The main configure information is in \webapps\iserver\WEB-INF. See Catalog introduction after installing.
Configuration file introduction
WEB-INF stores server information and configuration information. The structure of the folder is as follows:
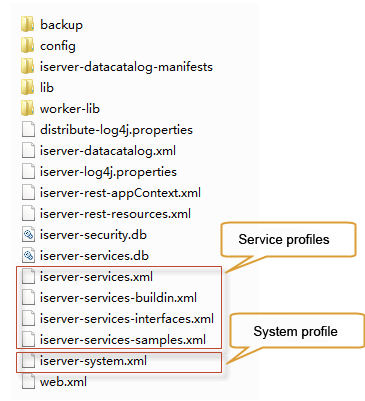
including:
- backup folder: the backup of the server configuration information. See Backup and restore server configuration.
- config folder: configuration files, including caching schemes for Bing Maps, Tianditu, Cloud service, etc.
- iserver-datastores-manifests: stores the configuration infos of data in data catalog service.
- lib folder: stores the jar files that SuperMap iServer depends on.
- worker-lib: stores the servlet-api.jar which is used to starting Workers nodes.
The main contents of each configuration file are as follows:
Contents of Configuration File
| File Name | Description |
| iserver-datacatalog.xml | The configuration file of data catalog service, including the config of data storage and other config infos. |
| iserver-log4j.properties | The configuration file for log. |
| iserver-rest-appContext.xml | REST configuration file that defines the mapping relations between representation types and URI suffix. |
| iserver-rest-resources.xml | The resource configuration file for extensive resources. Users can specify the extensive name, URI, type, representation encoder name, parser name, etc. |
| iserver-services-interfaces.xml | Service interface instance, including the interface instances which are used by iserver-services-samples.xml and iserver-services-user.xml, such as : rest, restjsr, wms111, wms130, wfs100, wmts100, wmts-china, wcs111, wcs112, handler, gspserver. |
| iserver-services-samples.xml | The configure information of the sample service. |
| iserver-services.xml | The configure information of services published by users When you name this file with a prefix "iserver-services", the server can recongnise it as an configuration file for its own. You can set multi customized service configuration file, such as: iserver-services-1.xml, iserver-services-2.xml. |
| iserver-services-buildin.xml | The config infos of iServer built-in services. |
| iserver-system.xml | Sytem level configuration for SuperMap iServer, including meta information, cluster, kml style configurations, etc. |
| web.xml | Initialization configuration file for SuperMap iServer, which defines the mapping relations between functions and classes. |
| iserver-security.db | A database is used to store the information of users and roles |
| iserver-services.db | A database is used to store the information of service authorization. |
Service configuration file
All the configuration information is stored in service configuration files. iserver-services-interface.xml is for service interface configuration; iserver-services-samples.xml is for sample services configuration; iserver-services.xml is for the services published by users. The latter two are similar in structure, so this does not go into details.
Through these files, you can:
- configure service provider through XML file
- configure service providers set through XML file
- configure service component through XML file
- configure service components set through XML file
- configure service interfaces through XML file
Service interface configuration File
The service interface configuration file, iserver-services-interface.xml, includes service interface instances. The root node is <application> element, and its subnode is <interfaces> element. And each interface element is used to configure a specific service interface with the following properties:
- name, the name of service interface.
- class, the implementation class of the service interface.
- config, the configuration information of service interface.
Sample service instance configuration file
The sample service instance configuration file, iserver-services-samples.xml, includes configuration information of sample services supported by SuperMap iServer. The root node is <application> element, and it has following subnodes:
1. <components>
Each component is used to configure a specific service component.
- name, the name of service component。
- alias, service component alias, can be set to Chinese.
- class, the implementation class of the service component.
- interfaceNames, service interface which service component bounds with.
- providers, service provider used by service component.
