The streaming service uses the stream processing model as the service provider, which specifies the necessary information when running service.
The process of stream data processing includes:

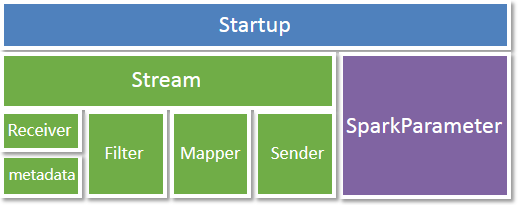
The stream processing model consists of four parts: Receiver, Filter, Mapper, and Sender. Each part as a node, can be connected and merged together to build a real-time data processing stream: Stream. In addition to Stream, there are some auxiliary parameters as the operating conditions of the entire service, which is stored together in the startup parameter type-Startup. The processing model is as follows:
Configuration Parameters
The stream processing model is defined in JSON format. You can refer to the parameters described below and the corresponding examples to write a stream processing model file and publish it as Streaming Service. You can also use the Streaming Model Editor to build the model and set the parameters.
SparkParameter
Used to set Spark Streaming operation parameters, include:
- checkPointDir: Sets the Save directory of the CheckPoint feature of Streaming. String type.
- interval: int type. Sets the interval at which Streaming runs in milliseconds.
Stream
- nodeDic: the dictionary that holds the running nodes.
- StreamNode: node base class for runtime stream, which records the basic information such as name, source, and description of the node, and the order in which the most important node is running. Use prevNodes to record the list of nodes before the current node, nextNodes to record the list of nodes after the current node. The values of prevNodes and nextNodes are an array and each element of the array is the name of each corresponding node; that is, each node can have more than one predecessor node or more than one subsequent node. For Receiver node, prevNodes is empty; For Sender node, nextNodes is empty. If a node has more than one predecessor node , then the metadata of theses predecessor nodes must be the same; otherwise, the execution will report errors.
Receiver
Inherited from StreamNode, as the entry of stream data processing, receiving data from a variety of sources, including Socket, WebSocket, Http, file system, etc. Receiver need to set metadata parameter to receive information. Receiver node consists of three parts: their own description information such as name, source, etc .; message metadata: metadata; message read format: reader.
Streaming services support the following receive methods:
SocketReceiver: inherited from Receiver, used to receive Socket message. The parameters to be specified are:
ipAddress——String type. The IP address of the Socket service from which SocketReceiver receives message.
port—— int type, the port number of the Socket service
Example:
{
"ipAddress" : "127.0.0.1",
"port" : 9527,
"name" : "socketReceiver",
"source" : "Socket Receiver",
"description" : "Receive some message from socketServer",
"prevNodes" : [],
"nextNodes" : [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.receiver.SocketReceiver "
}
MultiSocketReceiver: inherited from Receiver, while receiving multiple nodes of the Socket message, the received message content must be the same. The parameters to be specified are:
servers——Array[String] type. Multiple service addresses to receive. Each array object is an address, and the address and the port is separated by a colon.
Example:
{
"servers": [
"192.168.1.1:9527",
"192.168.1.1:9528",
"192.168.1.2:9527"
],
"name": "multiSocketReceiver",
"source": "MultiSource Socket Receiver",
"description": "Receive message from multi socket server",
"prevNodes": [],
"nextNodes": [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.receiver.MultiSocketReceiver"
}
SocketServerReceiver: inherited from Receiver, Socket server receiving node, used as a server to receive other Socket customers to send the message. The parameters to be specified are:
Port: int type. The started listening port on the socket server.
{
"port": 9527,
"name": "socketServerReceiver",
"source": "SocketServer Receiver",
"description": "Receive message from socket client",
"prevNodes": [],
"nextNodes": [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.receiver.SocketServerReceiver"
}
WebSocketReceiver: inherited from Receiver, receive WebSocket message node. The parameters to be specified are:
Url: String type. WebSocket service address.
{
"url": "ws://192.168.1.1:9527/websocket ",
"name": "webSocketReceiver",
"source": "WebSocket Receiver",
"description": "Receive message from websocket server",
"prevNodes": [],
"nextNodes": [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.receiver.WebSocketReceiver"
}
TextFileReceiver: inherited from Receiver, monitor the specified directory, and read the contents of the new file. The parameters to be specified are:
directoryPath——directory of monitored files, such as HDFS directory: hdfs:///data/; directory in Linux system: /user/share/data; directory in Windows system: C:/data.
