Instructions
The Scene Beautification function supports replacing the material of S3M tiles whose material type is UE material (only Rendering Engine V2), achieving data beautification; It also supports batch adding vegetation or static models in the scene.
Through the Scene Beautification function, the Asset Manager can be opened. The Asset Manager supports viewing and editing materials, vegetation, or static models.
- Materials: Through the Materials button in the Asset Manager, you can access the built-in material library of the software (storage path: SuperMap iDesktopX installation path\templates\Materials), including PBR (Physically Based Rendering) materials such as concrete, masonry, metal, plastic, stone, etc. If you need to use more other material resources in the software, place them in the same path as the default materials. More Material Resources (extraction code: smsw) can be accessed by clicking the blue text.
- Vegetation: Through the Vegetation button in the Asset Manager, you can access the built-in vegetation feature library of the software (storage path: SuperMap iDesktopX installation path\templates\Assets\Plant\Samples), including Platanus, birch, etc. If you need to use more other vegetation features in the software, place them in the same path as the default vegetation features. More Feature Resources (extraction code: smsw) can be accessed by clicking the blue text.
- Static Models: Through the Static Models button in the Asset Manager, you can access the built-in model feature library of the software (storage path: SuperMap iDesktopX installation path\templates\Assets\Asset), including characters, urban plot accessories, sports facilities, road accessories, etc. If you need to use more other features in the software, place them in the same path as the default static models. More Feature Resources (extraction code: smsw) can be accessed by clicking the blue text.
Function Entrance
- Scene Tab->Scene Beautification Group->Scene Beautification Button
Operation Steps
Replacing Materials
- Open a scene or create a new scene, open the S3M tile data to be operated, select the model dataset layer in the Layer Manager, right-click Quickly Locate to This Layer.
- Click the Scene Beautification button in the Scene tab's Scene Beautification group. The "Asset Manager" dialog box will pop up at the bottom of the current window. Select "Materials" in the dialog box to display the software's built-in material resources.
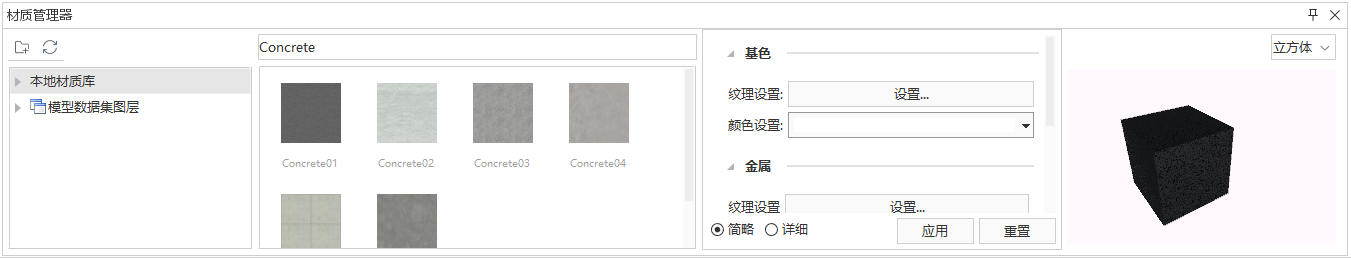
- The Asset Manager includes a toolbar, material library list, material list, etc.
- The toolbar provides back, refresh, and search functions.
- Back: Supports returning to the previous menu from the current list.
- Refresh: Refreshes the content in the current material library list.
- Search: Enter the specified asset name in the text box on the upper right side of the specific material list to display only related materials in the current material list.
- Material Library List: Displays the current software's built-in PBR material types such as Concrete, Masonry, Metal, and Stone.
- Material List: Displays all materials in the currently selected material library and also supports displaying the effect of materials after parameter adjustments.
- Right-click a specific material to perform operations such as copy, rename, open containing folder, delete, etc.
- Copy: Copies the current material texture to the clipboard.
- Rename: Modifies the name of the currently selected material file.
- Open Containing Folder: Opens the folder where the currently selected material is located.
- Delete: Deletes the currently selected material file from the current material library.
- Right-click a blank area in the material list to perform new, paste, and open folder operations.
- New: Creates a new PBR material in the current material library.
- Paste: Pastes the previously copied material into the current material library.
- Open Folder: Opens the folder where the current material library is located.
- The material library node's right-click menu provides rename and delete folder functions.
- Rename: Sets a new name for the currently selected material library.
- Delete Folder: Deletes the local folder corresponding to the currently selected material library.
- The toolbar provides back, refresh, and search functions.
- Material Editing: The Asset Editing Panel supports adjusting and saving various parameters of the selected material.
- Base Color Adjustment
- Texture Settings: Sets the texture map file representing the surface color of the object. By clicking the texture image, you can edit the texture image source (replace, delete, export), texture offset/rotation/scale, and other parameters in the popped-up "Asset Editor" dialog box.
- Base Color: Sets the surface color of the object. Specify the color by clicking the drop-down menu and selecting from the color table.
- Translation: Enables translation movement of the base color texture. Translation movement supports setting the speed along the U and V directions, in texture coordinate units per second.
- Period: The time taken for a single translation, in seconds.
- U: The movement speed of the texture along the X-axis (set to a positive value to move along the negative X-axis; set to a negative value to move along the positive X-axis).
- V: The movement speed of the texture along the Y-axis (set to a positive value to move along the negative Y-axis; set to a negative value to move along the positive Y-axis).
- Scale: Enables scaling movement of the base color texture. Scaling movement supports setting the scaling change speed along the U and V directions, in texture coordinate units per second.
- Period: Sets the time taken for a single scale, in seconds.
- U: Sets the scaling speed of the base color texture along the X-axis (set to a positive value to scale along the negative X-axis; set to a negative value to stretch along the positive X-axis).
- V: Sets the scaling speed of the base color texture along the Y-axis (set to a positive value to scale along the negative Y-axis; set to a negative value to stretch along the positive Y-axis).

