Feature Description
Binary raster thinning is a thinning method for processing binary images. If the input data is not a binary image, it will first be converted to one. Users only need to specify a NoData value, where all values except NoData will undergo thinning. This function supports both raster datasets and image datasets.
It is suitable for road data raster thinning or scenarios where source data is binary grid/image data. Compared to regular raster thinning, binary raster thinning offers faster and more efficient processing.
Feature Entry
- Click the Spatial Analysis Tab -> Raster Analysis group -> Vector-Raster Conversion -> Binary Raster Thinning.
- Toolbox -> Raster Analysis -> Vector-Raster Conversion -> Binary Raster Thinning.
Parameter Description
Configure parameters including source datasource, NoData value, tolerance, and result data in the "Binary Raster Thinning" dialog. For detailed parameter descriptions, refer to Raster Thinning.
Save as raster dataset: When the source data is an image dataset, check this box to generate the result as a raster dataset.
Application Example
For existing road data in a region, applying binary thinning can reduce the number of pixels representing roads in the raster data, thereby improving vectorization speed and accuracy. After configuring the binary raster thinning parameters, results as shown in the following figure are obtained.
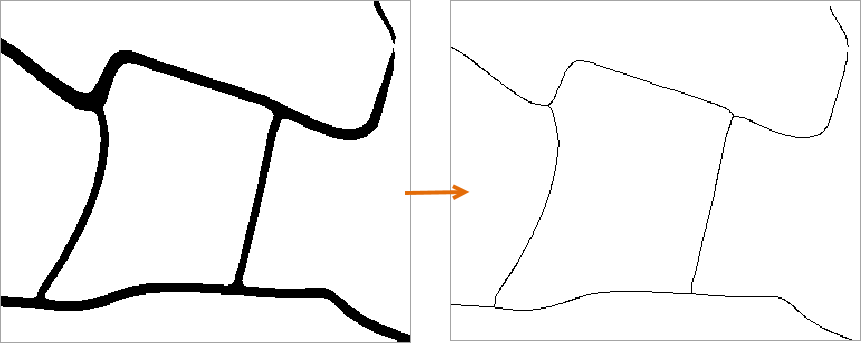 |
| Figure: Comparison of Binary Thin Raster Results |
 Caution:
Caution:- The NoData tolerance refers to the tolerance range of the user-specified NoData value and is independent of original NoData values in the raster.
- It is recommended to click the pick button to select NoData values from opened raster datasets. If the specified NoData value does not exist in the dataset's cell values, calculation results may be incorrect or raster thinning may fail.



