数据可视化
热力图
热力图通过地图颜色的变化趋势,直观地展现点数据的数据分布特征。
静态热力图
ArrayList<ChartPoint> mheatDatas = new ArrayList<ChartPoint>();
//从数据集中读取数据(数据可视化仅限点数据)
Recordset rd = ((DatasetVector)m_workspace.getDatasources().get(0).getDatasets().get("高等院校")).getRecordset(false, CursorType.DYNAMIC);
while (!rd.isEOF()) {
Point2D point = rd.getGeometry().getInnerPoint();
mheatDatas.add(new ChartPoint(point,50));//权重值可根据点的类型不同设置为不同的值
rd.moveNext();
}
rd.dispose();
HeatMap mheatChart = new HeatMap(this,m_mapView);
mheatChart.setRadious(13); //设置热力图圆点半径,单位dp, 默认20
mheatChart.setSmoothTransColor(true);//设置使用渐变显示,即不同分段颜色显示时平滑过渡
mheatChart.addChartDatas(mheatDatas);//添加统计数据
mheatChart.setTitle("热力图");//设置图表的标题
//以下设置为可选设置,不设置则显示默认效果
ChartLegend chartLegend = mheatChart.getLegend();//获取图表关联的图例
chartLegend.setAlignment(ChartLegend.BOTTOM);//设置图例位置(默认右下)
chartLegend.setOrient(false);//设置横向排列图例(默认纵向)
ColorScheme colorScheme = new ColorScheme();
float[] ranges = new float[]{0,50,200,500,1000};
colorScheme.setSegmentValue(ranges); //设置图例范围
colorScheme.setColors(new Color[]{//设置显示颜色(注意:颜色必须与范围的个数一致,否则设置失败,显示默认的风格)
(new Color(116,49,142)),(new Color(230,0,39)),
(new Color(240,131,43)),(new Color(255,226,40)),
(new Color(255,255,255))
});
try {
mheatChart.setColorScheme(colorScheme);//设置图例的颜色表
}catch (Exception e){
} |
| 图:热力图 |
实时热力图
Timer realTimer = new Timer();
realTimer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
ArrayList<ChartPoint> mheatDatas = new ArrayList<ChartPoint>();
……//数据读取过程省略
m_heatChart.addChartDatas(mheatDatas);
}
},50,2000);