- config element, the configuration information of service component. It includes class, outputPath, outputSite, workspacePath properties, etc. To see specific information, please refer to configure service component through XML file. If there are no attributes of outputPath and outputPath, it will use the value in <properties> element correspondingly. A data service component has editable property in addition. It indicates whether the data service component is editable. True for editable means it's editable.
2. <providers>
Each provider element is used to configure a specific service provider.
- name, the name of service provider.
- class, the implementation class of the service provider.
- inner-providerNames element, used to set service providers which clustered by the cluster service provider when using cluster service provider; or used to set service providers which aggregated by the aggregation service provider when using aggregation service provider。 when using the cluster service provider or the aggregation service provider, it is used to set the service providers clustered or aggregated.
- config element, configuration information of service provider, including settings for workspace. It has class, outputPath, outputSite properties, etc. To see specific information, please refer to configure service provider through XML file. If there are no attributes of outputPath and outputPath, it will use the value in <properties> element correspondingly.
3. <componentSets>
Each componentSet element is used to configure a service component set. Each component set can reference multiple service components.
4. <providerSets>
Each providerSet element is used to configure a service provider set. Each provider set can reference multiple service providers.
Built-in service cofiguration file
The built-in service configuration file iserver-services-buildin.xml includes the config info of geometry service offered by iServer. The root node is <application>, which includes the following child nodes:
1. <componentSets>
Each componentSet element in componentSets is used to configure a set of service components, one componentSet can reference multiple service components.
2. <providerSets>
Each providerSet element in providerSets is used to configure a set of service providers, one providerSet can reference multiple service providers.
3. <components>
Each component element in components is used to configure a specific service component, including:
- config element, the config info of a service component. It has attributes like class, enabled, instanceCount, interfaceNames, etc., for details, see: Configuring service components through XML file.
4. <providers>
Each provider element in providers is used to configure a specific service provider, including:
- config element, the config info of a service provider. It has attributes like class, enabled, etc., for details, see: Configuring service providers through XML file.
System configuration file
iserver-sytem.xml contains the system configuration information. The root node is <server> lement. <server> node currently mainly includes <properties>, <management>, <hosts>, <clustering>, <harLog>, <queryFilter> subnode elements.
1. <properties> element
Used to configure global sytem properties information for SuperMap iServer, such as service default outputPath, outputSite, whether check enviroment or not:
- <outputPath>: the outputPath for cached images, the default value is "./webapps/iserver/output".
- <outputSite>: the publishing website for map images, namely, the URI of the root directory for accessing cached images. The default value is like "http://{ip}:{port}/iserver/output/".
- <realspaceSecurityEnabled>: enables or disables the security control for three dimension data. The default value is true.
- <realspaceCacheAccessKey>: the password for dimension data.
- <envCheckEnabled>: indicates to check the enviroment or not. The default value is true.
- <restartWhenCrash>: indicates to restart the server automatically or not after it's stopped because of some unnormal reasons. The default value is true.
- <checkDatasourceConnectionInterval>: the time interval for cheking whether "database type workspace" changes or "database type datasource" is disconnected. The unit is second. Smaller than 0 or equal to 0 indicates never to check. The default value is 30 seconds.
- <refreshDatasource>:enables or disables updating data source whose type is Database. The default is false.
- <{iServerData1}>, <{iServerDataPath1}>:indicates the variables of workspace or path. To see specific information, please refer to preset local workspace path.
Among them, the global properties: outputPath, outputSite can also be set through iServer WebManager. Please refer to Global Properties Setting.
2. <management> element
The <management> element is used to configure the metadata information of SuperMap iServer . The metadata information of service component types (<component-types>), service provider types (<provider-types>) and service interfaces (<interface-types>) are included.
