SuperMap currently provides 7 overlay analysis operators. Below are the descriptions of them:
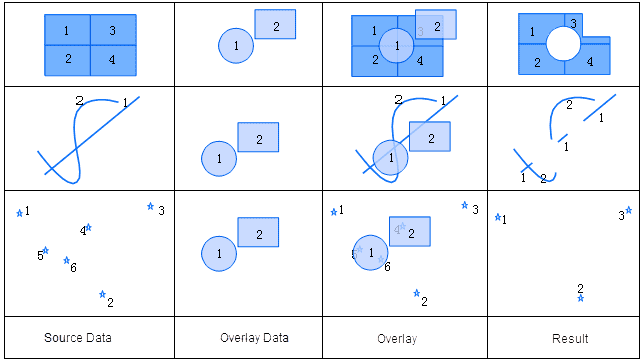
Clip
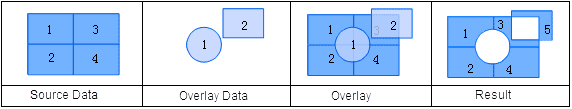
Clip is a process of extracting a set of features from a clipped dataset using a clip dataset. The set of polygons in the clip dataset define the clipping region. The features or feature parts that fall outside of these polygons are to be erased, and the ones that fall within the polygons will be output to the result dataset.
The attribute table of the output result of a Clip operation comes from the attribute table of the clipped dataset. The attribute table structure is the same with that of the clipped dataset. Only fields such as area, perimeter, and length need to be recalculated. All the other field values in the clipped dataset A are retained in the output. As demonstrated in the figure below, all the fields in dataset A are added automatically.
Union
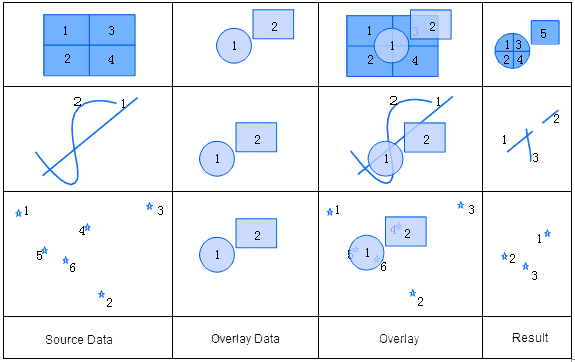
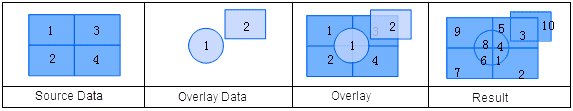
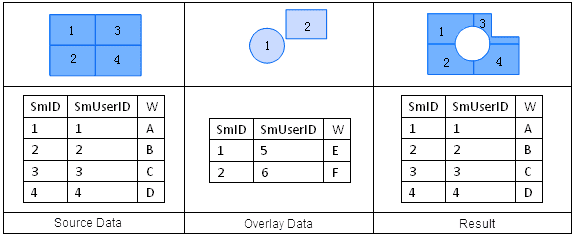
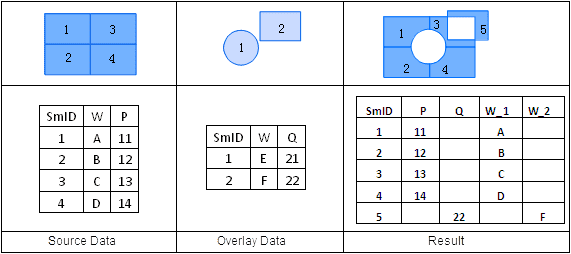
Union is an operation that finds the union of two datasets. After a union operation, the polygons are split where the two region datasets intersect. Topology is rebuilt, and the geometric and attribute information for the two datasets are all output to the result dataset.
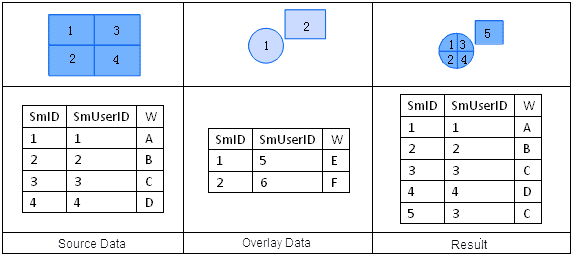
The attribute table of the output result of a union operation comes from the attribute tables of both input datasets. During a union operation, the user can select attribute fields that need to be reserved from the attribute tables of dataset A and B.
The fields in the overlay analysis result are named as “FieldName1” and “FieldName2” here, as shown in the figure below.