m_heatChart.setUpdataInterval(2.0f);// 实时数据更新间隔时间时空热力图
第一步:在资源文件中添加时间轴控件
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/layout_timeline"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="8dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="70dp"
android:layout_marginRight="70dp"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="55dp">
</FrameLayout>第二步:功能实现。
int nSteps = 16;//时间轴上时间点的个数
ArrayList<ChartPoint> mheatDatas = new ArrayList<ChartPoint> ();
for(int j=0;j<nSteps;j++){
……//数据读取过程省略
m_heatChart.insertChartDataset(mheatDatas,String.valueOf(nSteps-j)+"h",0); //插入统计数据表
}
m_heatChart.setPlayInterval(1.0f);// 渲染时空数据
m_heatChart.setIsLoopPlay(true); //设置循环播放
FrameLayout frameLayoutLayout = (FrameLayout)findViewById(R.id.layout_timeline);
frameLayoutLayout.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
TimeLine timeLine = new TimeLine(frameLayoutLayout,this);
timeLine.addChart(m_heatChart);// 添加时间轴关联图表
timeLine.load();//加载时间轴
m_heatChart.startPlay();//开启渲染时空数据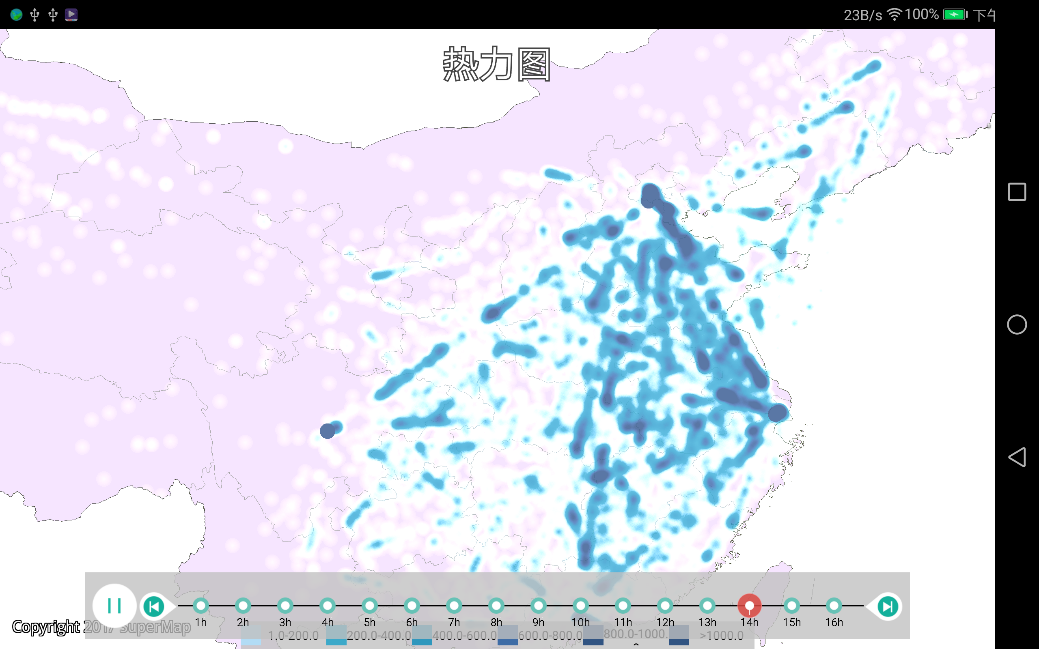 |
| 图:时空热力图 |
格网热力图
格网热力图,通过网格和不同的颜色直观展现点数据的空间分布与统计特征。
静态格网热力图
ArrayList <ChartPoint> mGridDatas = new ArrayList<ChartPoint>();
Recordset rd = ((DatasetVector)m_workspace.getDatasources().get(0).getDatasets().get("科教文化服务")).getRecordset(false, CursorType.DYNAMIC);
while (!rd.isEOF()) {
Point2D point = rd.getGeometry().getInnerPoint();
mGridDatas.add(new ChartPoint(point,0));
rd.moveNext();
}
rd.dispose();
GridHotChart mGridChart = new GridHotChart(this,m_mapView);
mGridChart.addChartDatas(mGridDatas);//添加统计数据
