Principle
The data is organized and managed by dividing the data into multi-layer grids. The basic method of Dynamic Index is to divide the Dataset into equal or unequal grids according to certain rules, and record the grid position occupied by each geographic object. Regular grid is commonly used in GIS. When the user performs Spatial Query, the grid where the user query object is located is first calculated, and the selected geographic object is quickly queried through the grid. Query operations can be optimized. As shown in the figure:
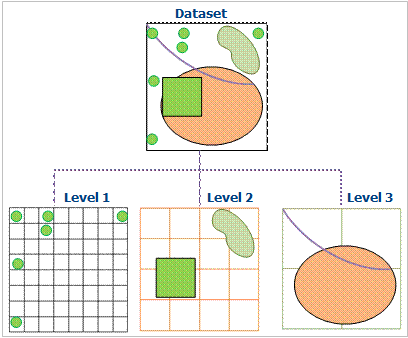 |
| Figure: Diagram of Dynamic Index |
The current version defines the indices of the grid as primary, secondary, and tertiary. Each level has its own division rules. The grid of the first level is the smallest. More than 50% of the data will fall into the grid of the first level. The grids of the second and third levels are correspondingly larger than those of the previous level.
Characteristic
- When the Dataset is being browsed, the Dynamic Index mode is faster;
- Good index update and concurrency capability;
- The spatial retrieval accuracy of the index is high.
Note: This index type supports dynamic concurrent editing of Dataset and Database-type Datasource.
Applicable conditions
Dynamic Index is a new type of index provided by SuperMap in 5.3, which combines the advantages of R-tree index and Q-tree index, provides very good concurrent editing support, and has good universality. Establish the default type for Spatial Index in The current version and later.
If you are not sure which Spatial Index the data applies to, it is recommended to establish a Dynamic Index.
 Remark
Remark
- Engine types that support the establishment of Dynamic Index include SQLPlus and OraclePlus.
- After the establishment of Dynamic Index, users can perform local caching according to the map sheet, which can greatly improve the speed of query and browsing, especially for GB-level data. For data stored by map sheet, such as national Basic Scale topographic map, Dynamic Index can be established according to the size of map sheet.