Erase
Erase is a process of erasing polygon parts in an erased dataset where it overlaps with the erase dataset. The set of polygons in the erase dataset define the erasing region. The features or feature parts that fall within these polygons are to be erased, and the ones that fall outside of the polygons will be output to the result dataset. The Erase operation works similarly to the Clip operation. The only difference is that the content reserved in the result is different.
The attribute table of the output result of an Erase operation comes from the attribute table of the erased dataset. The attribute table types are the same. As demonstrated in the figure below, all the non-system fields in dataset A are added automatically.
Intersect
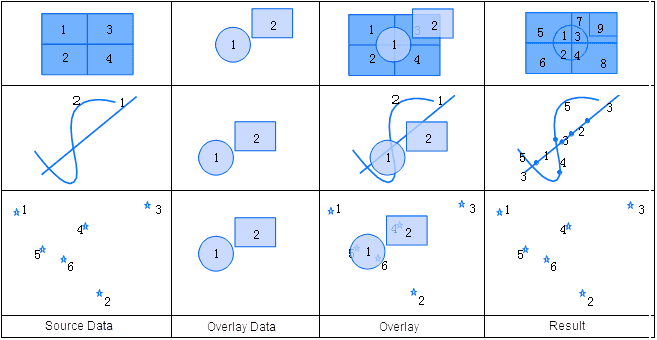
An Intersect operation finds the intersection of two datasets. The feature objects (except point objects) in the intersected dataset are split where they intersect with the polygons in the intersect dataset. The spatial information for a result dataset from an Intersect operation is the same with that from a Clip operation. But the clip operation does not process attribute information, whereas an Intersect operation allows the user to select attribute fields to be reserved.

The attribute table of the output result of an Intersect operation contains its own attribute fields, and all attribute fields of the intersected dataset and the intersect dataset. The user can select attribute fields need to be reserved from the attribute tables of dataset A and B.

Identity
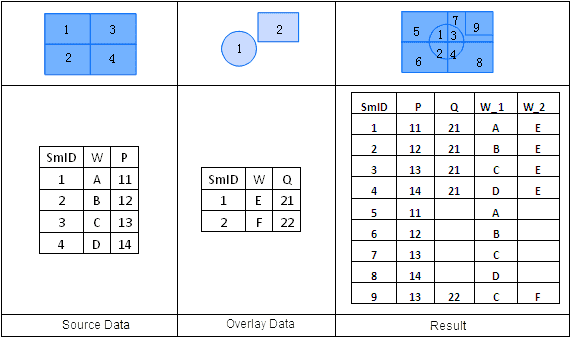
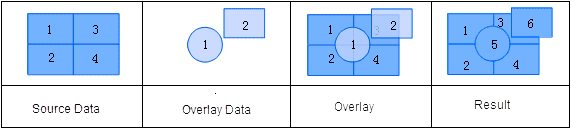
The result dataset has the same extent as the source dataset layer, but it contains geometric shapes and attributes data from the overlay dataset layer. An Identity operation is a process of performing an Intersect operation on the source dataset and the overlay dataset and then a Union operation on the intersection result and the source dataset. If the first dataset is a point dataset, all the objects in the first dataset will be retained in the newly generated dataset; if the first dataset is a line dataset, all the objects in the first dataset will also be retained in the newly generated dataset, but the objects in the second dataset are split where the two datasets intersect; if the first dataset is a region dataset, all the source dataset’s polygons that lie within the controlling boundary will be retained in the result dataset, and the objects in the second dataset are split where the two datasets intersect.
The attribute fields, except for the system fields, of the output result of an Identity operation comes from the attribute fields of both input datasets. The user can select attribute fields that need to be reserved from the attribute tables of the source dataset and the overlay dataset, as shown below.
XOR
The symmetry difference analysis on two region datasets. For each region object, the operation erases the part that overlaps with geometric objects in the other dataset, and then the rest part of the object is reserved.
The attribute table of an XOR operation output contains the non-system fields of the two input datasets, as shown in the figure below:
Update
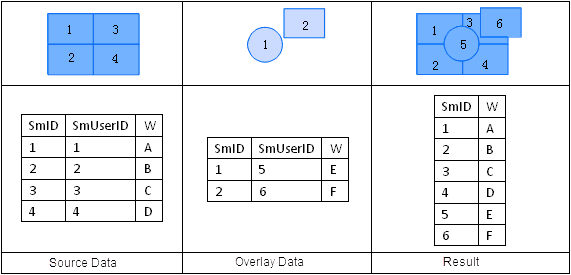
Update is a process of replacing object parts in an updated dataset with corresponding parts in an update dataset where the two datasets overlap. It is an erasing process followed by a pasting process. The geometric shapes and attribute information in the update dataset are reserved in the result dataset.
The attribute table of an Update operation output is shown in the following figure. The attribute values of the geometric object parts where dataset A and B overlap are updated with the corresponding attribute values in dataset B.