mGridChart.setTitle("格网热力图");//设置图表的标题
float[] ranges = new float[]{1,5,10};
ColorScheme colorScheme = new ColorScheme();
colorScheme.setSegmentValue(ranges);//设置图例范围
colorScheme.setColors(new Color[]{//设置显示颜色
(new Color(126,0,35)),(new Color(102,0,153)),
(new Color(255,153,51))
});
try {
mGridChart.setColorScheme(colorScheme);//设置图例的颜色表
}catch (Exception e){
}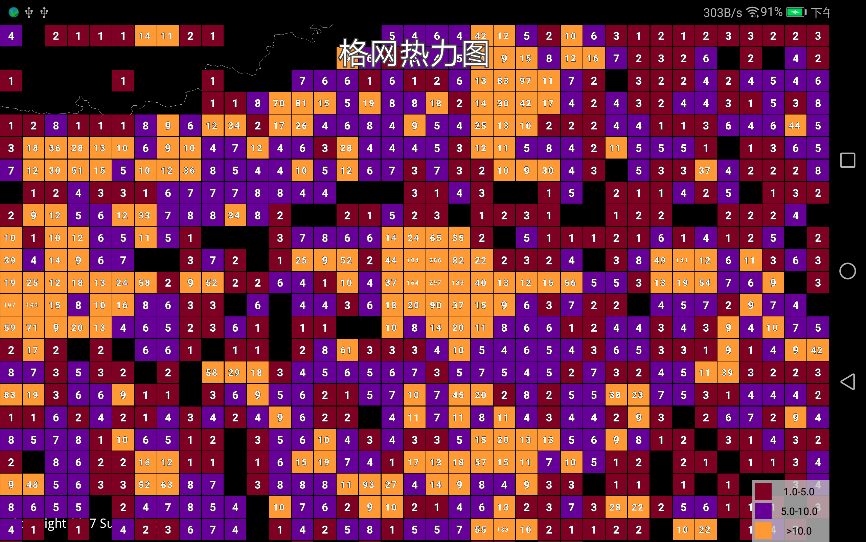 |
| 图:静态格网热力图 |
实时格网热力图
Timer realTimer = new Timer();
realTimer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
Random rand = new Random();
int nCount = 5000 + rand.nextInt(m_gridDatas.size()+5000);
ArrayList<ChartPoint> mGridDatas = new ArrayList<ChartPoint>();
……//数据读取过程省略
m_gridChart.addChartDatas(mGridDatas);
}
},50,2000);
m_gridChart.setUpdataInterval(2.0f); // 实时数据更新间隔时间时空格网热力图
第一步:在资源文件中添加时间轴控件(同“时空热力图”,略)。
第二步:功能实现。
int nSteps = 12;//时间轴上时间点的个数
for(int j=0;j<nSteps;j++){
ArrayList<ChartPoint> mGridDatas = new ArrayList<ChartPoint>();
……//数据读取过程省略
m_gridChart.insertChartDataset(mGridDatas,String.valueOf(nSteps-j)+"月",0);// 插入统计数据表
}
m_gridChart.setPlayInterval(1.0f);// 渲染时空数据
m_gridChart.setIsLoopPlay(true); //设置循环播放
FrameLayout frameLayoutLayout = (FrameLayout) findViewById(R.id.layout_timeline);
frameLayoutLayout.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
TimeLine timeLine = new TimeLine(frameLayoutLayout,this);
timeLine.addChart(m_gridChart);// 添加时间轴关联图表
timeLine.load();//加载时间轴
m_gridChart.startPlay();//开启渲染时空数据 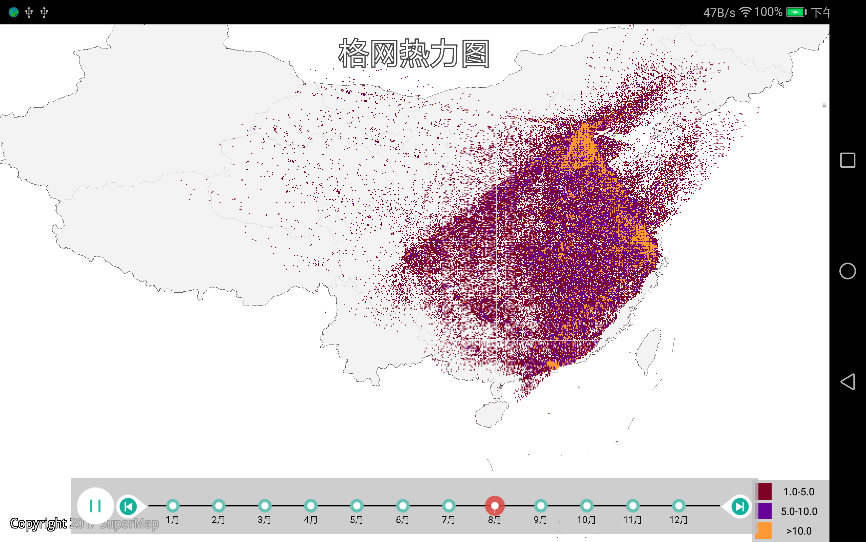 |
| 图:时空格网热力图 |
密度图
密度图能够渲染海量数据点,并根据密集程度呈现颜色的变化。
