URI
-
<fields_uri>/{fieldName}[.<format>]
-
<fields_uri>/{fieldIndex}[.<format>]
Supported methods
Parent resource
Child resources
Introduction
The field resource represents a field in a dataset. fieldName in the URI specifies the name of the field. Note: Because it's not safe to operate field in a non-empty dataset, you can only add a field in an empty dataset.
Supported Methods:
- GET: Gets the field information.
- PUT: creates or modifies the field information.
- DELETE: Deletes the field.
- HEAD: Checks the existence of the field resource and whether it can be accessed by the client.
Supported output formats: rjson, json, html, xml.
Resource hierarchy
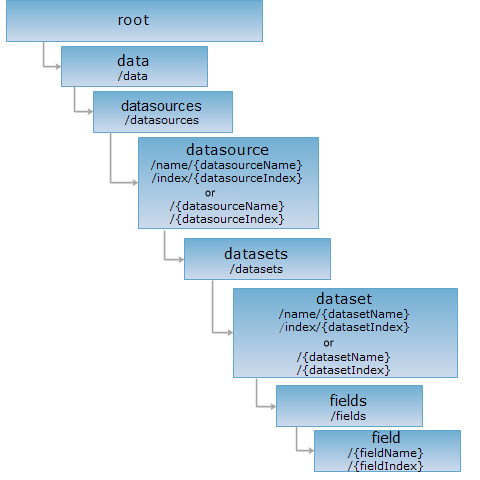
HTTP request methods
Implement the HTTP request on the following URI, where supermapiserver is the server name and World is a datasource on the server, Ocean is a dataset in the datasource, and SMID is a field in the Ocean dataset, and the response is in rjson format.
http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/data-world/rest/data/datasources/name/World/datasets/name/Ocean/fields/SMID.rjson
GET request
Gets the field information. The field information includes the field name, the field type, the field alias, the field default value, whether or not allowed to be null , the maximum length of the field, whether the length allowed to be zero, etc.
Response structure
When implementing the GET request on the field resource, the structure of the response is as follows:
| Field | Type | Description |
| name | String | The field name. Uniquely identifies a field. |
| caption | String | The field alias. Different fields can have the same alias. |
| type | FieldType | The field type. |
| defaultValue | String | The default value of the field. |
| isRequired | boolean | Whether it is required. True represents a required field; while false represents a non-required field. |
| isSystemField | boolean | Whether it is SuperMap system field. True represents the SuperMap system field. The SuperMap system field is prefixed with SM, except the SMUserID. |
| isZeroLengthAllowed | boolean | Whether the length can be zero. |
| maxLength | int | The maximum length of the field. |
Example usage
Implement the GET request on the sample field resource with http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/data-world/rest/data/datasources/name/World/datasets/name/Ocean/fields/SMID.rjson to get the representation of the SMID field in the Ocean dataset in rjson format:
{
"childUriList": [
"http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/data-world/rest/data/datasources/name/World/datasets/name/Ocean/fields/SMID/MAX",
"http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/data-world/rest/data/datasources/name/World/datasets/name/Ocean/fields/SMID/MIN",
"http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/data-world/rest/data/datasources/name/World/datasets/name/Ocean/fields/SMID/AVERAGE",
"http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/data-world/rest/data/datasources/name/World/datasets/name/Ocean/fields/SMID/STDDEVIATION",
"http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/data-world/rest/data/datasources/name/World/datasets/name/Ocean/fields/SMID/SUM",
"http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/data-world/rest/data/datasources/name/World/datasets/name/Ocean/fields/SMID/VARIANCE"
],
"fieldInfo": {
"caption": "SmID",
"defaultValue": "",
"isRequired": true,
"isSystemField": true,
"isZeroLengthAllowed": true,
"maxLength": 4,
"name": "SMID",
"type": "INT32"
}
}
PUT request
Create a new field in the null dataset or modify the fields of the null dataset.
Request parameter
URI parameter {fieldName} and corresponding request body parameters need to be passed in before "?" while implementing the PUT request on the field resource.
Parameters in the URI:
| Field | Type | Description |
| {fieldName} | String | [Required parameter] Name of the field to be modified or created. |
Corresponding field info needs to be included in the PUT request body, that is, following parameters need to be passed in:
| Field | Type | Description |
| name | String | [Required parameter] Field name. Uniquely identifies a field and cannot repeat. If users modify the field, this parameter cannot be modified. If users create a new field, it should be identical to {fieldName}. |
| caption | String | [Required parameter] The field alias. Different fields can have the same alias. It is identical to field name by default. |
| type | FieldType | [Required parameter, cannot be modified] The field type. |
| defaultValue | String | [Required parameter] The default value of the field. |
| isRequired | boolean | [Required parameter, cannot be modified] Whether it is required. True represents a required field; while false represents a non-required field. The default is false. |
| isSystemField | boolean | [Required parameter, cannot be modified] Whether it is SuperMap system field. True represents the SuperMap system field. The default is false. The SuperMap system field is prefixed with SM, except the SMUserID. |
| isZeroLengthAllowed | boolean | [Required parameter, cannot be modified] Whether zero length is allowed. The default is false. |
| maxLength | int | [Required parameter, cannot be modified] The maximum length of the field. The default is 8 bit. |
Response structure
When implementing the PUT request on the field resource, the representation of the resource returned is included in the entity body of the response message, as shown below:
| Field | Type | Description |
| succeed | boolean | Whether the operation is successful. |
| newResourceLoaction | String | The URI of the newly created field. Exists when creating a field. |
| error | HttpError | Error message. If the creation is successful, this field will be absent. |
Example usage
Since the Ocean dataset corresponding to the sample fields resource is not empty, therefore, the PUT request cannot be implemented to add a new field. Assume that there is an empty dataset NewDataset in the World datasource. The URI sees as follows:
http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/data-world/rest/data/datasources/World/datasets/NewDataset.rjson
Then you can implement the PUT request on the non-existing field to add a new field. The URI is http://supermapiserver:8090/iserver/services/data-world/rest/data/datasources/World/datasets/NewDataset/fields/NewField.rjson. Parameters in the PUT request see as follows:
{
"isZeroLengthAllowed": "false",
"maxLength": "4",
"isRequired": "true",
"name": "NewField",
"caption": "NewField",
"type": "INT32",
"isSystemField": "true"
}
The response in json format is as follows:
{"succeed":true}
DELETE request
Deletes the field. It can only be performed on an empty dataset.
Request parameter
None.
Response structure
When implementing the DELETE request on the field resource, the representation of the resource returned is included in the entity body of the response message, as shown below:
| Field | Type | Description |
| succeed | boolean | Whether the delete operation is successful. |
| error | HttpError | Error message. If successful, the field will not exist. |
Example usage
If you successfully delete NewField of NewDataset created in PUT Request Example, the response in rjson format is as follows:
{"succeed":true}
HEAD request
Asks for the response identical to the one that would correspond to a GET request, but without the response body. This is useful for retrieving meta-information written in response headers, without having to transport the entire content. The meta-information includes the media-type, content-encoding, transfer-encoding, content-length, etc.
The HEAD request helps check the existence of the field resource and whether it can be accessed by the client. By implementing the HEAD request on the URI, with .<format> appended to the end, we can quickly get to know whether the field resource supports the representation in <format> or not.