Instructions for Use
Spatial query refers to constructing a filter based on spatial relationships between geometries, querying objects that satisfy the filter from existing data, while supporting setting a query distance for the query objects. It currently supports spatial query functions for points, lines, and regions.
As long as there are non-empty point, line, polygon, text, or CAD datasets in the current map, the Spatial Query function is available.
When the spatial query dialog is open, you can also select search objects in the map.
Function Entry
- Spatial Analysis tab > Query->Spatial Query button.
Operation Instructions
- Set the spatial query type for the layers to be queried.
- Select Spatial Query to query sub-objects of the entire dataset when performing spatial query.
- Select Spatial Attribute Query to query sub-objects of the dataset that meet the Attribute Query Condition when performing spatial query.
- Select the layer to return search results, and set Spatial Query Mode and Attribute Query Condition.
- Spatial Query Mode: Click the drop-down button in the Spatial Query Mode column, and select a spatial query tool supported by the system from the drop-down list. After selecting a spatial query tool, the Tool Description area will illustrate and explain the selected tool. Currently, the application supports eight types of spatial query tools; for details, please refer to Basic Spatial Query Tools.
- Attribute Query Condition: Click the ... command in the Attribute Query Condition column to pop up the SQL Expression dialog, constructing property field query conditions for the layers to be queried. For example, to query cities that a river flows through and have a population greater than 1 million, you can set the population field of the city to >1000000 in the SQL Expression. This item can be left empty, in which case the search result for the corresponding layer will be all objects that meet the spatial query condition. Note: If Spatial Attribute Query is selected in the previous step, the Attribute Query Condition function can be displayed and set.
- Set the query layer.
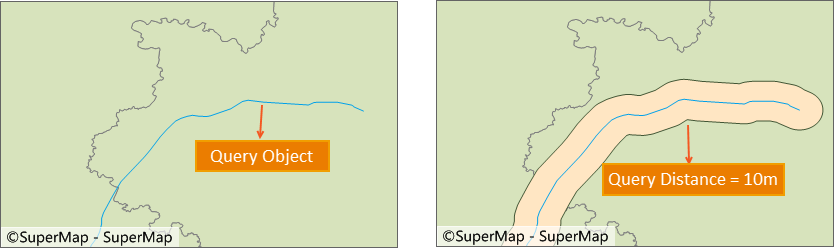
Illustration of setting query distance Note: Some spatial query conditions do not take effect for setting query distance. The table below details whether each query condition supports setting query distance: √ indicates support for setting query distance; × indicates that setting query distance does not take effect; -- indicates an unsupported query tool.
Query Object Queried Object Cross Contain Contained By Overlap Disjoint Adjacent Coincide Intersect Point Point -- √ × -- √ -- × √ Line -- -- × -- √ × -- √ Polygon -- -- √ -- √ × √ √ Line Point -- √ -- -- √ × -- √ Line × √ × × √ × × √ Polygon × -- √ -- √ × -- √ Polygon Point -- √ -- -- √ × -- √ Line -- √ -- -- √ × -- √ Polygon -- √ √ √ √ × × √ - All Objects:
- Perform spatial query only on selected objects: If one or multiple objects of the query layer are selected in the map, the program automatically selects perform spatial query only on selected objects (1 object selected), with the number in parentheses changing based on the count of selected objects. Here, one object is selected as an example.
- Expression:
- Query Distance: Check the Query Distance checkbox to set the query distance and unit. The query object will perform buffer analysis with the specified radius, and then query the area within the buffer range. For example, to query residential areas within 30m of a road, set the query distance to 30m, simplifying the user's conventional operation of first analyzing and then querying.
- Set show results.
- Browse Attribute Table: Check this checkbox to display the query results in the map's attribute window after completing the spatial query.
- Highlight in Map: Check this checkbox to highlight the results in the map.
- Save Results: Check this checkbox to save the search results to a dataset.
Application Example
For road expansion, it is necessary to query residential areas that need to be demolished within 30m on both sides of the road. Select the road to be expanded as the query object, set the residential area polygon dataset as the queried object, set the spatial query condition to Intersect_LinePolygon, set the query distance to 30m. The search result is the polygon objects that intersect within the query range (blue box), as shown in the figure below.
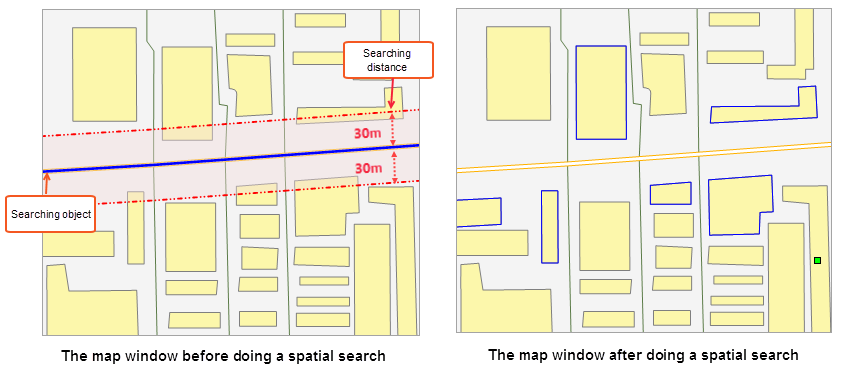 |
Notes
- Supports spatial query on maps with dynamic projection enabled. The query object can be projected onto the target layer for querying, and the coordinate system of the result dataset is consistent with the target layer.
- Spatial query conditions for the searched layer can only be set after selecting a search object; otherwise, a prompt "Please specify a search object" will appear in the output window.
- When performing spatial query on a CAD Dataset (a CAD dataset is a type of CAD that may contain geometries such as points, lines, polygons, etc.), the available tools in the spatial query condition include all tools supported for spatial query between the search object and point, line, or region datasets.
Related Topics