- Metallic Roughness Settings
When the metallic roughness texture is not used, the metallic roughness effect is determined solely by the metallic factor and roughness factor. When the metallic roughness texture is used, the metallic roughness effect is determined by the product of the texture and the factors. The following figure shows an example of the metallic effect changing with the metallic value (when roughness is 0, the metallic effect changes from left to right, with metallic values of 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1 respectively).

The following figure shows an example of the roughness effect changing with the roughness value (when metallic is 0, the roughness effect changes from left to right, with roughness values of 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1 respectively)

- Texture Settings: Sets the metallic roughness texture map file. The R channel in the texture controls metallicness; the G channel controls roughness. By clicking the texture image, you can edit the texture image source (replace, delete, export), texture offset/rotation/scale, and other parameters in the popped-up "Texture Editor" dialog box.
- Metallic Factor: Controls the degree to which the material surface "resembles metal", with a value range of 0~1. A higher value indicates a higher level of metalness. Higher surface metalness means the surface color is more driven by environmental reflection, and the material's own appearance color is more blurred. Lower surface metalness means it is less affected by the reflective environment, and the material's own appearance color is more obvious.
- Roughness Factor: Controls the roughness of the material surface, with a value range of 0~1. A higher value indicates greater material roughness. The material's roughness affects the degree of light reflection: the rougher the surface, the higher the microsurface detail, and the more blurred the object's environmental reflection; the smoother the surface, the stronger the reflectivity, and the clearer the reflection of the object's environment.
- Normal Settings
- Texture Settings: Normal map texture file.
- Strength Factor: The influence degree of the normal map texture.

- Emission Settings
When the emission texture is not used, the emission effect is determined solely by the emission color value. When the emission texture is used, the emission effect is determined by the product of the emission texture and the color value. The emission effect is shown in the figure below.

- Texture Settings: By clicking the emission texture image, select the specified emission texture map (*.png/*.jpg/*.bmp/*.gif/*.tif/*.jpeg) in the popped-up browse folder dialog.
- Color Value: Enter the RGB value corresponding to the color in the input box after Emission to control the emission color of the material surface.
- Occlusion Settings: By clicking the occlusion texture image, select the specified occlusion texture map (*.png/*.jpg/*.bmp/*.gif/*.tif/*.jpeg) in the popped-up browse folder dialog.

- Mask: By clicking the mask texture image, select the specified mask texture map (*.png/*.jpg/*.bmp/*.gif/*.tif/*.jpeg) in the popped-up browse folder dialog.
- Alpha Rendering Mode: Sets the transparent rendering mode of the object.
- Opaque: This is the default setting, suitable for ordinary solid objects without transparent areas.
- Mask: In this mode, there are no semi-transparent areas; the texture is either fully transparent or fully opaque. Complex hollowed-out effects can be created using base color textures with transparency without needing to create complex models.
- Transparent: Renders by blending with the background according to the Alpha value in the material's texture or material color. A higher Alpha value results in a less clear background and a clearer foreground after blending, and vice versa. Suitable for rendering realistic transparent materials, such as transparent plastic or glass.