Examples of security configuration nodes are as follows:
<security> <accessControl> <SecuritySetting> <isSecurityEnabled>true</isSecurityEnabled> <cacheInfoToMemory>true</cacheInfoToMemory> <tokenKey>4da7ef8f2e734f56ab2ecfae20cce49a</tokenKey> <!-- Password anti-violence crack settings --> <passwordProtectedSetting> <passwordDiffCount>5</passwordDiffCount> <userPasswordErrorCounterSetting> <passwordErrorProtectEnable>false</passwordErrorProtectEnable> <lockedTime>1200000</lockedTime> <periodLength>600000</periodLength> <allowFailCountPerPeriod>5</allowFailCountPerPeriod> </userPasswordErrorCounterSetting> </passwordProtectedSetting> <!-- Security information storage configuration --> <storage class="com.supermap.server.config.SQLSecurityInfoStorageSetting"> <type>MYSQL</type> <connInfo> <username>root</username> <password>super123.</password> <dbType>MYSQL</dbType> <driverClass>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driverClass> <jdbcUrl>jdbc:mysql://192.168.120.44:3306/supermap?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8</jdbcUrl> <maxPoolSize>30</maxPoolSize> <initialPoolSize>5</initialPoolSize> <minPoolSize>5</minPoolSize> <maxIdleTime>0</maxIdleTime> <maxWait>3000</maxWait> </connInfo> </storage> <!-- Session storage configuration --> <session class="com.supermap.server.config.RedisSessionSetting"> <session class="com.supermap.server.config.RedisSessionSetting"> <type>Redis</type> <host>127.0.0.1</host> <port>6379</port> <maxActive>1024</maxActive> <maxIdle>200</maxIdle> <maxWait>10000</maxWait> <timeout>10000</timeout> <testOnBorrow>true</testOnBorrow> </session> </SecuritySetting> </accessControl> </security>
Among them, <isSecurityEnabled>is used to enable or disable the security control; <tokenKey> is used to set the share key of Token; <cacheInfoToMemory> is used to set whether save all user info in memory,and get the information from memory.The default is true,which represents saving all user info in memory.If there is a large number of users,you are advised to set it to false,which represents the user info can be get from database in real time,because there will need to a large amount of SQL query,which can cause the performance to slow down;<passwordProtectedSetting> is used to protect password from cracking violently, specific parameters include:
- <passwordDiffCount>: New input password can not be set the same as any previous setting for last N times. Default value is 5.
- <userPasswordErrorCounterSetting>: including subnodes, <passwordErrorProtectEnable>, <allowFailCountPerPeriod>, and <lockedTime>. <passwordErrorProtectEnable> is used to enable or disable password anti-voilence crack setting. <allowFailCountPerPeriod>, default value is 5 times, indicates number of consecutive failures allowed in the time peroid (<periodLength>, default value is 6000000 miliseconds, or 10 minutes). <lockTime> indicates the automatic lock time. The unit is miliseconds, default 1200000, or 20 minutes.
<storageSetting> is used to set the storage location of security information, including <type> field and <connInfo> field. <type> is used to set the database storage type, and currently supports SQLITE, MYSQL. <connInfo> is used to configure the connection information of database. Take the MYSQL database as an example, the connection information specific parameters include:
- <driverClass>: database connection driver class, com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
- <jdbcUrl>: the URL connection form for connecting database driver is jdbc:mysql://{ip}:{port}/{database}?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8. {ip} indicates the IP address of the machine where the MYSQL is located. {port} indicates the service port of MYSQL, and the default is 3306. {database} is the database name. You can configure these parameters according to the actual enviroment of MYSQL you installed.
- <username>: user name, the user who has access to the database {database}.
- <password>: the user's password.
- <initialPoolSize>: the connection pool size of initializing, that is, the number of initial connections. The default value is 5.
- <maxPoolSize>: the maximum number of active connections provided by the connection pool at the same time. You can set this value based on the performance of the MySQL server, which defaults to up to 30 active connections.
- <minPoolSize>: the minimum number of active connections provided by the connection pool at the same time. Default value is 5.
