistency of images.
SuperMap iDesktopX11i(2023) version starts to support this feature.
Function Entry
Imagery Tab->Geometric Correction Group->Generate Tie Points.
Parameter Description
- Input Image Type: Select the type of image used for generating tie points. Default is Panchromatic Image. It can also be switched to Multispectral Image, Forward-Looking Image, Rear-View Image, or Front View and Rear View Image based on specific image types.
- Refer to the Adjustment File: Utilize existing adjustment file information to make newly generated tie points approximate the accuracy of existing tie points. Use the Add and Delete buttons in the toolbar to conveniently manage multiple adjustment file references.
- Planar Accuracy: Image planar accuracy determines whether preprocessing is performed during tie point matching.
- Low: Generally indicates that the image planar accuracy error is greater than 40 pixels, requiring preprocessing.
- High: Generally indicates that the image planar accuracy error is less than 15 pixels, no preprocessing is needed.
- Medium: Select this option when the image accuracy is uncertain; the program will automatically estimate the accuracy.
- Error Threshold: Set the error threshold for gross error elimination during image matching when generating tie points. The value range is [0,40], default is 5, unit is px. A larger threshold preserves more tie points but increases the probability of retaining erroneous points.
- Point Distribution Mode: Select the tie point distribution mode. Options are Conventional and Uniform, default is Conventional.
- Conventional: Divides each overlapping area into N*M sub-regions, then selects n image blocks of 512*512 size from each sub-region for corresponding point matching to ensure stable and reliable tie points. Generated tie points will cover the entire overlapping area as much as possible.
- Density: Set the intensity for generating ground control points: Sparse is 3*3 sub-regions; Medium is 4*4 sub-regions; Dense is 6*6 sub-regions, default is Medium. Higher density requires longer computation and processing time.
- Matching Method: Provides five matching methods: MOTIF, AFHORP, RIFT, SIFT, and DEEPFT, default is MOTIF. Among them, AFHORP and RIFT support multi-modal data matching, and DEEPFT requires configuring an AI model and installing CUDA.
- MOTIF: A template matching algorithm for multi-modal images, characterized by using lightweight feature descriptors. MOTIF can overcome nonlinear radiometric distortions caused by differences between SAR and optical images.
- AFHORP: A feature matching algorithm for multi-modal images. AFHORP is highly resistant to radiometric distortions and contrast differences in multi-modal images and performs excellently in solving issues like directional reversal and phase extremum mutations.
- RIFT: A feature matching algorithm robust to large-scale nonlinear radiometric distortions. RIFT not only improves the stability of feature detection but also overcomes the limitations of using gradient information for feature description.
- SIFT: A method for extracting distinctive invariant features from images, used for reliable matching between objects or scenes from different viewpoints.
- DEEPFT: An image matching method based on deep learning.
- Maximum Points per Block: The maximum number of points retained within a block during image matching. Value range is [25,2048], default is 256.
- Uniform: Generated tie points will be evenly distributed in the overlapping area. The number of points is less than that of the regular distribution, but the distribution is more uniform, suitable for images with significant internal distortion.
- Number of Seed Points: Set the number of seed points for corresponding point matching on each image. Value range is [64,6400], default is 512. When image texture is poor, increase the number of tie points to ensure enough points are matched, improving subsequent image quality.
- Seed Point Search: Set the method for searching seed points. Options are Raster Center Point and Corner Point, default is Corner Point.
- Corner Point: Uses points with distinct features within the selected region as seed points.
- Raster Center Point: Uses the center point of the raster as the seed point. This search method is random.
- Template Size: Set the interval size between seed points. Value range is [1,256], default is 40, unit is px. Larger templates result in more reliable search points but take longer.
- Search Radius: Set the search radius for seed points during image matching. Value range is [0,256], default is 40, unit is px. A larger search radius increases the matching range but also increases processing time.
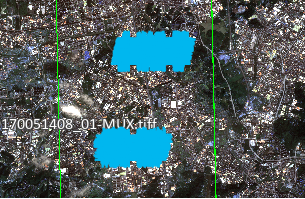
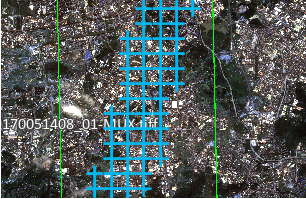
Figure: Regular Distribution Figure: Uniform Distribution - Conventional: Divides each overlapping area into N*M sub-regions, then selects n image blocks of 512*512 size from each sub-region for corresponding point matching to ensure stable and reliable tie points. Generated tie points will cover the entire overlapping area as much as possible.
- Semantic Culling of Non-Ground Points: Not selected by default. When selected, AI semantic technology is used to automatically remove tie points in cloud areas and building areas.
- Cloud Area: This parameter appears after selecting Semantic Culling of Non-Ground Points. Selected by default, it automatically removes tie points in cloud areas based on the set dataset. If not selected, tie points in cloud areas are retained.
- Building Area: This parameter appears after selecting Semantic Culling of Non-Ground Points. Selected by default, it automatically identifies building areas and removes tie points in those areas. If not selected, tie points in building areas are retained.
Related Topics
Generate Ground Control Points



