Buffer analysis is a method that creates areas of specified width around points, lines, or regions based on a given distance. It is widely used in GIS spatial analysis and often combined with overlay analysis to solve real-world problems. This technique finds applications in agriculture, urban planning, ecological protection, flood control, military operations, geology, environmental management, and more. For example, in environmental remediation, buffer zones around polluted rivers can delineate contaminated areas. In road expansion projects, buffers created around roads can be overlaid with building layers via overlay analysis to identify structures requiring demolition.
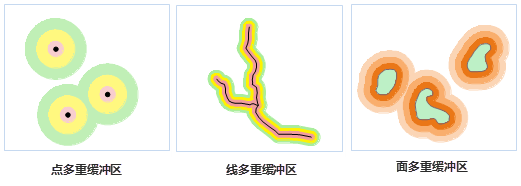
Buffer analysis operates on point, line, and region objects, supporting 2D points, lines, regions, and network datasets. For network datasets, buffers are generated along their arc segments. Buffer types include single buffer and multiple ring buffer. Below illustrates buffer generation methods for basic geometries:
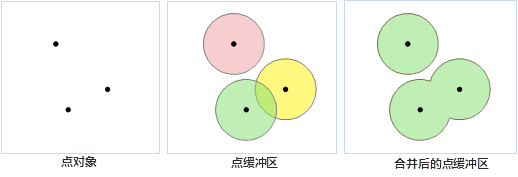
- Point Buffer
A point buffer is a circular area centered at the point with a specified radius. When buffer distances are large enough, buffers from multiple points may overlap. Selecting union buffer merges overlapping areas into a complex region object.
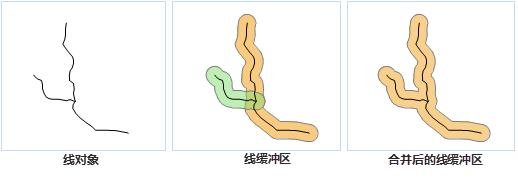
- Line Buffer
A line buffer is formed by offsetting the line to both sides by a specified distance and connecting the endpoints with smooth curves (or flat ends) to create a closed area. Overlapping line buffers can be merged similarly to point buffers.
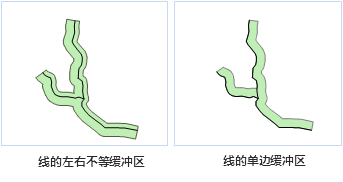
When the buffer type for line data is set to flat, asymmetric buffers with different left/right widths can be created, including single-sided buffers as shown:
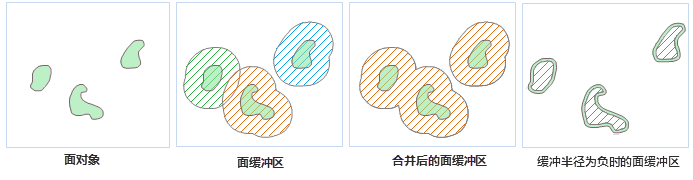
- Region Buffer
Region buffers extend or contract unilaterally from the boundary. Positive buffer radii expand outward, while negative values contract inward. Overlapping buffers can be unioned like point buffers.
- Multiple Ring Buffer
Multiple ring buffers create concentric zones around geometries using multiple specified radii. For lines, single-sided multiple ring buffers can be generated as shown:
Related Topics
Buffer Analysis Application Examples



