Update Attributes
Function Description
According to the spatial relationship, update the dataset object attributes. The Update Attributes function provides two operation modes for updating the target dataset: the first is to update the entire dataset; the second is to update by filter expression.
Function Entrance
- Data tab->Data Processing->Vector->Update Attributes, which pops up the Update Attributes dialog box.
- Toolbox->Data Processing->Vector->Update Attributes, which pops up the Update Attributes dialog box.
Parameter Description
- Data with Attributes Offered: Select the source and dataset for data with attributes offered. If a dataset is selected in the workspace manager, it will default to this dataset as the data with attributes offered.
- Target Dataset: Set the target dataset and its source for updating.
- Statistic Field: Select a field to store the count of updated sub-objects. Unupdated sub-objects are assigned 0, while updated sub-objects are counted sequentially as 1, 2, 3...
- Filter Expression: Click the button on the right to set field filters in the popped-up SQL Expression dialog box. Objects in the target dataset that meet the expression conditions will be filtered out during attribute update, and selected fields from the source dataset will not be updated to these object properties.
- Spatial Relationship: Spatial relationship refers to the spatial relationship between the attribute provider geometry and the target geometry, including Contain, Within, and Intersect. The spatial relationship description is as follows:
In the figure below, green represents objects from the attribute provider dataset, red represents targets satisfying the spatial relationship, and black represents targets not satisfying the spatial relationship.
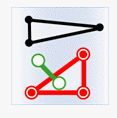
- Contain: The geometry in the attribute provider dataset contains the geometry in the target dataset.
Object Target Point Target Line Target Polygon Attribute Provider Point 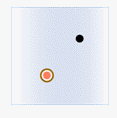


Attribute Provider Line 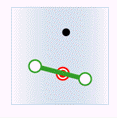
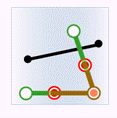

Attribute Provider Polygon 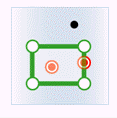
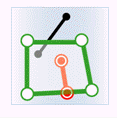
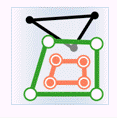
- Within: The geometry in the attribute provider dataset is contained by the geometry in the target dataset.
Object Target Point Target Line Target Polygon Attribute Provider Point 
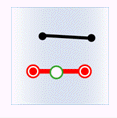
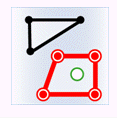
Attribute Provider Line 
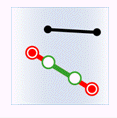
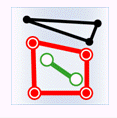
Attribute Provider Polygon 

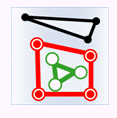
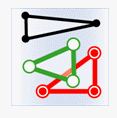
- Intersect: The geometry in the attribute provider dataset intersects with the geometry in the target dataset.
Object Target Point Target Line Target Polygon Attribute Provider Point 
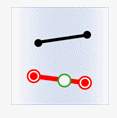
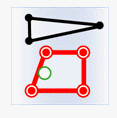
Attribute Provider Line 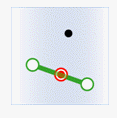
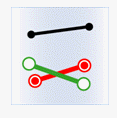
Attribute Provider Polygon 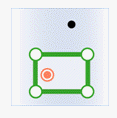
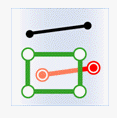
- Contain: The geometry in the attribute provider dataset contains the geometry in the target dataset.
- Boundary Handling: Used to determine whether the boundary of a polygon object belongs to its interior when judging spatial relationships. Can be set to Not Contain Border or Contain Border. This combo box is only activated when judging the containment relationship between polygons and points, or the intersection relationship between polygons and lines.
- Contain Border: Points on the polygon boundary are considered contained by the polygon. When a point on a line coincides with a point on the polygon boundary, it indicates the polygon intersects the line.
- Not Contain Border: Points on the polygon boundary are not considered contained. If a point on a line only coincides with the boundary point but is not inside the polygon, it is not considered an intersection.
- Value Assignment Method: If multiple objects satisfy the conditions and can provide attribute data, the attribute data from the provider objects are processed and assigned to the target using a specific method.
- Assign Value: Randomly take the attribute data of one object for updating. Suitable for one-to-one assignment.
- Average: Take the average value for updating. Valid for numeric fields.
- Sum: Take the sum of all objects' attributes for updating. Valid for numeric fields.
- Maximum: Take the largest value from all object properties for updating. Valid for numeric fields.
- Minimum: Take the smallest value from all object properties for updating. Valid for numeric fields.
- Max SMID: Take the object property value with the largest SmID for updating.
- Min SMID: Take the object property value with the smallest SmID for updating.
- Concatenate: Merge multiple attribute values using a connector and update them to a single target attribute value. Primarily used when multiple attribute values need to be updated to the same field simultaneously, such as counting multiple administrative regions a river flows through. When using this method, the target type only supports text and character types.
- Maximum Intersection Area: If multiple intersecting sub-objects exist in space, take the object property value with the largest intersection area for updating.
- Connector: When the value assignment method is set to concatenate, the connector parameter must be set to separate multiple attribute values, with the default being a comma.
- Field Settings: In the list, check the Provide Attribute Fields to update data. Click the corresponding Target Field once to select it, then click again to set (choose the target field to update to).
 Note:
Note:Supports cross-type storage of update results, reducing secondary processing by users, and allows creating new target fields for attribute updates.
- After updating, the fields in the target dataset attribute table (new or existing fields) will be updated with corresponding field values from the source dataset.
 Note:
Note:- The coordinate system of the data with attributes offered dataset and the target dataset must be consistent; otherwise, the update may fail.
- The default length of character fields is 1. If the target field type is character, modify the field length to an appropriate value before updating; otherwise, the update may fail.
- Provide attribute fields and target fields must correspond one-to-one. If types do not match, conversion is forced during update; if conversion fails, the update for that target field is abandoned.
- Different statistical methods require different statistic fields. For value assignment methods like average, sum, maximum, and minimum, the source field type must be numeric.
Related Topics