静态密度图
ArrayList<ChartPoint> mDensityDatas = new ArrayList<ChartPoint>();
Recordset rd = ((DatasetVector)m_workspace.getDatasources().get(0).getDatasets().get("point")).getRecordset(false, CursorType.DYNAMIC);
while (!rd.isEOF()) {
Point2D point = rd.getGeometry().getInnerPoint();
mDensityDatas.add(new ChartPoint(point,0));
rd.moveNext();
}
rd.dispose();
PointDensityChart mDensityChart = new PointDensityChart(this,m_mapView);
mDensityChart.setRadious(4);//设置原始点半径,默认3
mDensityChart.addChartDatas(mDensityDatas); //添加统计数据
mDensityChart.setTitle("密度图");//设置图表的标题
float[] ranges = new float[]{1,3,10};
ColorScheme colorScheme = new ColorScheme();
colorScheme.setSegmentValue(ranges); //设置图例范围
colorScheme.setColors(new Color[]{//设置显示颜色
(new Color(174,221,129)), (new Color(107,194,53)),
(new Color(6,128,67))
});
try {
mDensityChart.setColorScheme(colorScheme); //设置图例的颜色表
}catch (Exception e){
}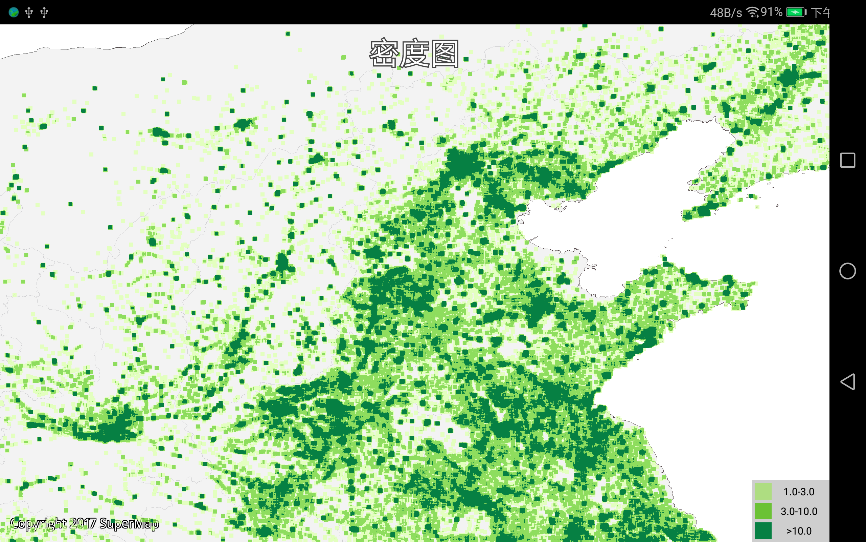 |
| 图:静态密度图 |
实时密度图
Timer realTimer = new Timer();
realTimer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
ArrayList<ChartPoint> mDensityDatas = new ArrayList<ChartPoint>();
……//数据读取过程省略
m_densityChart.addChartDatas(mDensityDatas);
}
},50,2000);
m_densityChart.setUpdataInterval(5.0f); //实时数据更新间隔时间时空密度图
第一步:在资源文件中添加时间轴控件(同“时空热力图”,略)。
第二步:功能实现。
int nSteps = 10;//时间轴上时间点的个数
for(int j=0;j<nSteps;j++){
ArrayList<ChartPoint> mDensityDatas = new ArrayList<ChartPoint>();
……//数据读取过程省略
m_densityChart.insertChartDataset(mDensityDatas,String.valueOf(nSteps-j)+"d",0);
}
m_densityChart.setPlayInterval(1.0f); // 渲染时空数据
