You could be familiar with the relationship between different SuperMap iMobile for Android products, by reading class structure diagram of SuperMap iMobile for Android which is also called Component Objects Model Diagram (COMD).
Class structure diagram is drawn based on UML (Unified Modeling Language). By the diagram, programmer could know the classes relationship and how to get one object from another, to select the right interface and get the member needed such as properties and methods. It helps to build the application system. There are diagrams in online help.
You should know how many classes in SuperMap iMobile for Android structure and how to use them before read the diagram.
Class type of SuperMap iMobile for Android
There are 5 classes shown as below: Abstract Class, Create-able Class, Un-create-able Class, Static Class and Enumeration Class.
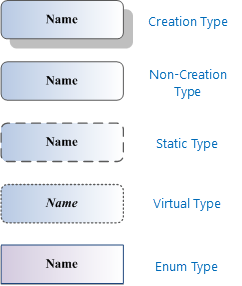 |
| Figure:Five kinds of legends |
Abstract class, also called empty class and could not be of instance. Namely, it has no instance. But many concrete classes could be inherited from it. E.g., Geometry is an abstract class. There is no Geometry object. But concrete classes such as GeoPoint, GeoLine and GeoRegion are inherited from Geometry class. GeoPoint instance is 2D point geometry object. GeoLine is 2D line geometry object. GeoRegion is 2D surface geometry object. Member defined by abstract class could be inherited by its sub-class.
Create-able class, its instance object could be created and initialized by keyword: New. Its instance object could exist without other objects and the life cycle could be without other objects' management. Users could create a Workspace object by sentences below if Workspace is a create-able class.
- Workspace workspace = new Workspace();
Un-create-able class, instance object could not be generated directly, but be obtained by other class's method. Its object could not be created by keyword: New and there is no constructor function. If Datasource is an un-create-able class, it could be created by Datasource method of Workspace class. E.g.:
- Datasources datasources = workspace.getDatasources();
Static class, its members are all static objects and have no instances. They could be used directly. Static class is like a toolbox for geography handling. Every method of it is a tool of geography handling and input is its parameter, while output is return value. E.g., Geometries is a static class and could be used by pathway below:
- GeoRegion geoRegion3 = Geometrist.intersect(geoRegion1, geoRegion2);
Enumeration Class, it defines the relative constant and have no instance object. E.g., EncodeType is an Enumeration Class.
- datasetVectorInfo.getEncodeType(EncodeType.INT32);
Relationship between SuperMap iMobile for Android classes
There are 3 relationships between classes: integration, inheritance and connection. While there are 3 types of integration which could be described by UML connection relationships.
Integration relationship
There are 3 relationships of integration shown as below
- A contains one B means A must contain or match a B, no more or less. E.g., A Datasource must match a Datasets;
- A contains 0 or 1 B means A could only have 0 or 1 B. E.g., Layer could match one Theme or no Theme;
- A contains 0 or more B. In this relationship, A is collection of B. E.g., 1 Datasource could contain multiple Datasource objects.
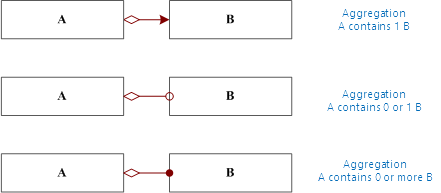 |
| Figure:Aggregation relationship |
Inheritance relationship
One abstract class could not generate one object directly. It could only realize its properties and methods by its sub-class. Sub-class will inherit all non-private methods and properties from its parents class. Sub-class could be considered as one kind of its parent class. The relationship of sub and parents is inheritance.
Shown as below is the inheritance diagram. B is inherited from A. A is parent class while B is sub class. Inheritance is kind of extension of the class function. Namely, sub-class will have its own behavior and properties based on its parent's. Such as GeoPoint, GeoLine, GeoRegion and GeoText are all inherited from Geometry abstract class. Of course the inheritance is not limited between abstract class and its sub-class, while in SuperMap iMobile for Android, this inheritance relationship is the most common.
 |
| Figure:Inheritance relationship |
Connection relationship
A and B have certain connections. If you could access object of B from object A, they are connection relationship. Diagram is shown as below.
 |
| Figure:Relationships |
It reflects the relatively loose relationship between classes. In SuperMap iMobile for Android, there are 2 connection relationships between classes:
- 1st one, is the relationship of use and be used. E.g., the use of enumeration class by the main class, the use of properties class by the main class and the information type when creating main class. E.g., the connection relationship between Datasource and EngineType, Datasource set its engine type by EngineType; the connection relation between DatasetVector and Tolerance; the connection relationship between Workspace and WorkspaceConnectionInfo, Workspace could be created, opened and saved by WorkspaceConnectionInfo object.
- 2nd one, is the operation relationship. E.g., DatasetVector and Recordset, by performing the search operation to the DatasetVector, you could get Recordset. You could get the matched DatasetVector object by Recordset object.



