Relation Dataset
A dataset used to store the association relationships between objects in two datasets. This type of dataset can permanently store the relationships between objects in one dataset and objects in another dataset, serving as an advanced management mechanism compatible with both spatial data and non-spatial data.
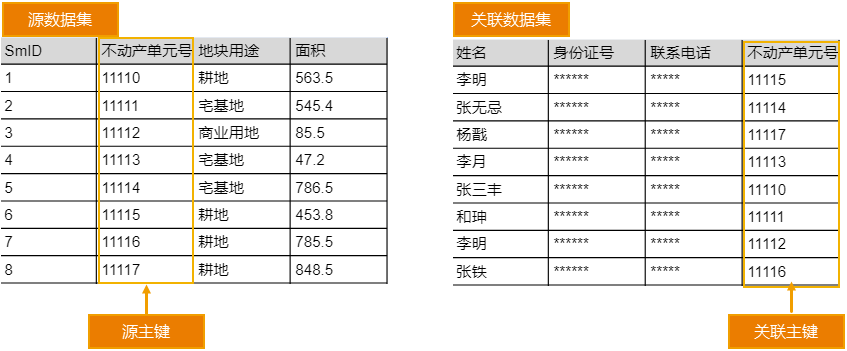
For example, Dataset A stores information about real estate units (parcels) within a certain administrative region (e.g., real estate unit number, land use type, area), while Dataset B stores information about right holders (e.g., name, ID number, contact phone number, real estate unit number). By establishing a relationship between Dataset A and Dataset B based on the key field "Real Estate Unit Number," when browsing or querying a specific parcel in Dataset A, all corresponding information of the right holder for that parcel can be instantly associated and retrieved. When urban planning involves land expropriation or usage adjustment for specific parcels, this relationship can be used to accurately and quickly notify the relevant right holders for communication.
Source Data and Link Data
Source Dataset
The dataset corresponding to the relation.
Source Object
Objects in the source dataset. In the figure below, each row (excluding the header) represents an object.
Relation
The dataset corresponding to the source dataset.
Referenced Object
Objects in the relation. In the figure below, each row (excluding the header) represents an object.

Relationship Attribution
Relationship attribution refers to managing the association between the source dataset and relation objects by introducing a third relationship table. The attributes corresponding to this relationship table are stored in the relation dataset, and the association between objects in the two datasets can be specifically defined by editing its attribute table.
In a non-attributed relation dataset, the source primary key of the source dataset is directly associated with the source foreign key (which is in the relation), without the need for maintenance through the attributes of the relation dataset. This method is typically suitable for one-to-one or one-to-many relational models, where a record in one table can be associated with one or multiple records in another table, but does not support reverse tracing from the associated table back to the source table.
Primary Key and Foreign Key
Source Primary Key
In non-attributed one-to-one and one-to-many relationships, the source primary key is the field in the source dataset associated with the relation. In attributed or many-to-many relationships, the source primary key is the field in the source dataset associated with the relation dataset.
Source Foreign Key
In non-attributed one-to-one and one-to-many relationships, the source foreign key is the field in the relation associated with the source dataset. In attributed or many-to-many relationships, the source foreign key is the field in the relation dataset associated with the source dataset.
Associate Primary Key
In attributed or many-to-many relationships, the associate primary key is the field in the relation associated with the relation dataset.
Associate Foreign Key
In attributed or many-to-many relationships, the associate foreign key is the field in the relation dataset associated with the relation.
 |
| Figure: Non-attributed One-to-One and One-to-Many Relationships |
 |
| Figure: Attributed or Many-to-Many Relationships |
Type of Relationship
SuperMap iDesktopX categorizes the type of relationship in relation datasets into weak correlation and strong correlation.
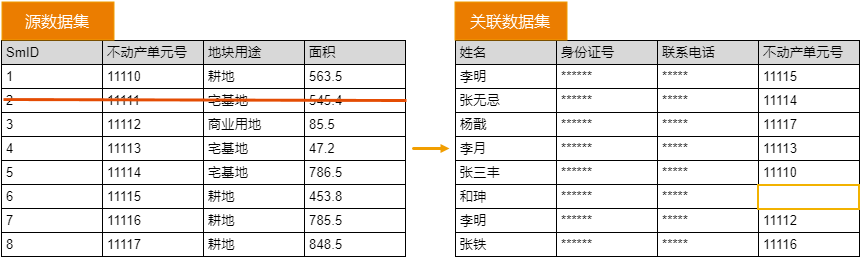
Weak Correlation
In a weak correlation relationship, deleting an object in the source data will set the key field value of the referenced object to null, without deleting the referenced object. This feature is not supported in the current version.