m_densityChart.setIsLoopPlay(true); //设置循环播放
FrameLayout frameLayoutLayout = (FrameLayout) findViewById(R.id.layout_timeline);
frameLayoutLayout.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
TimeLine timeLine = new TimeLine(frameLayoutLayout,this);
timeLine.addChart(m_densityChart); // 添加时间轴关联图表
timeLine.load();//加载时间轴
m_densityChart.startPlay();//开启渲染时空数据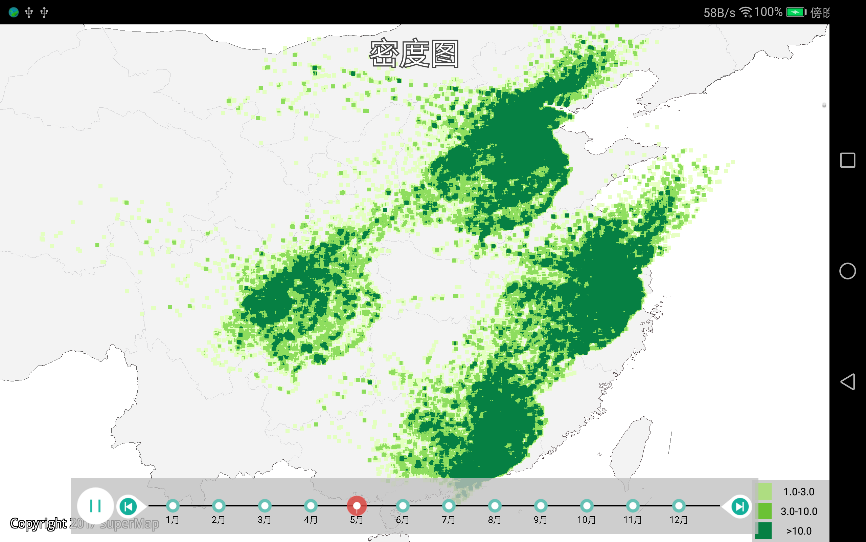 |
| 图:时空密度图 |
聚合图
聚合图能够将高密度的散点抽稀,聚合显示。
静态聚合图
ArrayList<ChartPoint> mPolymerDatas = new ArrayList<ChartPoint>();
Recordset rd = ((DatasetVector)m_workspace.getDatasources().get(0).getDatasets().get("名胜景点")).getRecordset(false, CursorType.DYNAMIC);
while (!rd.isEOF()) {
Point2D point = rd.getGeometry().getInnerPoint();
mPolymerDatas.add(new ChartPoint(point,0));
rd.moveNext();
}
rd.dispose();
PolymerChart mPolymerChart = new PolymerChart(this,m_mapView);
mPolymerChart.setMaxRadious(45);//设置聚合点显示最大半径,默认60
mPolymerChart.addChartDatas(mPolymerDatas);//添加统计数据
mPolymerChart.setTitle("聚合图");//设置图表的标题
float[] ranges = new float[]{1,5,20,50,500,2000};
ColorScheme colorScheme = new ColorScheme();
colorScheme.setSegmentValue(ranges);//设置图例范围
colorScheme.setColors(new Color[]{//设置显示颜色
(new Color(222,156,83)),(new Color(222,211,140)),
(new Color(201,186,131)),(new Color(137,190,178)),
(new Color(113,57,53)), (new Color(117,27,19))
});
try {
mPolymerChart.setColorScheme(colorScheme);//设置图例的颜色表
}catch (Exception e){
}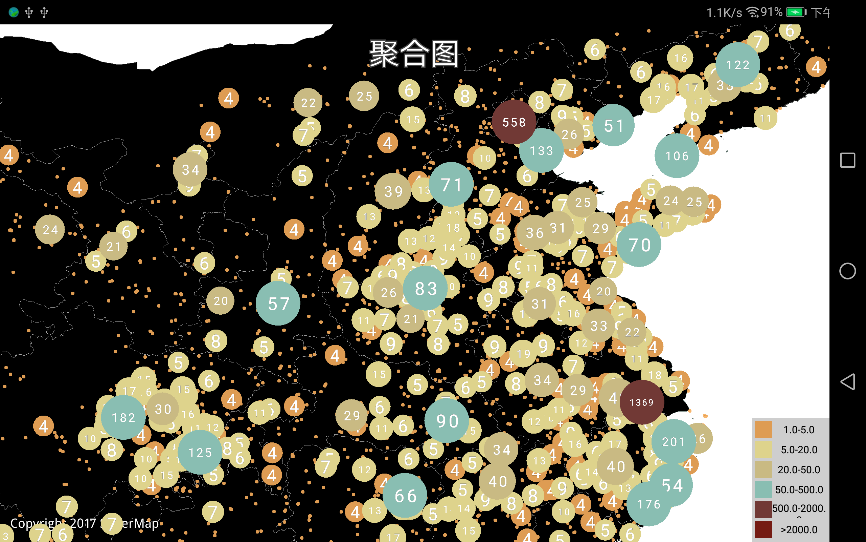 |
| 图:静态聚合图 |
实时聚合图
Timer realTimer = new Timer();
