Function Description
The polygon command is used to create a polygon. The polygon mentioned here includes arbitrary polygon, regular polygon, orthogonal polygon, etc. Polygon is one of the most commonly used surface objects, often used to represent closed areal features such as administrative regions, soil, vegetation, lakes, etc. It can also represent some special areal feature types in geography, such as islands, rings, enclaves, etc.
Function Entry
- Features tab->Objects group->Polygon drop-down list->Polygon.
Operation Instructions
Draw Polygon by Inputting Coordinate Values
The process of drawing a polygon is as shown below:
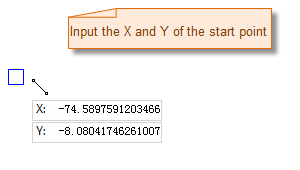 |
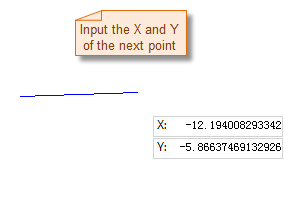 |
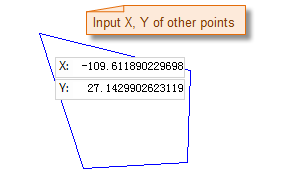 |
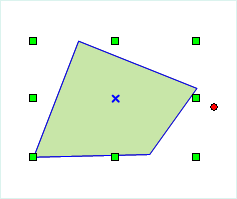 |
The process of drawing a polygon by holding the Q key is as shown below:

Draw Polygon by Length and Angle
- In the Features tab, in the Objects group, click the Polygon drop-down button, and select the Polygon (Length, Angle) option.
- Move the mouse to the map. You can see that as the mouse moves, the coordinate values of the point are displayed in real-time in the parameter box following it. Enter the coordinate values of the first node of the polygon in the box (you can switch between the two parameter input boxes by pressing the Tab key), then press Enter to confirm the starting position of the polygon.
- Move the mouse. You can see that as the mouse moves, the length of the line connecting the mouse position to the previous control point and its angle to the positive X-axis are displayed in real-time in the map. Type the length value and angle value in the parameter input box (you can switch between the two parameter input boxes by pressing the Tab key), then press Enter to execute the input and confirm the drawing of the first segment of the polygon.
- Enter the distance (length) between the next node and the previous node, and the angle of the connecting line to the positive X-axis (you can switch between the two parameter input boxes by pressing the Tab key), then press Enter to draw the next segment of the polygon.
- Repeat the above steps to continue drawing other segments of the polygon.
- Right-click to end the current drawing operation.
Draw Regular Polygon
The drawing process of a regular polygon is as shown below:
 |
 |
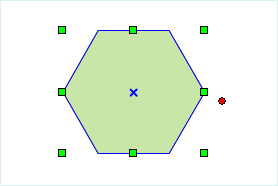 |
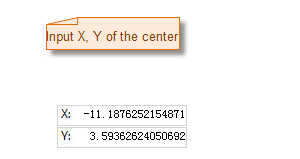
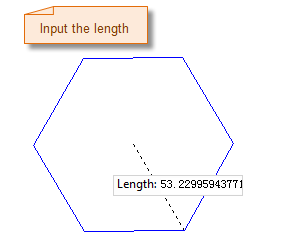
| Specify the center point of the regular polygon | Specify the length and angle of the regular polygon | Result diagram of the regular polygon |
- In the Features tab, in the Objects group, click the Polygon drop-down button, and select the Regular Polygon option.
- The Parameters dialog box pops up. Enter the number of sides for the regular polygon to be drawn in the dialog box. The number of sides must be greater than 3. The default number of sides is 5.
- Move the mouse to the map. You can see that as the mouse moves, the coordinate values of the mouse position are displayed in real-time in the parameter box following it. Enter the coordinate values of the center point of the regular polygon in the box (you can switch between the two parameter input boxes by pressing the Tab key), then press Enter to confirm.
- Move the mouse again, and enter the radius (length) of the circumcircle of the regular polygon and the angle between the circumcircle radius and the horizontal axis in the parameter input box following it, then press Enter to complete the drawing of the regular polygon.