{
"directoryPath": "'hdfs:///data/'",
"name": "textFileReceiver",
"source": "Text File Receiver",
"description": "Listen new file in folder",
"prevNodes": [],
"nextNodes": [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.receiver.TextFileReceiver"
}
SingleTextFileReceiver: inherited from Receiver, monitor the specified file, and read the contents of the specified file according to the settings. Supported file formats include Json, GeoJSON and CSV. The parameters to be specified are:
-
readInterva: read time interval.
-
rowsOneTime: number of rows to read each time.
{
"version": 9000,
"sparkParameter": {
"checkPointDir": "tmp",
"interval": 5000
},
"stream": {
"nodeDic": {
"TextFileReceiver": {
"filePath": "G:\\QQRev\\test.json",
"readInterva": 1000,
"rowsOneTime": 100,
"reader": {
"isJsonArray": false,
"arrayExpression": "",
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.formatter.JsonFormatter"
},
"metadata": {
"title": "",
"epsg": 3857,
"fieldInfos": [
{
"name": "X",
"source": "lon",
"nType": "DOUBLE"
},
{
"name": "Y",
"source": "lat",
"nType": "DOUBLE"
},
{
"name": "mbbh",
"source": "mbbh",
"nType": "TEXT"
}
],
"featureType": "POINT",
"idFieldName": "mbbh",
"dateTimeFormat": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
},
"name": "TextFileReceiver",
"caption": "",
"description": "",
"prevNodes": [],
"nextNodes": [
"ConsoleSender"
],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.receiver.SingleTextFileReceiver"
},
"ConsoleSender": {
"formatter": {
"separator": ",",
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.formatter.CSVFormatter"
},
"name": "ConsoleSender",
"caption": "",
"description": "",
"prevNodes": [
"TextFileReceiver"
],
"nextNodes": [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.sender.ConsoleSender"
}
}
}
}
KafkaReceiver: A node that inherits from Receiver and receives kafka messages. The parameters to be specified are:
- servers - String type. Server list. If there are multiple items, separate servers by commas, and separate the ports with semicolons ";"
- topics ——Array [String] type. kafka topic array
- groupid——String type. kafka's groupID
- offset——String type. The location read by kafka. The default value is latest, that is, to read the latest news
{ "servers": "192.168.1.1:9092, 192.168.1.2:9092, 192.168.1.3:9092 ,192.168.1.4:9092",
"topics": [
"topic1",
"topic2"
],
"groupid": "groupId",
"offset": "latest",
"name": "kafkaReceiver",
"source": "Kafka Receiver",
"description": "Receive message from Kafka",
"prevNodes": [],
"nextNodes": [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.receiver.KafkaReceiver"
}
HttpReceiver: inherited from Receiver, a message node to receive HTTP. Currently only the Get method of HTTP is supported.
Url: String type. Http service address.
{
"url": "https://api.wheretheiss.at/v1/satellites/25544",
"name": "httpReceiver",
"source": "HTTP Receiver",
"description": "Get message from web",
"prevNodes": [],
"nextNodes": [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.receiver.HttpReceiver"
}
JMSReceiver: A node that inherits from the Receiver, receives the JMS standard protocol message, and receives messages such as ActiveMQ, RabbitMQ, and other message middleware.
url——JMS message service address
port——int type. Message service port
queueName ——String type Message Queue Name
jdniName——String type. The JDNI name of the corresponding message middleware. You need to find it from the official website of the middleware
username——String type. username
password——String type. password
{
"url": "192.168.1.1",
"port": 9527,
"queueName": "data",
"jdniName": "org.apache.activemq.jndi.ActiveMQInitialContextFactory",
"userName": "user",
"password": "password",
"name": "jmsReceiver",
"source": "JMS Receiver",
"description": "Receive message from JMS(Java Message Service) for ActiveMQ",
"prevNodes": [],
"nextNodes": [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.receiver.JMSReceiver"
}
metadata
metadata is written in the Receiver parameter, which is the metadata of the received message, used to describe the definition format of the message. The following information need to be specified:
- title: The name of the metadata used to distinguish between other metadata. String type.
- featureType: FeatureType class. The geographic feature type converted from the received message, such as POINT, LINE, REGION, etc.
- epsg: int type. The Projected EPSG coding of metadata geographic elements.
- fieldInfos: field information converted from the message received. You need to specify:
- name: String type. Field name, unique identifier for the field
- source: String type. The position of the field in the original information which determines from which position to parse the information. If the original information is in CSV format, the value of source should be the field number in the CSV, such as, "source": "4" represents the fifth field in the CSV data; If the original data is in json format, then the value of source is the key of key-value-pair in json data.
