Tutorial
Basic Services Management
SuperMap iManager supports to manage basic services. Users can access the client of services; redeploy the services; adjust the specs of service; stop/start the services; modify the images of service; transfer the services to specified host; expose/hide the services address; view the container logs; control the container command pad.
Service Management
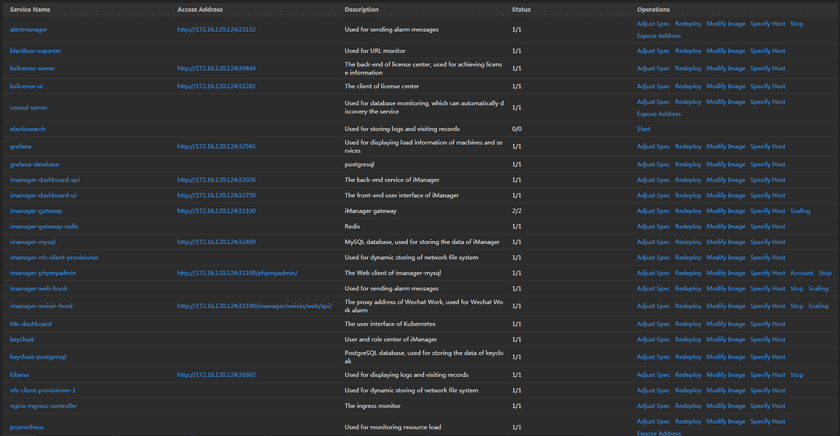
Clicks Basic Services on the iManager webpage to enter the services list.
Manage the services by the following functions:
- Service Name: The list shows all the basic services that running in iManager, click on the service name to enter the container page.
- Address: The address of the service, users can access the client of service by the address link.
- Description: Explains the funtion of the service.
- Status: Shows the number of running/total replicas in the service.
- Adjust Spec: Adjusts the service’s CPU and Memory spec.
- Redeploy: Redeploys the service.
- Modify Image: Change the image of service, used for rolling upgrade. The image format is: Registry/Namespace/Imagename:tag.
- Specify Host: Specify the host node for the services. Select Not Specified by default or node name in the drop-down menu.
- Account: Clicks to view the account’s username and password.
- Stop/Start: Clicks to stop/start the service, reduces the useage of system resource. The services do not support to stop if the icon is not existing.
- Expose Address: Exposes the service access address.
Container Management
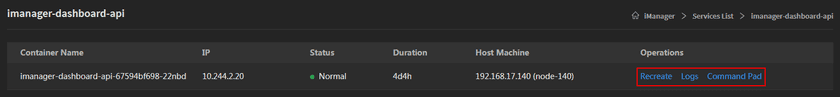
Clicks on the service name to enter the container details page, the page shows the information of container name, IP, status, duration, and host machine. If any container malfunctioned, you can recreate the container, the service would stop working until finishing recreating.
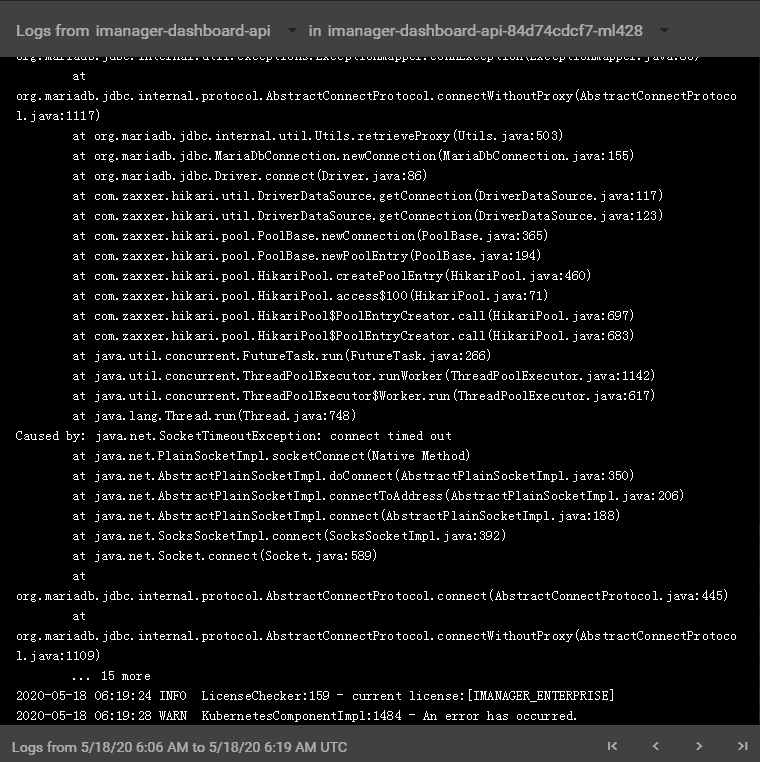
Clicks on Logs to enter the container log, the log records the running status and running history of the container.
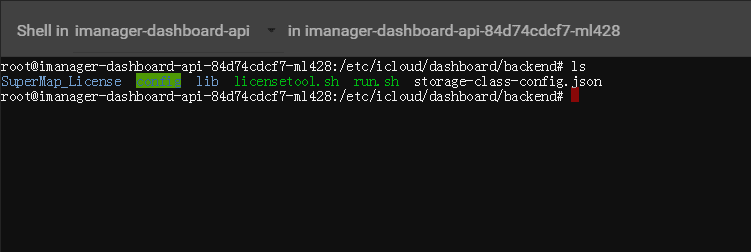
Clicks on Command Pad to control the container, administrator can execute commands in the interface to operate the container.
For example, executes ‘ls’ command to view the files in the directory.
Notes:
Using [shift + insert] to paste the commands into the Command Pad.