realTimer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
ArrayList<ChartPoint> arrTmp = new ArrayList<ChartPoint>();
……//数据读取过程省略
m_polymerChart.addChartDatas(arrTmp);
}
},50,2000);
m_polymerChart.setUpdataInterval(2.0f); // 实时数据更新间隔时间时空聚合图
第一步:在资源文件中添加时间轴控件(同“时空热力图”,略)。
第二步:功能实现。
int nSteps = 24;//时间轴上时间点的个数
for(int j=0;j<nSteps;j++){
ArrayList<ChartPoint> mPolymerDatas = new ArrayList<ChartPoint>();
……//数据读取过程省略
m_polymerChart.insertChartDataset(mPolymerDatas,String.valueOf(nSteps-j)+"h",0);// 插入统计数据表
}
m_polymerChart.setPlayInterval(1.0f);// 渲染时空数据
m_polymerChart.setIsLoopPlay(true);//设置循环播放
FrameLayout frameLayoutLayout = (FrameLayout) findViewById(R.id.layout_timeline);
frameLayoutLayout.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
TimeLine timeLine = new TimeLine(frameLayoutLayout,this);
timeLine.addChart(m_polymerChart);
timeLine.load();//加载时间轴
m_polymerChart.startPlay();//开启渲染时空数据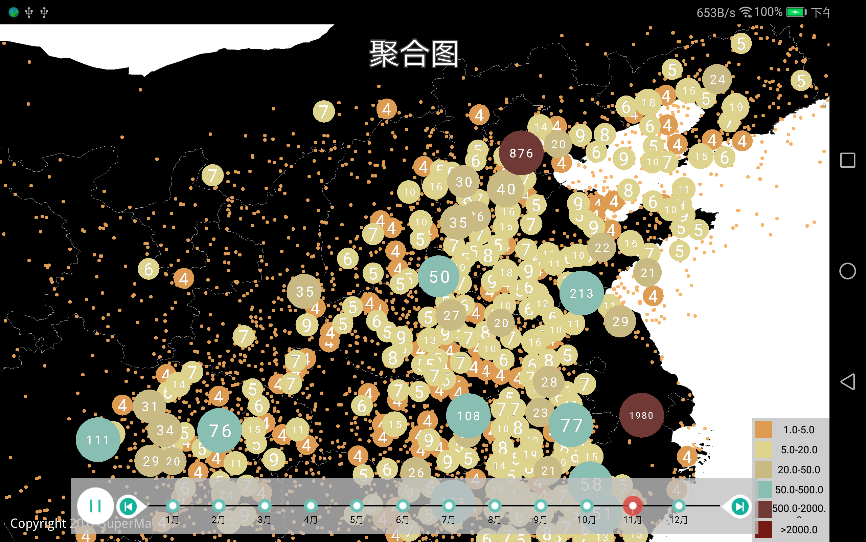 |
| 图:时空聚合图 |
关系图
关系图以关系线的形式反映对象之间的关联。
静态关系图
ArrayList<RelationalChartPoint> m_relativeDatas = new ArrayList<RelationalChartPoint>();
Recordset rd = ((DatasetVector) m_workspace.getDatasources().get(0).getDatasets().get("point")).getRecordset(false, CursorType.DYNAMIC);
while (!rd.isEOF()) {
Point2D point = rd.getGeometry().getInnerPoint();
RelationalChartPoint relPoint = new RelationalChartPoint(point, 0);
relPoint.setRelationName((String) rd.getFieldValue("name"));
m_relativeDatas.add(relPoint);
rd.moveNext();
}
rd.dispose();
ArrayList<RelationalChartPoint> targetArr = new ArrayList<RelationalChartPoint>();