- <maxIdleTime>: idle connection waiting time. That is, when the current connection is idle, the time that can be retained in milliseconds. If the time is not operated out of maxIdleTime, the current connection is automatically closed. The default value is 3000. If set to 0, the idle connection is always retained.
- <maxWait>: the waiting miliseconds for an abnormal connection. When the connection is not restored during this time period, the current connection is automatically closed. The default value is 300000.
- <useStoredAdmin>: for the case where the initial administrator (for example, admin1) has been stored in the database. The default value is false. If it is false, the current initial administrator (admin2) will be used; If it is true, the administrator (admin1) which is stored in the database will be used, not the current one (admin2).
<Session> is used to specify the storage location of the session information, including the Redis database connection pool configuration. Specific parameters are as follows:
- <type>: database type.
- <host>: the IP address of the machine where the Redis dababase is located.
- <port>: the service port of Redis dababase.
- <MaxActive>: the maximum number of active connections provided by the connection pool at the same time.
- <MaxIdle>: Maximum number of free connections.
- <MaxWait>: the maximum waiting time in milliseconds for a available connection. After the timeout, an exception will be throwed.
- <Timeout>: The time of the client is in an idle state after it is connected to the database. After the timeout, the connection will be disconnected.
- <TestOnBorrow>: When using a connection, it detects whether the connection is available; true means the resulting connection is available.
3. <hosts> element
The <host> element is used to configure the host of SuperMap iServer. There can be multiple <host> elements. A host example is as follows:
<host port="8090" type="webapp" uriBase="/services"> <interface-type>com.supermap.services.wms.WMSServlet</interface-type> <interface-type>com.supermap.services.rest.RestServlet</interface-type> <interface-type>com.supermap.services.wfs.WFSServlet</interface-type> <interface-type>com.supermap.services.wmts.WMTSServlet</interface-type> </host>
The subnode of <host>, <interface-type>, indicates the type of service contained in the service host; The attributes of <host> have the following meanings:
- port, the port number of the service host. The service through which the user accesses the service host, matches the port number of the servlet container, and synchronizes with the port number of the servlet container when accessing the SuperMap iServer service.
- type, the type of service host. "webapp" means that this is a Web service; It can also be set to rmi, soap, indicateing other host type.
- uriBase, the root path of the service host. It is counted from the root directory of the servlet.
4. <clustering> element
Including applications such as cluster configuration.. For more information about the elements of cluster subnodes, refer to using the configuration file to manage cluster which is under the cluster configuration topic .
5. <harLog> element
It used to configure the service access logs, such as whether to enable the service access log, the file name of service access log, the settings of service URI address:
- <enabled>: set whether to enable the service access log, the default is false.
- <name>: the name of the service access log. The default name is iServerHTTPArchive
- <monitorURLs>: the service URL address of SuperMap iServer to be monitored.
6. <queryFilter> element
It is used in the SQL query filter configuration to prevent SQL injection. SQL injection means to insert the strings that illegal or go against the user wishes into SQL query expression in data or map SQL query.
- <enabled>: set whether to enable SQL query filtering, the default is true.
- <filterString>: sets the SQL query filter string, supports any string (data manipulation language (DML), expression, wildcard, special characters, etc.), separated by semicolons, such as: <filterString>delete;SMID=.</filterString> . When users use data or map SQL query, if there is delete or SMID=arbitrary value in the expression, the system will regard the query expression as illegal and return 400 parameter exception, which protect the security of user data. If you do not set the SQL query filter string, The semicolon in the SQL query expression will be shielded by the system.
7. <repository> element
Used to set the storage location for temporary resources. For more information, please refer to: Temporary Resource Lifecycle.
8. <relayService> element
The relay service configuration for iEdge is only used in iEdge products.
- <enabled>: Whether to enable relay service.
- <IsLocalPriority>: whether to use the local service for the same name service. If true, the local service is used first, and the service of the same name in the relay server will be hidden. If false, the relay service will be used first, and the local service will be hidden.