As shown in the figure below, deleting the object with the real estate unit number "11111" in the source dataset will clear the cell with the value "11111" in the real estate unit number column of the relation.
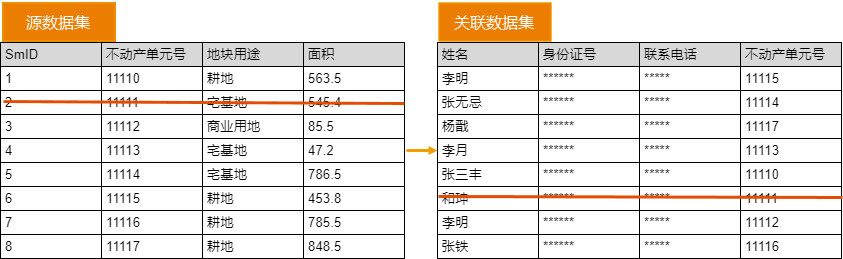
Strong Correlation
In a strong correlation relationship, deleting a source object will simultaneously delete the referenced object. This feature is not supported in the current version.
As shown in the figure below, deleting the object with the real estate unit number "11111" in the source dataset will simultaneously delete the object with the value "11111" in the real estate unit number column of the relation.
Relational Model
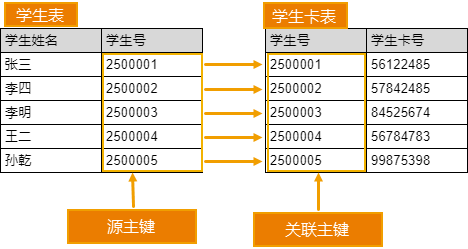
One-to-One
One record in the source dataset can only correspond to one record in the relation, and one record in the relation can only correspond to one record in the source dataset.
As shown in the figure below, in the student table and student card table, one student can only correspond to one student card, and one student card can only correspond to one student.
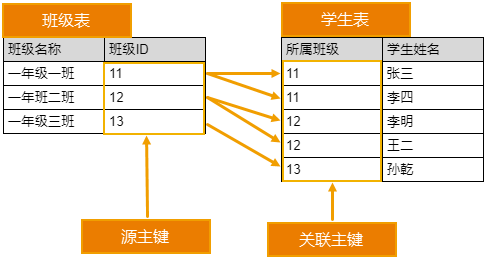
One-to-Many
One record in the source dataset can correspond to multiple records in the relation, but one record in the relation can only correspond to one record in the source dataset.
As shown in the figure below, in the class table and student table, one class can consist of multiple students, but one student can only belong to one class.
Many-to-Many
One record in the source dataset can correspond to multiple records in the relation, and one record in the relation can also correspond to multiple records in the source dataset.
As shown in the course table and student table below, one course can be taken by multiple students, and one student can take multiple courses. Since this association cannot be directly implemented using foreign keys in either table, an association table is typically introduced to store the primary keys of the course table and student table as foreign keys. This association table establishes a mapping between courses and students, thereby achieving a many-to-many relationship.

Relationship Label
Forward Relationship Label
The relationship description displayed when viewing referenced objects through source objects.
Reverse Relationship Label
The relationship description displayed when viewing source objects through referenced objects.
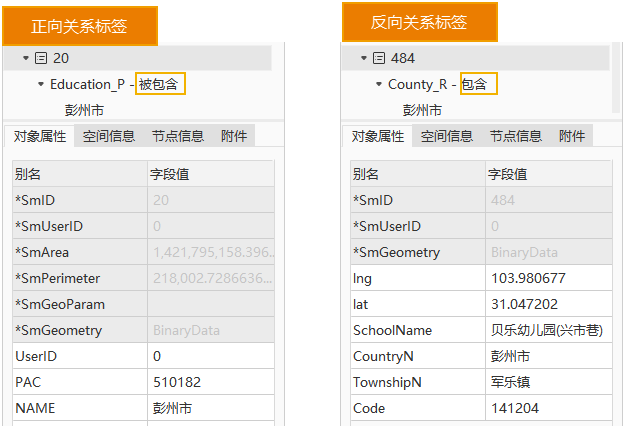
As shown in the figure below, with Country_R as the source data and Education_P as the link data, a relational dataset is created. The forward relationship label is set to "Contained By," indicating that objects in Education_P are contained by objects in Country_R. The reverse relationship label is set to "Contains," indicating that objects in Country_R contain objects in Education_P. When selecting an object in Country_R and viewing its object properties, the Education_P dataset will display "Contained By." Conversely, when selecting an object in Education_P and viewing its object properties, the Country_R dataset will display "Contains."
Related Topics
View Associated Object Properties Information
View Relationship Dataset Properties



