According to the different sources of data, it can be divided into aboveground data and underground data. The following details the different altitude modes for each of these two types of data:
Aboveground Data
- ClampToGround
When ClampToGround mode is used, the altitude of 3D Data is completely ignored, and each 3D Object is attached to the terrain surface according to its latitude and longitude and the relief of the terrain surface, that is, the height relative to the terrain surface is zero. As shown in the following figure, when ClampToGround mode is used, the altitude information of the surface object is ignored, and the surface object will be attached to the undulating terrain surface according to the latitude and longitude coordinate information and the trend of terrain undulation.
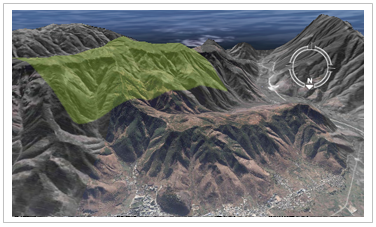
Note: The ground mode is the default height mode. In this mode, it is not allowed to set whether the data comes from the ground or underground.
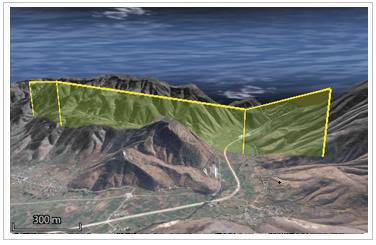
- Absolute Mode (Absolute) The altitude value in
Absolute mode (Absolute) is the altitude relative to sea level. This mode ignores the actual altitude of the terrain. This altitude mode is useful when the exact altitude value is known. As shown in the following figure, a face object in the scene, whose boundary nodes have an elevation value of 5800 meters, has the Display Status shown below when Absolute mode is used.
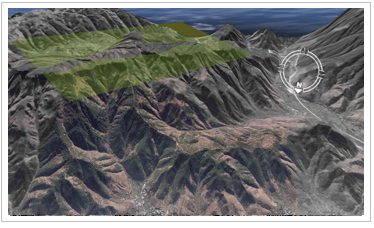
- Relative to Ground Height Mode (RelativeToGround) The altitude value in the
Relative to Ground altitude mode (RelativeToGround) is the altitude based on the ground level (terrain surface) directly below the longitude and latitude coordinate values. As shown in the following figure, for a pulled line object in the scene, if the elevation values of each node of the line object are equal, the Display Status is as follows in the Relative to Ground height mode.
- Modify Terrain
When the Modify Terrain height mode (ModifyTerrain) is used, the Terrain Data will rise and fall with the Vector Data, and the height of the terrain will completely coincide with the Vector Data, that is, the Terrain Data will be flattened by the phase surface data. As shown in the following figure, when using the Modify Terrain height mode, the relief of Terrain Data under the face object is consistent with the face Returns the height of the object. The Modify Terrain Height mode is often used in Terrain Data scenes.

- ClampToObject
When using the ClampToObject mode, the Vector Data is completely attached to the Model Data as the Model Data rises and falls, that is, the height relative to the Model Data is zero. As shown in the following figure, when the object height mode is used, the altitude information of the face object is ignored, and the face object is attached to the Model Data surface according to the undulating trend of the model. The Paste Object Height mode is often used in Oblique Photography Model scenes.

Subsurface Data
- Relative to Underground Height Mode (Relative ToUnderground)
When using the Relative to Underground height mode (Relative ToUnderground), the Bottom Altitude value can be negative, that is, the Geometry or Model Object can be placed below the ground surface. It is mainly used for browsing underground scenes, such as Underground Pipelines and seabed, which is very useful. If the height mode is set to Relative to Underground and the surface elevation is set to -100, the Geometry will be 100 meters below the surface and the datum will be the toposurface.
- Absolute UnderGround The altitude value in Absolute Underground
mode (AbsoluteUnderGround) is the altitude relative to sea level, and the actual altitude of the terrain is ignored. The Relative to Underground mode is useful for application scenarios such as Underground Pipelines and the seabed. The elevation is calculated on the basis of the spherical surface and is not affected by the terrain. When the height mode is set to this mode, the underground object can be visible by adjusting the Transparent Surface degree or excavation.
- ClampToObject
When using the ClampToObject mode, the Vector Data is completely attached to the Model Data as the Model Data rises and falls, that is, the height relative to the Model Data is zero. As shown in the following figure, when the object height mode is used, the altitude information of the face object is ignored, and the face object is attached to the Model Data surface according to the undulating trend of the model. The Paste Object Height mode is often used in Oblique Photography Model scenes.
The following figure shows the datum plane corresponding to different height modes and the height area where the corresponding Geometry is placed after the height value (Z value) is set. It can be seen from the following figure that the altitude datum plane of Absolute mode is sea level, and the positive direction is consistent with the arrow direction in the following figure; In the ground mode, objects are attached to the toposurface. The altitude datum plane of the Relative to Ground and Relative to Underground altitude modes is the toposurface, and the positive direction is the same as the direction of the arrow in the following figure.
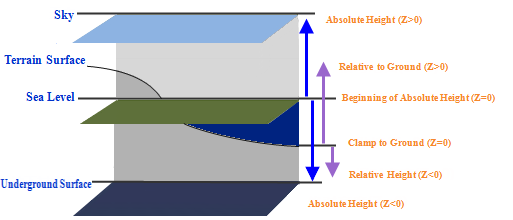 |
Remark
For settings for the height of 3D layers of the Vector Dataset type, see Set Bottom Altitude and Extended Height . Set fields values through the combo box to the right of the Bottom Altitude "label or manually enter anchor level values for the layer.