- Alpha Filter Threshold Setting: In Mask rendering mode, areas below the set filter threshold are displayed as fully opaque; areas above the set filter threshold are displayed as fully transparent.
- Double Sided: Sets whether to enable double-sided rendering.
- Not enabled means using single-sided rendering. Single-sided rendering means only one side of the model surface is rendered, not the back. This means only the model surface facing the camera is affected by lighting and materials, while the surface facing away from the camera is not rendered. This rendering method is suitable for most situations, especially when the back of the model is invisible or has no important details. Single-sided rendering can improve rendering performance and reduce unnecessary computational overhead.
- Enabled means using double-sided rendering, which renders both sides of the model surface, increasing rendering overhead.
- Base Color Adjustment
-
After setting is completed, click Save in the Asset Editing Panel to save the adjusted modifications.
-
Apply Material: Select the target material in the material list and drag it to the specified object in the scene to apply it.
-
Save Beautification Result: Click the Save Beautification Result button in the Scene Beautification tab to save the material application effect.
Adding Vegetation Sketch
- Open a scene or create a new scene, click the Scene Beautification button in the Scene tab's Scene Beautification group. The "Asset Manager" dialog box will pop up at the bottom of the current window. Select "Vegetation" in the dialog box to display the software's built-in vegetation feature resources.
- The Asset Manager includes a toolbar, vegetation list, etc.
- The toolbar provides back, refresh, and search functions.
- Back: Supports returning to the previous menu from the current list.
- Refresh: Refreshes the content in the current vegetation list.
- Search: Enter the specified asset name in the text box on the upper right side of the specific vegetation list to display only related vegetation features in the current vegetation list.
- Vegetation List (Library): Displays the software's built-in vegetation features (library) such as Platanus, birch, etc.
- Right-click a specific vegetation feature to perform operations such as open containing folder, etc.
- Open Containing Folder: Opens the folder where the currently selected vegetation feature is located.
- Right-click a blank area in the vegetation feature list to perform open folder operations.
- Open Folder: Opens the folder where the current vegetation feature library is located.
- The vegetation feature library's right-click menu provides open containing folder, rename and delete folder functions.
- Open Containing Folder: Opens the folder where the currently selected vegetation feature library is located.
- Rename: Sets a new name for the currently selected vegetation feature library.
- Delete Folder: Deletes the folder corresponding to the currently selected vegetation feature library.
- The context menu for blank areas in the Vegetation Library list provides options to create a new folder and open the parent directory.
- New Folder: Create a new vegetation folder within the current list.
- Open Parent Directory: Locate the parent folder containing all current list items.
- The toolbar provides back, refresh, and search functions.
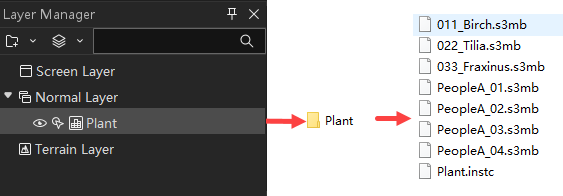
- Add Vegetation: After selecting a specific vegetation feature in the vegetation list, you can set relevant parameters in the Asset Editing Panel on the right side of the software and add vegetation to the scene. After adding, an instantiated layer with the specified name will be added to the Layer Manager.
- Layer: Sets the name of the instantiated layer where the vegetation feature is located, default is Plant.
- Group Name: Sets the name of the group where the vegetation feature is located, default is Group1.
- Add Mode: Sets the adding mode of the vegetation feature in the scene, including area addition, along-line addition, and single addition.
- Draw: After selecting the add mode and setting the corresponding parameters, click the Draw button, move the mouse to the scene to draw the placement path for the vegetation feature.
- When selecting area addition, start drawing a polygon area by left-clicking the mouse, and end drawing by right-clicking the mouse.
- When selecting along-line addition, start drawing a line by left-clicking the mouse, and end drawing by right-clicking the mouse.
- When selecting single addition, left-click at the specified position in the scene, and end drawing by right-clicking the mouse.
- Spacing: Sets the spacing between two vegetation features, default value is 15, unit is meters.
- Random Size: After checking the Random Size checkbox, set the scaling ratio range for the vegetation feature (default is 1~5), and the vegetation will be scaled according to a random proportion. If not checked, and enter the scaling ratio for the vegetation feature in the first text box, vegetation features of the specified scale will be drawn in the scene.
- Random Angle: After checking the Random Angle checkbox, when drawing, the vegetation feature will rotate around the Z-axis at a random angle. If not checked, the vegetation feature will be drawn at a fixed angle.