//创建关系点
for(int i = 0;i<m_relativeDatas.size();i++)
{
RelationalChartPoint relPoint = m_relativeDatas.get(i);
relPoint.getRelationalPoints().clear();
String name = relPoint.getRelationName();
if(
name.equalsIgnoreCase("北京大学") ||
name.equalsIgnoreCase("复旦大学") ||
name.equalsIgnoreCase("中山大学") ||
name.equalsIgnoreCase("四川大学") ||
name.equalsIgnoreCase("新疆大学") ||
name.equalsIgnoreCase("湖南大学") ||
name.equalsIgnoreCase("内蒙古大学") ||
name.equalsIgnoreCase("云南大学")
){
targetArr.add(relPoint);
}
}
//创建关系线
for(int j=0;j<targetArr.size();j++){
RelationalChartPoint relPoint = targetArr.get(j);
for(int k=0;k<targetArr.size();k++)
{
RelationalChartPoint relPoint1 = targetArr.get(k);
if(relPoint1.getRelationName().equalsIgnoreCase("北京大学")){
relPoint1.setWeighted(50);
}else if(relPoint1.getRelationName().equalsIgnoreCase("复旦大学")){
relPoint1.setWeighted(45);
}else if(relPoint1.getRelationName().equalsIgnoreCase("中山大学")){
relPoint1.setWeighted(36);
}else if(relPoint1.getRelationName().equalsIgnoreCase("四川大学")){
relPoint1.setWeighted(40);
}else if(relPoint1.getRelationName().equalsIgnoreCase("湖南大学")){
relPoint1.setWeighted(50);
} if(relPoint1.getRelationName().equals(relPoint.getRelationName())==false){
relPoint.getRelationalPoints().add(relPoint1);
}
}
}
Resources res = MainActivity.this.getResources();
Bitmap bmp= BitmapFactory.decodeResource(res, R.drawable.icon_plan);
m_relationChart = new RelationPointChart(this,m_mapView);
m_relationChart.setIsAnimation(true);// 设置开启动画效果
m_relationChart.setLineWidth(0.75f);// 设置关系线宽度