- nType: FieldType type. Field type, such as: TEXT, DOUBLE, INT and so on.
reader
The content format of the received message, including CSV format, JSON format, or GeoJson format.
CSVFormatter: Indicates that the content of the received message is in CSV format. You need to specify:
separator: Specifies the delimiter, the default is a comma
"reader": {
"separator": ",",
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.formatter.CSVFormatter"
}
JsonFormatter: The format of the received message content is JSON. Here is an example:
"reader": {
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.formatter.JsonFormatter"
}
GeoJsonFormatter: The format of the received message content is GeoJSON. Here is an example:
"reader": {
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.formatter.JsonFormatter"
}
Filter
Inherited from StreamNode, used to filter the current data, and cleaning and sorting the data. You need to specify:
- filter: If you need to get the field value for logical operations, use the keyword [], such as [ID]> 10. Multiple expressions can be used to connect directly with && (or) or || (or), and use parentheses () to adjust the priority order, such as [ID]> 10 && ([X]> = 10 || [ = 65.32). Note that the use of the keywords IN, MATCHES, EXISTS, ISNULL, together with other expressions, must be enclosed in brackets, such as ([ID] IN 1,3,5,7,9) && [X]> 100.
Table 1 list of logical operators supported by the filter parameter
Operator |
Description |
| == | Is equal to (=) This operator holds objects whose attribute value is equal to the specified value. For example, [ID] = 3. Note: double type, the contrast accuracy is10E-10. Must be used carefully. |
| != | Is not equal to (! =) This operator retains objects whose attribute value is not equal to the specified value. For example, [Name]! = "A". Note: double type, the contrast accuracy is10E-10. Must be used carefully. |
| > | Greater than (>) This operator retains objects whose property value is greater than the specified value. For example, [Speed]> 50 |
| >= | Greater than or equal to (> =) This operator retains objects whose property value is greater than or equal to the specified value. For example, [Speed]>= 50 |
| < | Less than (<) This operator retains an object whose attribute value is less than the specified value. For example, [X] < 10.231 |
| <= | Less than or equal to (<=) This operator retains an object whose attribute value is less than or equal to the specified value. For example, [Y] <= 40 |
| IN | IN In the specified list the operator retains the object when the value of the specified field exists in the comma-separated list of values. For example, [Code] IN HK1,HK3,HK5 |
| MATCHES | MATCHES Regular Expression Match This operator holds the object when the value of the specified field matches the regular expression. For example, [Code] MATCHES "^ HK [135]” Note: Regular expressions that need to be matched need to be enclosed in quotation marks |
| EXISTS | Whether the EXISTS field exists When the specified field exists in the received event scenario, the operator holds the object. For example, EXISTS [X]. |
| ISNULL | ISNULL whether it is empty When the specified field contains a null value, the operator retains the object. For example, [X] ISNULL. |
Mapper
Inherited from StreamNode, used to create field mapping and managing the fields, including: field mapping, adding fields, deleting fields, field operations and geofence.
Add a field
- insertIndex——int type Location to add a field
- fieldname——String type The name of the field to add
- nType——SFieldType type The type of the field to add
- expression——String type The field value to add can be the value of an operation expression for an existing field:
"insertMapper": {
"insertIndex": 1,
"fieldName": "XX",
"nType": "DOUBLE",
"expression": "[X] * 2",
"name": "insertMapper",
"source": "Insert Field",
"description": "Insert Field by X * 2",
"prevNodes": [],
"nextNodes": [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.map.FeatureInsertMapper"
}
Delete field
- deleteFieldNames: delete the field name array
"deleteMapper": {
"deleteFieldNames": [
"F1",
"F2"
],
"name": "deleteMapper",
"source": "delete Field",
"description": "delete Field F1 and F2,
"prevNodes": [],
"nextNodes": [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.map.FeatureDeleteMapper"
}
Field mapping
- srcToDesIndexPair: the correspondence between the field in the source data (the serial number of the field in the stream) and the name
srcToDesNamePair: the correspondence between the field name and the new name
"mapMaper": {
"srcToDesNamePair": {
"ID": "newID_Name",
"Y": "newY_Name",
"X": "newX_Name"
},
"srcToDesIndexPair": {
"ID": 0,
"Y": 2,
"X": 1
},
"name": "mapMaper",
"source": "Map Fields",
"description": "Map Fields with new name and index",
"prevNodes": [],
"nextNodes": [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.map.FeatureMapMapper"
}
Field operation
- fieldName: The target field name
- expression: The expression of the field
"calculateMapper": {
"fieldName ": Fcal,
"expression": "[X] * 2",
"name": "calculateMapper",
"source": "calculate Field",
"description": "calculate Field by X * 2",
"prevNodes": [],
"nextNodes": [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.map.FeatureCalculateMapper "
}
Geofence
- connection: The source of the geofence object.
type——String type. Datasource type
Info——Array[DsInfo] type. Datasource connection information.
