Instructions for use
Slope Analysis is used to calculate slope values for individual pixels in the Raster Dataset (typically using DEM data). The greater the slope value, the steeper the terrain; the smaller the slope value, the flatter the terrain.
The pixel value in the DEM data is the elevation value of the point, and the slope of the point is calculated by the elevation value. Since it is meaningless to calculate the slope of a point, in SuperMap, the slope is calculated as the average value of each pixel plane, and three forms of slope expression are provided: degree, radian and percentage. For the principle of Slope Analysis and the Calculator Method, see the Slope and aspect section of About Surface Analysis.
Note: Slope Analysis cannot be performed directly for Geographic Coordinate System data. Please convert Data to Projected Coordinate System before performing Slope Analysis.
Application Example
Open the Terrain "Datasource under the Exercise Data/Raster Analysis folder, and there is DGM data with a resolution of 5 meters, which we will use as an example.
Function entrance
- On the Spatial Analysis tab-> Raster Analysis-> Surface Analysis-> Slope Analysis;
- Toolbox-> Raster Analysis Tools-> Surface Analysis-> Terrain Calculation-> Slope Analysis. (iDesktopX)
Main parameters
- Source data
- Datasource: All the Datasources in the Current Workspace are listed. Select the Datasource where the Dataset for Slope Analysis is located.
- Dataset: Lists all Raster Dataset (GRID) in the Current Data source. Select the Dataset to be used for Slope Analysis in the list. Generally, we will select the DEM data with elevation values. The Dataset selected in Workspace Manager is automatically located here.
- Parameter Settings
- Slope unit type: Select the Slope Analysis unit to be used, including angle, radian and percentage. The user can select the appropriate type for Slope Analysis as required.
- Elevation Scaling Multiplier: Used to set the degree to which the elevation is stretched. The higher the value, the greater the stretch and the more exaggerated the terrain. When the coefficient is 1, it means no stretching. Values are in multiples, that is, multiples of the stretch of the elevation relative to the original height.
- Result Settings
- Datasource: All the Datasources in the Current Workspace are listed. Select the Datasource where the Result Dataset is located. Default is the same as Source Datasource.
- Dataset: Sets the name of the Result Dataset. The newly generated slope Dataset is a Dataset of the same size and resolution as the Source Dataset.
- Execute the Slope Analysis operation to obtain the following results.
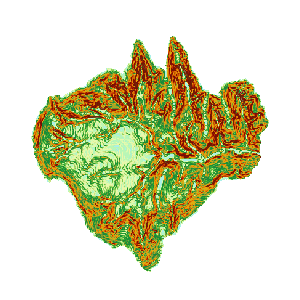 |
| Figure: Calculate Slope Result |




 Related topics
Related topics