m_relationChart.setMaxRadious(30);// 设置关系点显示最大半径
m_relationChart.setAnimationImage(bmp);//设置沿关系线移动的图形
m_relationChart.addChartRelationDatas(targetArr);//添加关系点数据集
m_relationChart.setTitle("关系图");//设置标题
ColorScheme colorScheme = new ColorScheme();
colorScheme = m_relationChart.getColorScheme();
colorScheme.setColors(new Color[]{
(new Color(23,44,60)),(new Color(39,72,98)),
(new Color(153,80,84)),(new Color(217,104,49)),
(new Color(230,179,61)),(new Color(248,134,137))
});
try {
m_relationChart.setColorScheme(colorScheme);
}catch (Exception e){
}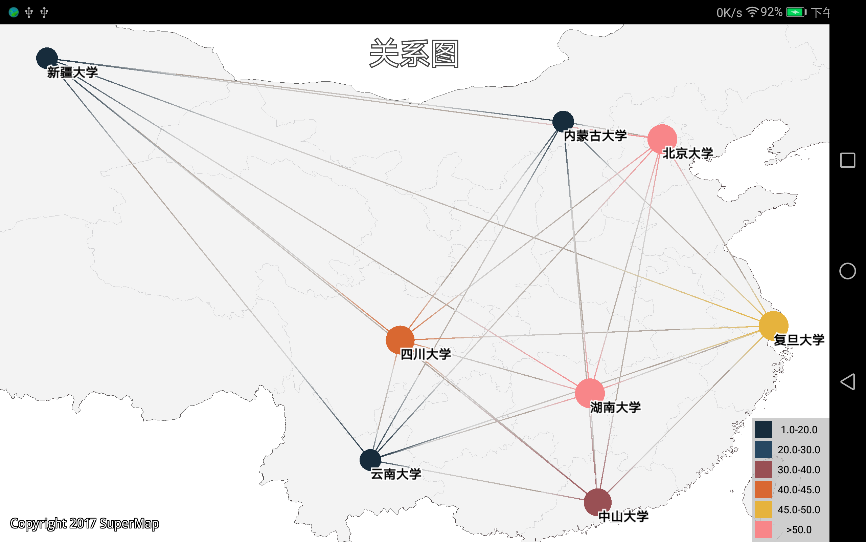 |
| 图:静态关系图 |
实时关系图
Timer realTimer = new Timer();
realTimer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
ArrayList<ChartPoint> arrTmp = new ArrayList<ChartPoint>();
……//数据读取过程省略
m_relationChart.addChartDatas(arrTmp);
}
},50,2000);
m_relationChart.setUpdataInterval(2.0f); // 实时数据更新间隔时间时空关系图
第一步:在资源文件中添加时间轴控件(同“时空热力图”,略)。
第二步:功能实现。
int nSteps = 12;
for(int j=0;j<nSteps;j++){
ArrayList<ChartPoint> arrTmp = new ArrayList<ChartPoint>();
……//数据读取过程省略
m_relationChart.insertChartDataset(arrTmp,String.valueOf(nSteps-j)+"月",0);
}
m_relationChart.setPlayInterval(1.0f);
m_relationChart.setIsLoopPlay(true);
FrameLayout frameLayoutLayout = (FrameLayout) findViewById(R.id.layout_timeline);
frameLayoutLayout.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
TimeLine timeLine = new TimeLine(frameLayoutLayout,this);
timeLine.addChart(m_relationChart);
timeLine.load();
m_relationChart.startPlay();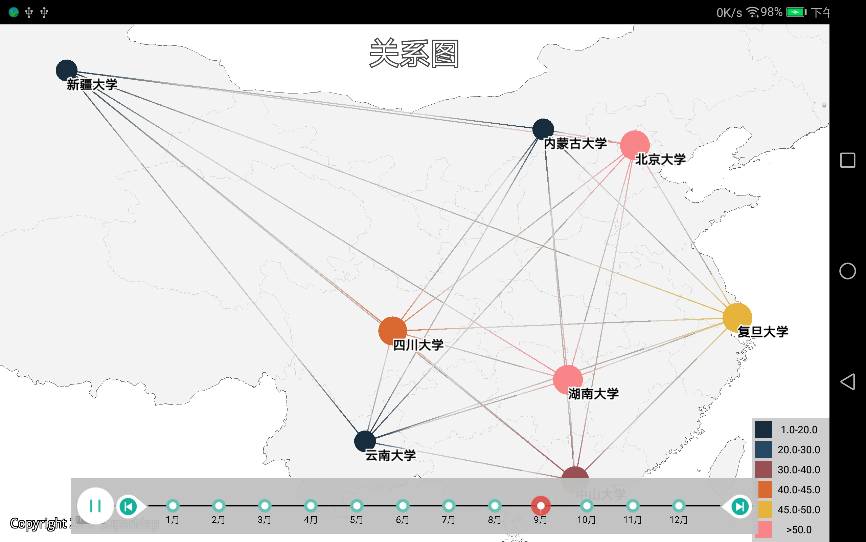 |
| 图:时空关系图 |