- Edit Vegetation: After selecting the vegetation feature to be edited in the scene, you can view and set parameters such as translation, rotation angle, scaling ratio, etc., in the Asset Editing Panel on the right side of the software.
- Set Translation: Enter the translation distance along the X/Y/Z axis in the X/Y/Z text boxes respectively, unit is meters.
- Set Rotation Angle: Enter the counterclockwise rotation angle around the X/Y/Z axis in the X/Y/Z text boxes respectively, unit is degrees.
- Set Scaling Ratio: Enter the scaling ratio along the X/Y/Z axis in the X/Y/Z text boxes respectively, unit is times.
- After setting, click the Apply button to adjust the feature's effect according to the specified parameters.
-
Save Beautification Result: After setting is completed, click the Save Beautification Result button in the Scene Beautification tab. The instantiated layer where the vegetation feature is located and the corresponding vegetation feature will be saved in the folder with the specified asset name under the specified project path.
Adding Static Models
- Open a scene or create a new scene, click the Scene Beautification button in the Scene tab's Scene Beautification group. The "Asset Manager" dialog box will pop up at the bottom of the current window. Select "Static Models" in the dialog box to display the software's built-in static model feature resources.
- The Asset Manager includes a toolbar, vegetation list, etc.
- The toolbar provides back, refresh, and search functions.
- Back: Supports returning to the previous menu from the current list.
- Refresh: Refreshes the content in the current static model list.
- Search: Enter the specified asset name in the text box on the upper right side of the specific list to display only related features in the current list.
- Static Model List (Library): Displays the software's built-in features (library) such as characters, urban plot accessories, sports facilities, road accessories, etc.
- Right-click a specific static model to perform operations such as open containing folder, etc.
- Open Containing Folder: Opens the folder where the currently selected feature is located.
- Right-click a blank area in the model feature list to perform open folder operations.
- Open Folder: Opens the folder where the current feature library is located.
- The static model feature library (characters/urban plot accessories, etc.) right-click menu provides open containing folder, rename and delete folder functions.
- Open Containing Folder: Opens the folder where the currently selected feature library is located.
- Rename: Sets a new name for the currently selected model feature library.
- Delete Folder: Deletes the folder corresponding to the currently selected model feature library.
- The context menu for blank areas in the Static Model Library list provides options to create a new folder and open the parent directory.
- New Folder: Create a new static model folder within the current list.
- Open Parent Directory: Locate the parent folder containing all current list items.
- The toolbar provides back, refresh, and search functions.
- Add Static Model: After selecting a specific feature in the static model feature list, you can set relevant parameters in the Asset Editing Panel on the right side of the software and add static models to the scene. After adding, an instantiated layer with the specified name will be added to the Layer Manager.
- Layer: Sets the name of the instantiated layer where the feature is located.
- Group Name: Sets the name of the group where the feature is located, default is Group1.
- Add Mode: Sets the adding mode of the feature in the scene, including along-line addition and single addition.
- Draw: After selecting the add mode and setting the corresponding parameters, click the Draw button, move the mouse to the scene to draw the placement path for the feature.
- When selecting along-line addition, start drawing a line by left-clicking the mouse, and end drawing by right-clicking the mouse.
- When selecting single addition, left-click at the specified position in the scene to complete the drawing.
- Interval Array: When selecting along-line addition, after checking Interval Array, model objects will be placed on the specified path at specified intervals.
- Spacing: Sets the interval distance between static model objects, unit is meters, default is 20.0.
- Continuous Array: When selecting along-line addition, after checking Continuous Array, model objects will be continuously distributed along the specified path.
- Smoothing Factor: Sets the smoothness of object distribution along the path, value range 1~5. Increasing this value will increase the number of interpolation points, making the trajectory smoother, but also increasing computation time. To ensure performance, it is recommended not to exceed 3.
- Translation: Enter the translation distance along the X/Y/Z axis in the X/Y/Z text boxes respectively, unit is meters.
- Rotation Angle: Enter the counterclockwise rotation angle around the X/Y/Z axis in the X/Y/Z text boxes respectively, unit is degrees.
- Scaling Ratio: Enter the scaling ratio along the X/Y/Z axis in the X/Y/Z text boxes respectively, unit is times.
- Edit Static Model: After selecting the static model to be edited in the scene, you can view and set parameters such as translation, rotation angle, scaling ratio, etc., in the Asset Editing Panel on the right side of the software. After setting, click the Apply button to adjust the feature's effect according to the specified parameters.
-
Save Beautification Result: After setting is completed, click the Save Beautification Result button in the Scene Beautification tab. The instantiated layer where the static model feature is located and the corresponding feature will be saved in the folder with the specified asset name under the specified project path.