- server: The data server
- datasetNames: Array [String] type. The dataset name used for the geofence
- fenceName——String type. The Name field of the object that is within the geofence.
- fenceID——String type. The ID field of the object that is within the geofence. That is, the field that uniquely identifies the object.
- withinFieldName——String type. The field name of the new field, which is used to record whether the current object is in the geographic fence.
- statusFieldName——String type. The field name of the new field, which is used to record whether the current object's state is entering the geo-fence or leaving the geo-fence.
"GeoFenceMapper": {
"connection": {
"type": "udb",
"info": [
{
"server": "Z: \\airport.udb",
"datasetNames": [
"airports_40"
]
}
]
},
"fenceName": "NAME",
"fenceID": "SmID",
"withinFieldName": "geoWithin",
"statusFieldName": "geoStatus",
"name": "GeoFenceMapper",
"source": "Geomark Transformation",
"description": "",
"prevNodes": [
"SocketReceiver"
],
"nextNodes": [
"GeoJsonSocketSender",
"FenceWithinFilterOut",
"FenceWithinFilterIn"
],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.map.GeoTaggerMapper"
}
Sender
Inherited from StreamNode, as exit for stream data processing, sending data outwards. Includes:
- EsAppendSender
- EsUpdateSender
- FileSender
- JMSSender
- SenderBase
- SMSSender
- SocketClientSender
- SocketServerSender
- WebSocketClientSender
- WebSocketTool
Take the example of the commonly used WebSocket protocol, the configuration of sending data is shown as follows:
"webSocketSender": {
"path": "ws://127.0.0.1/data",
"name": "webSocketSender",
"source": "WebSocket Sender",
"description": "Send message to WebSocket Server",
"prevNodes": [],
"nextNodes": [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.sender.WebSocketClientSender"
}
Take outputting to ElasticSearch as an example:
"ESSender": {
"url": "192.168.168.33",
"queueName": "aircondition",
"directoryPath": "test1",
"bitmap$0": false,
"formatter": {
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.formatter.GeoJsonFormatter"
},
"name": "ESSender",
"source": "ES sender
"description": "",
"prevNodes": [
"TextFileReceiverJson"
],
"nextNodes": [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.sender.EsAppendSender"
}
With the example settings above, you can output the result of the analysis of the data to the spatio-temporal database created by iServer DataStore.
Write a stream processing model file
According to the above parameters description, write a complete stream processing model file as the example shown below, then save it with a suffix of .streaming. Now you can quickly publish it as a streaming service. In the configuration information option, you can choose to specify the path of the .streaming file then publish, or you can fill in the content of the file in "Configuration information" option then finish publishing.
{
"version": 9000,
"sparkParameter": {
"checkPointDir": "tmp",
"interval": 10000
},
"stream": {
"nodeDic": {
"AQIReceiver": {
"url": "http://www.supermapol.com/iserver/services/aqi/restjsr/aqi/pm2_5.json?bounds=-113.90625001585,-52.029966847235,113.90625001585,69.175579762077&to=910111",
"reader": {
"isJsonArray": true,
"arrayExpression": "airQualityList", "className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.formatter.JsonFormatter"
},
"metadata": {
"title": "",
"epsg": 3857,
"fieldInfos": [
{
"name": "X",
"source": "location.x",
"nType": "DOUBLE"
},
{
"name": "Y",
"source": "location.y",
"nType": "DOUBLE"
},
{
"name": "positionName",
"source": "positionName",
"nType": "TEXT"
},
{
"name": "aqi",
"source": "aqi",
"nType": "DOUBLE"
}
],
"featureType": "POINT"
},
"name": "AQIReceiver",
"caption": "",
"description": "",
"prevNodes": [],
"nextNodes": [
"WebSocketClientSender"
],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.receiver.HttpReceiver"
},
"WebSocketClientSender": {
"path": "ws://127.0.0.1:8800/iserver/services/dataflow/dataflow/broadcast",
"formatter": {
"separator": ",",
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.formatter.GeoJsonFormatter"
},
"name": "WebSocketClientSender",
"caption": "",
"description": "",
"prevNodes": [
"AQIReceiver"
],
"nextNodes": [],
"className": "com.supermap.bdt.streaming.sender.WebSocketClientSender"
}
}
}
}