Instructions for use
Slope analysis is used to calculate the slope value of each cell in a raster dataset (typically using DEM data). The larger the slope value, the steeper the terrain; the smaller the slope value, the flatter the terrain.
The cell value in DEM data represents the elevation at that point, and the slope is calculated based on this elevation. Since calculating the slope for a single point is not practically meaningful, in SuperMap, the slope is computed as the average value over each cell plane, with three representation types provided: degrees, radians, and percentage. For the principles of slope analysis and resampling methods, refer to the Slope and Aspect section in About Surface Analysis.
Note: Data in geographic coordinate systems cannot be directly used for slope analysis. Please convert the data to a projected coordinate system first before performing slope analysis.
Application Example
Open the "Terrain" data source under the "ExerciseData/RasterAnalysis" folder, which contains DEM data with a resolution of 5 meters. We will use this data as an example.
Function Entrances
- In the Spatial Analysis tab -> Raster Analysis -> Surface Analysis -> Slope Analysis;
- Toolbox -> Raster Analysis tool -> Surface Analysis -> Terrain Calculation -> Slope Analysis.
Main Parameters
- Source Data
- Datasource: Lists all data sources in the current workspace. Select the data source containing the dataset for slope analysis.
- Dataset: Lists all raster datasets (GRID) in the current data source. Select the dataset for slope analysis from the list; typically, we choose DEM data with elevation values. This will automatically locate to the selected dataset in the workspace manager.
- Parameters
- Slope Unit Type: Select the unit for slope analysis, including degrees, radians, and percentage. Users can choose the appropriate type based on their needs.
- Elevation Scale Factor: Used to set the degree of elevation stretching. A larger value indicates greater stretching, making the terrain more exaggerated. A factor of 1 means no stretching. The unit is times, representing the multiple by which the elevation is stretched relative to the original height.
- Result Settings
- Datasource: Lists all data sources in the current workspace. Select the data source for the result dataset. Defaults to the same as the source datasource.
- Dataset: Set the name of the result dataset. The newly generated slope dataset is a dataset with the same size and resolution as the source dataset.
- Perform the slope analysis operation to obtain the following result.
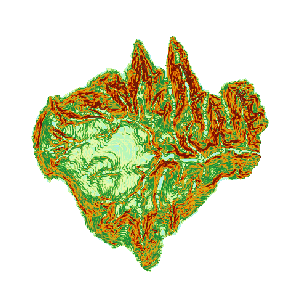
Figure: Calculate Slope Result
Related Topics



