The engine is the data pump for SuperMap, providing and maintaining a complete set of data models. In addition to supporting the traditional database engine and file engine, SuperMap SDX + extends SDX + in Newest Version by adding a Web engine and accessing the network Data Service based on OGC. The data engine types supported by SuperMap SDX + are shown in the following figure. Through the continuous expansion of the engine, the popular Spatial Info storage platform in the industry can be integrated with SuperMap as much as possible, thus reducing the complexity of end users and improving the integrity and flexibility of GIS integrated applications.
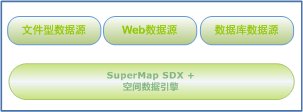 |
| Figure: Datasource supported by SuperMap SDX + |
1.Database Engine
Since the 21st century, the mainstream of GIS Application development is to use relational database to manage data, including Spatial Data and business data. Compare with that traditional file mode, the Spatial data library technology has obvious technical advantages in many aspect, It includes massive Data Management capability, integrated storage of graphics and attribute data, multi-user concurrent access (reading and writing), perfect Access Permissions control and data security mechanism.
At present, the database engine includes the O series based on ODBC data access protocol and the Oracle series developed by OCI (API provided by database vendors). The O series is mainly represented by SQLPlus engine, and includes PostgreSQL engine, DM engine, KingBase engine, etc. OraclePlus engine and Oracle Spatial engine developed based on OCI (there was Oracle engine before 3.0, but it has been abandoned at present). In the long run, the development of many database engines is bound to use the API development of database vendors, so as to make better use of the characteristics of each database and maximize its performance.
At present, Spatial Data database technology is gradually replacing the traditional file, and becoming the Solution of Spatial Data storage and application in more and more large and medium-sized GIS Application systems.
Database engine is mainly used for Oracle, SQL Plus, Kingbase and other relational Database Management systems; Spatial Data Database refers to the database for storing and managing Spatial Data. SuperMap Spatial Data Database uses a large relational database as a storage container, manages and operates through SuperMap SDX +, and stores Spatial Data and attribute data into a large relational database. Such as Oracle, SQL Server, Sybase, and DM3.
The SQL Server engine is a purely relational database space engine based on the large database SQL Server. SuperMap Objects is implemented by DB Library, a development tool provided by Microsoft. Like UDB and MDB engines, this engine uses the data structure defined by SuperMap Objects. SQL Server engine is suitable for building large Spatial Data applications.
Because The support of Oracle Spatial for Topology, 3D Data, Raster Data and parametric objects is difficult to meet the requirements of SuperMap Objects, and the performance is not high. SuperMap Objects has developed a Spatial Data Library engine based directly on the Oracle RDBMS. The Oracle engine is suitable for building large Spatial Data applications.
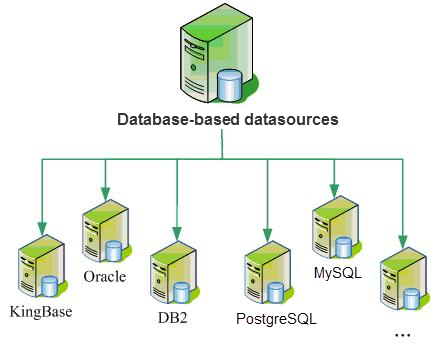 |
2. File Engine
There are four types of file engines: SuperMap custom UDB engine (read-write), UDBX engine (read-write), image plug-in engine (direct access to some Image Data), and Vector File engine.
- UDB Engine is the only file-based Spatial Data engine in the SuperMap Objects custom format. This engine uses the traditional file + database hybrid storage mode. A data project of UDB engine includes two files. The file with the extension of UDB stores Spatial Data and adopts OLE compound document technology. The file with the extension of UDD is attribute database and adopts MDB database format of Access. Because UDB files use compound document technology, they provide the ability to store multiple Datasets in one UDB project. This is different from other technologies such as Arc/Info Coverage and MapInfo Table files. UDB is mainly used for small and medium-sized systems and desktop applications, aiming at improving efficiency and making up for the shortcomings of pure database engines in this respect.
- UDBX Engine, which can read, write, and manage Spatialite Spatial Data. Spatialite is an open source library used to extend the kernel of SQLite. It provides a complete and powerful spatial Database Management system with cross-platform and lightweight features, and supports fully mature spatial SQL functions. In addition, Spatialite uses R-Tree as Spatial Index to retrieve Spatial Data efficiently. SuperMap's new UDBX file engine makes full use of Spatialite's ability to efficiently manage Spatial Data and the characteristics of lightweight databases.
- There is no need to install and deploy the database system
- when using the UDBX file engine. Because the Spatialite database simply corresponds to a single file and the file size is not limited, when using the UDBX file engine to create the Datasource, A UDBX File Database (*.udbx) will be created, which is essentially a database file. Compared with the existing UDB File Database, it has the characteristics of more openness and safer and more stable data operation.
- In the UDBX File Database, you can Create a Dataset or import data from other sources. Dataset types supported by UDBX File Database include: point, line, surface, text, CAD, property sheet, 3D point/line/region, EPS composite point/line/region/text, grid, image, and Mosaic Dataset.
- In addition, the UDBX file engine is more open and supports direct operation of Spatial Data imported into the Spatialite Spatial Data database by a third party, such as display and Edit Data. To apply, simply load the Spatialite Spatial Data library file (*.sqlite) into the iDesktop as a File Database.
- Image Plug-in Engine, which supports read-only display of raster data in SuperMap, and currently supports Raster Data (BMP) in BMP, JPEG, RAW, TIFF, SCI, SIT, and ERDAS IMAGINE formats. JPEG is general Raster Data type, RAW and TIFF are remote sensing Image Data type, SCI is map pre-cache Picture File defined by SuperMap, and SIT is Raster Data type defined by SuperMap. Therefore, there are seven types of plug-in engines: BMP read-only engine, JPEG read-only engine, RAW read-only engine, TIFF read-only engine, SCI read-only engine, SIT read-only engine and ERDAS IMAGINE read-only engine.
- Vector File Engine supports editing and saving of Vector File for general vector formats such as SHP, tab, DWG, etc.
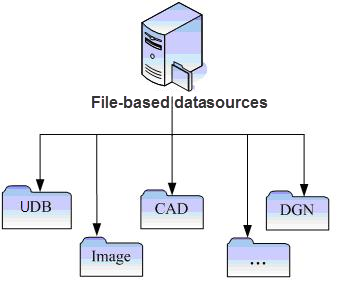 |
| Figure: Datasource supported by SuperMap SDX + |
3. Web Engine
WFS, WMS and WCS are executive specifications formulated according to OGC standards, among which WFS (Web Feature Service) is the executive specification of vector maps. WMS (Web Map Service) is the implementation specification of the grid map, and WCS (Web Coverage Service) is the implementation specification of the Image layer.
Web Engine can directly access the Web services provided by WFS, WMS, WCS and so on. This kind of engine is to deal with the Web server that conforms to the OGC standard on the network as the Datasource of SuperMap, through which the map and data published on the network can be completely combined with the map and data of SuperMap. The application of WFS and WMS is integrated into the technical system of SuperMap, which expands the application field of SuperMap data engine. The Web engine is read-only.
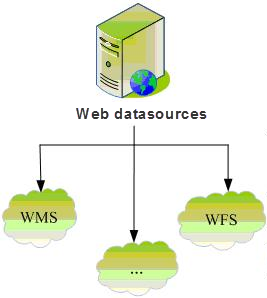 |
| Figure: Datasource supported by SuperMap SDX + |



