Tutorial
Geo-Blockchain
SuperMap iManager supports to ‘one-click’ creating Geo-Blockchain. A blockchain is a type of data store that stores anything of digital value. Each new transaction is stored in a block that gets added to a chain of existing records. A typical blockchain duplicates data across an open network so all parties in the blockchain see updates simultaneously, and all updates are validated through a public verification process that ensures accuracy without the need for a central authority, like a bank. Spatial blockchain is combining blockchain technology with GIS, to achieve a high credibility distributed spatial database, used for spatial data storing and sharing.
For monitoring and managing, users can view the topological diagram to understand the associations between the services; redeploy the problem services; adjust the specs of service; modify the images of service; view the log of the services; enter the command pad of containers; and manual/automatic scaling the services.
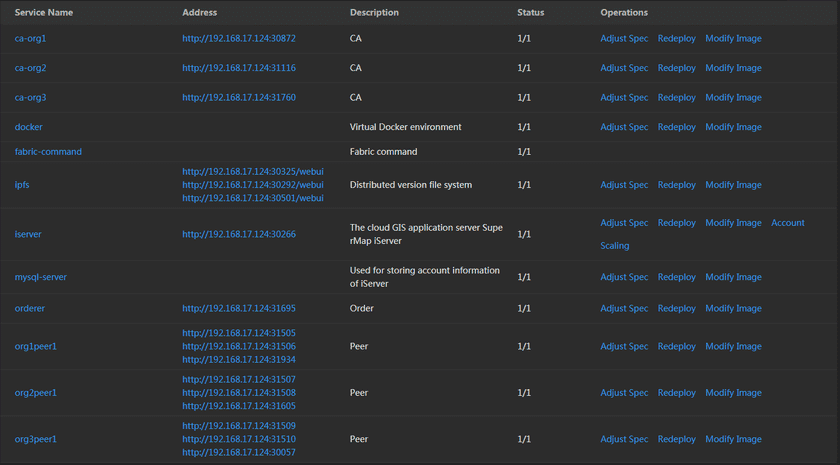
The services in the Geo-Blockchain environment:
- ca-org(1-3): CA node, the certification center. Used for receiving the register application from client, return a password to the client for achieving the identify certification.
- docker: The virtual Docker environment.
- fabric-command: The command pad of Fabric.
- ipfs: Distributed file versions system.
- iserver: GIS Server. The data directory is /opt/iserverOPTs/iserver_data.
- mysql-server: Database, used for storing accounts information of iServer.
- orderer: Orderer node, a node running the communication service that implements a delivery guarantee, such asatomic or total order broadcast.
- org(1-3)peer1: Peer node, a node that commits transactions and maintains the state and a copy of the ledger. Besides, peers can have aspecial endorser role.