Instructions for use
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Analysis is an unordered path analysis. The traveling salesman can decide the starting and ending order of visiting these nodes by himself, and the goal is to minimize (or nearly minimize) the total impedance of the travel route. For a detailed introduction to Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Analysis, See Traveling Sale sman Problem (TSP) Analysis Overview .
Operation steps
- Open the Network Dataset for Network Analysis.
- Before proceeding with Network Analysis, the Network Analysis environment needs to be set up. On the Traffic Analysis tab-> Road Network Analysis group-> select the Environment Settings check box, the Environment Settings Dock Bars will pop up. Set Network Analysis parameters in this window, such as weight field, node/Edge ID Field, etc. For an introduction to the Environment Settings window, see Network AnalysisEn vironment Settings window Page.
- On the Traffic Analysis tab-> Road Network Analysis group-> click Gallery Drop-down Button-> select Traveling Sale sman Problem (TSP) Analysis to create an instance of the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Analysis. For an introduction to instance windows, see Introduction to Instance Management window Pages.
- Click in the current Network Data layer to select the site location to add. There are two ways to Add Site, one is to click the mouse in the Network Data layer to complete the addition of the site; the other is to import the point object of the Point Dataset as the site. See the Add site dialog box for details.
Note: In the Network Analysis management window, you can set the type of the site. Select a site and set it as the start point, end point, intermediate point or start-stop point in the pop-up Context Menu. Start indicates that the point is the start point of the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Analysis; End indicates that the point is the end point of the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Analysis through which the analysis path will last; A start-stop point means that the point is both a start point and an end point, that is, the point from which the path of the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Analysis begins and to which it must return. By default, the first site is the starting point, and the other sites are intermediate points.
In the - same way, you can set barrier points for Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Analysis. Barrier point management can be found on the barrier point management page. Click the Parameter Settings "button
- in the Network Analysis Instance Management window, The Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Analysis Settings dialog box pops up to set the Analysis Parameters.
- Save node information
Select whether to save all node information passed by Analyst Result. If the check box is selected, save the node information as Point Dataset and give it a name. The Dataset is saved to the Datasource where the Network Dataset resides. The node information records the node ID (NodeID) and the ID (RouteID) of the Result Route where the node is located.
- Save arc segment information
Select whether to save the information of all arc segments passed by the path analysis. If you select the check box, save the arc segment information as a Line Dataset and give it a name. The Dataset will be saved in the Datasource where the Network Dataset is located. The arc segment information records the ID (EdgeID) of the arc segment through which the Result Route passes.
- Site Statistic Infomation
Select whether to save the site Statistic Infomation. If the checkbox is selected, save the Site Statistic Infomation as a Tabular Dataset and give it a name. This Dataset will hold some Statistic Infomation of the analysis site, including the starting site, the ending site, the cost, etc.
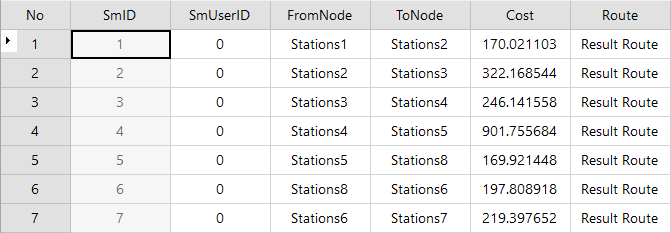
As shown in the following figure, it is a Statistic Infomation attribute table of a site. The order in which the Analyst Result passed through each site and the cost used are recorded in the table. The fields FromNode and ToNode represent the starting site and the ending site, the Cost field represents the cost between adjacent sites, and the Route field represents the name of the route generated by the analysis.
- Enable Path Guide
Select whether to generate Driving Guidance during analysis. Driving Guidance records the path information in the Transportation Analysis result. A Driving Guidance object corresponds to a driving route from the start point to the end point. When the Enable Path Guide "checkbox is checked, it indicates the path information of the Output Analysis Results in the Driving Guidance window. For an introduction to Driving Guidance, see the Driving Guidance page.
When - Save node information
- all Parameter Settings are complete, Click the Execute button in the Road Network Analysis group on the Traffic Analysis tab or click the Execute button in the Instance Management "window, and you can set the parameters. Perform a Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Analysis operation. After
The execution completed, the Analyst Result will be automatically displayed Add to Current Map. At the same time, the Output Window will prompt: "Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Analysis succeeded.".
 Precautions
Precautions
- For the Stop Info added to the site directory tree, you can Export as Point dataset it to facilitate the use of similar Network Analysis in the future.
- Stations must be located on network arcs and network nodes, or in areas within set tolerances. You can set the Node Tolerance in the Analysis Environment "window to change the appropriate tolerance size.
- If you need to modify the site location, you can select the site to be moved through the Move Site button, and drag it to the appropriate location.
- If obstructing points are set in a Network Analysis layer, the obstructing point information is displayed in the Network Analysis management window, and the obstructing points can be managed in this window. Refer to the Barrier point management for instructions on how to add obstacle points.
- Application supports simultaneous management of multiple Network Analysis instances. Click the Network Analysis "button again and select Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Analysis from the pop-up menu. A new Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Analysis can be created. In the Instance Management "window, use the drop-down boxes to toggle between Network Analysis types. If an analysis instance is no longer needed, click Delete Instance "to delete the current instance, and the Application will automatically switch to the next analysis instance for display.
 Related topics
Related topics
 Traveling Sale sman Problem (TSP) Analysis Overview
Traveling Sale sman Problem (TSP) Analysis Overview