Automatic Face Construction (Drawing Face)
The drawing process of automatic face construction (drawing face) is as shown below:
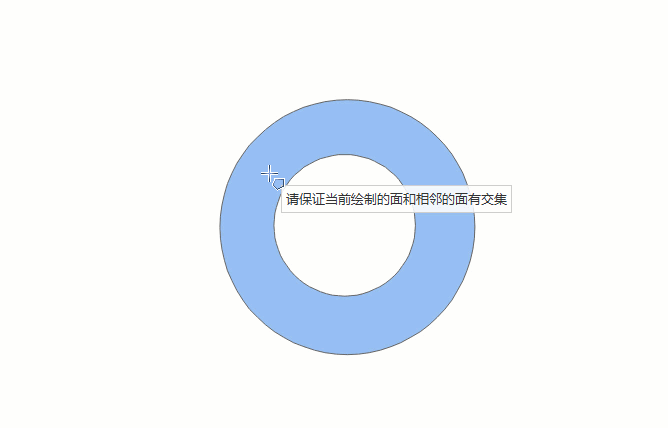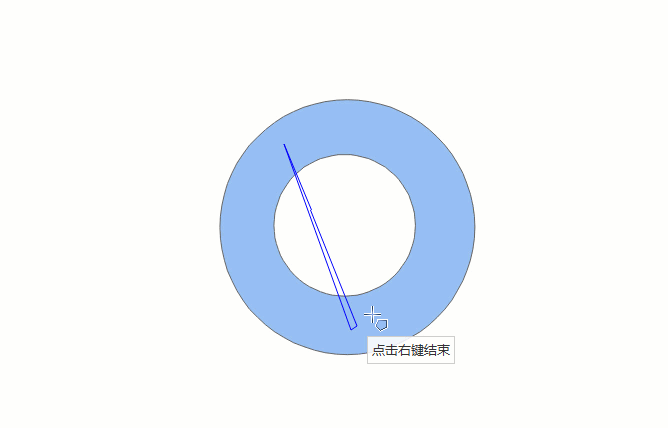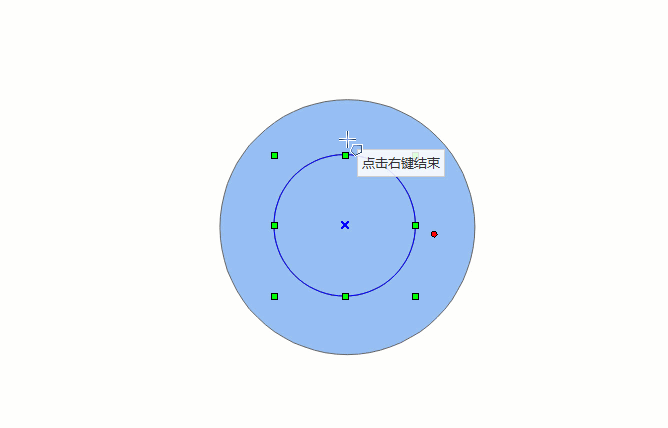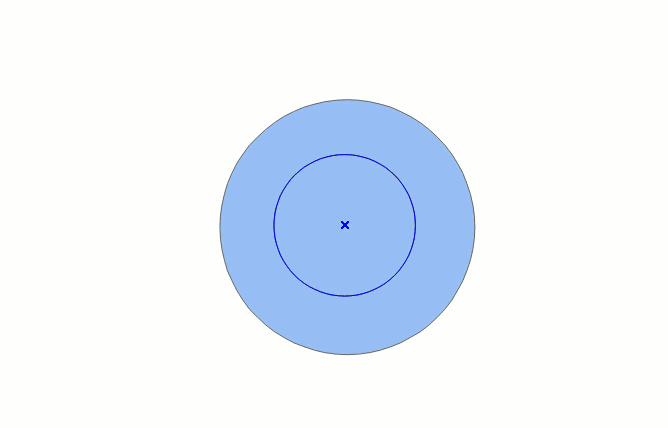
- In the Features tab, in the Objects group, click the Polygon drop-down button, and select the Automatic Face Construction (Drawing Face) option.
- The drawn face intersects with existing face objects, and the enclosed area formed by the face and the common edge is the new face object.