- <remoteServices>: The list of remote service in the relay service, such as: http://<server>:<ip>/iserver/services.
- <updateInterval>: The interval at which the relay service is dynamically updated. If the remote service list has changed, the relay service dynamically updates according to this interval. In milliseconds (ms), the default is 60000ms.
9.<license> element
Used to save the license information of the current iServe, including the version being used and the extended service license Refer to Select the license in iServer. Example is as follows:
<license> <enabledmodules> <string>CHART</string> <string>NETWORK</string> <string>SPACE</string> <string>SPATIAL</string> <string>TRAFFIC_TRANSFER</string> <string>PLOT</string> <string>SPATIAL_PROCESSING</string> <string>SERVICE_NODE_ADDITION</string> <string>ENTERPRISE</string> </enabledmodules> </license>
<enabledmodules> contains the license names used, including:
- "ENTERPRISE": Advanced Edition
- "PROFESSIONAL": Professional Edition
- "STANDARD": Standard Edition
- "CHART": Chart module
- "NETWORK": Network Analysis Service
- "SPACE": 3D service
- "SPATIAL": Spatial Analysis Service
- "TRAFFIC_TRANSFER": Traffic Transfer Service
- "SERVICE_NODE_ADDITION":Service Node
- "PLOT":Plotting Service
- "SPATIAL_PROCESSING":Distributed Processing Service
10.<multiworkers> element
Used to configure information about multi-process services. Such as the number of processes, port range, etc., for example:
<multiworkers> <enabled>true</enabled> <workerCount>4</workerCount> <workerIP>127.0.0.1</workerIP> <workerPortStart>8900</workerPortStart> <workerPortEnd>9000</workerPortEnd> <workerBaseDir>../../workers</workerBaseDir> <xmx>1024m</xmx> <communicationPort>8100</communicationPort> <requestDispatchMode>RANDOM</requestDispatchMode> <timeout>20</timeout> </multiworkers>
The specific parameters are described below:
- <enabled>: whether to enable multi-process mode.
- <workerCount>: number of processes.
- <workerIP>: set the communication IP between the main process and the child process.
- <workerPortStart>: the starting port number of the Worker process port range.
- <workerPortEnd>: end port number of the Worker process port range.
- <workerBaseDir>: the working directory of the child process.
- <xmx>: Java virtual machine memory settings.
- <communicationPort>: set the communication port number between the main process and the child process.
- <requestDispatchMode>: the way of the Master forwards requests to the Workers。(Including RANDOM and TO_LEAST_REQUEST_WORKER),
- <timeout>:the TIMEOUT to specify a time when the Master forwards requests to the Workers.
11.<processing> element
Used to configure the distributed analysis service, example is as follows:
<processing> <sparkHome>/home/supermap/spark-1.6.1-bin-hadoop2.6</sparkHome> <masterAddress>spark://sparkmaster:7077</masterAddress> </processing>
<processing> contains the basic configuration of the Spark cluster:
- sparkHome: Spark installation directory.
- masterAddress: master node address of the Spark distributed cluster.
Data storage configuration file
iserver-datastores.xml is used to configure the data storage. The root node is <application> element,and its subnode is <datastores>in which each datastore element is used to configure one data storage,Specific parameters are as follows:
- datastoreType:the type of data storage.
- type:the type of data
- name:the name of data
- url:the URL to specify the data location.
- commonsCSVMetaData:metadata of CSV file.
Example is as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <application> <datastores> <datastore> <datastoreType>BIGDATAFILESHARE</datastoreType> <type>FOLDER</type> <name>samples</name> <url>../../samples/data/ProcessingData</url> <commonsCSVMetaData> <xIndex>10</xIndex> <yIndex>11</yIndex> <separator>,</separator> </commonsCSVMetaData> </datastore> </datastores> </application>