Automatic Face Construction (Drawing Line)
The drawing process of automatic face construction (drawing line) is as shown below:
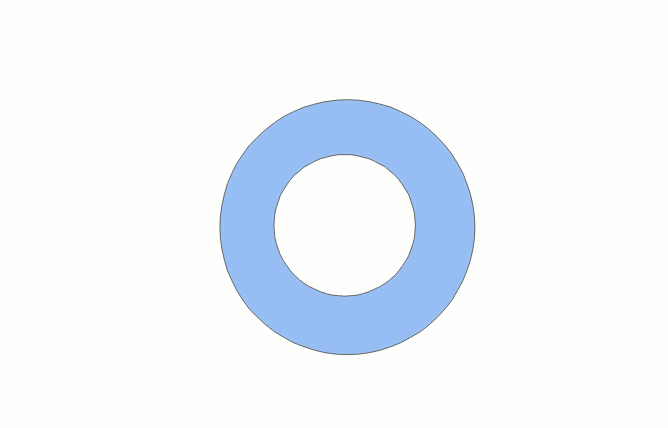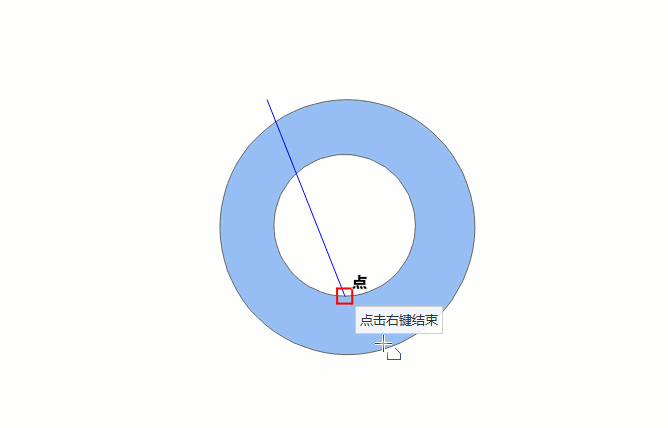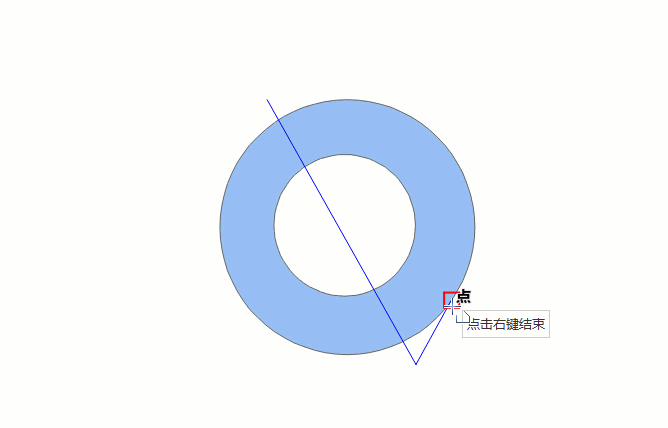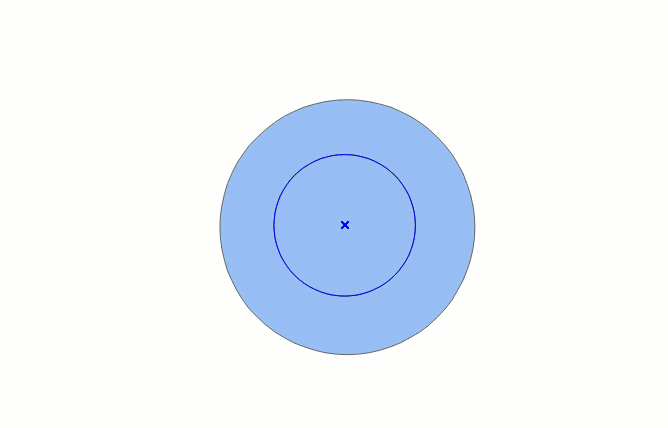
- In the Features tab, in the Objects group, click the Polygon drop-down button, and select the Automatic Face Construction (Drawing Line) option.
- The drawing line intersects an existing region object, and the enclosing area of the line and the common side is the new region object. If the enclosed area formed by the drawn line and the existing face object is located within the original face area, it cannot be drawn successfully.



