Label alongline is used to set whether text is labeled along the direction of line objects. It is widely applied in thematic mapping. For elements such as roads, rivers, contours, and nautical chart routes, label alongline is required for annotation.
The label alongline function can be used when creating uniform style or graduated color style label thematic maps. It is located in the Advanced tab of the Label Thematic Map window. This function is only effective for 2D line layers, route layers, and network layers.
The parameters involved in setting label alongline and their functions are detailed below.
Operation Steps
- Set Label Expression
Label expression is used to specify the display content of labels in thematic maps. It is located in the Properties tab of the Uniform Label Thematic Map window.
In the drop-down list to the right of label expression, all attribute fields of the dataset used for the current label thematic map are listed. You can select an appropriate property field as needed. When creating a new label thematic map, the system will select a matching field to generate thematic maps based on the property field name.
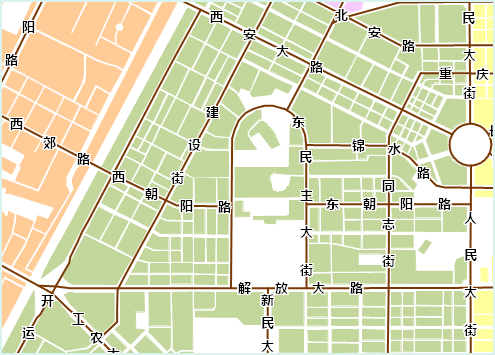
Figure: Displaying a Single Field Additionally, you can select "Expression..." in the drop-down list to the right of label expression to enter the "SQL Expression" dialog and customize the display content of labels.
If you want to display multiple fields simultaneously, use "Field Expression1 [/] Field Expression2 [/] Field Expression3 [/] ..." to set it. The fields are displayed in fractional form, where [/] serves as a whole symbol for displaying multiple fields together, and the [ ] symbols cannot be omitted. As shown in the figure below, when displaying multiple fields (expression: Name [/] Pop_Density99), the label alongline function is unavailable.
Figure: Displaying Multiple Fields - Set Label Alignment
Label alignment is used to set the placement position of text in label thematic maps. Starting from the anchor point of the text, the placement is determined by changing the relative position of the text object's anchor point to the labeled object to achieve alignment. Alignment is located in the Style tab of the Uniform Label Thematic Map window.
In the combo box drop-down list to the right of alignment, 12 types of alignment are listed, including 9 alignments and 3 baseline alignments. For detailed explanations of alignment, please refer to Text Alignment Explanation.
- Label Alongline Display Direction
Used to set the direction of text label alongline in labels. It is located in the Advanced tab of the Uniform Label Thematic Map window. The system provides 5 display methods (see the table below for details).
The system first determines whether the line direction is horizontal or vertical (criterion: connect the start and end points of the line object; if the angle between the connecting line and the horizontal direction is less than 60 degrees, the line direction is considered horizontal; otherwise, it is vertical). For horizontally oriented lines, labeling follows the left-to-right or right-to-left settings in the options, and top-to-bottom or bottom-to-top settings are ignored. Conversely, for vertically oriented lines, labeling follows the top-to-bottom or bottom-to-top settings, and left-to-right or right-to-left settings are ignored.
Alongline Display Direction Description along the normal of the line Labels are placed from top to bottom or left to right based on the direction of the line object. top to bottom, left to right Labels are placed from top to bottom or left to right based on the direction of the line at the label position. top to bottom, right to left Labels are placed from top to bottom or right to left based on the direction of the line at the label position. bottom to top, left to right Labels are placed from bottom to top or left to right based on the direction of the line at the label position. bottom to top, right to left Labels are placed from bottom to top or right to left based on the direction of the line at the label position. The labeling behavior patterns are shown in the table below:
Display Direction Left to Right Right to Left Top to Bottom Bottom to Top Illustration 



Additionally, the starting position of the label is related to its alignment. For how to choose an appropriate alignment, please refer to Text Alignment Explanation.
- Set Label Offset
Users can adjust the position of labels by setting offset settings. "Offset settings" is located in the Properties tab of the Uniform Label Thematic Map window.
For labels using the label alongline method, the offset is along the normal direction of the expressed object. The offset amount is controlled by the "Offset X" parameter, and "Offset Y" has no effect.
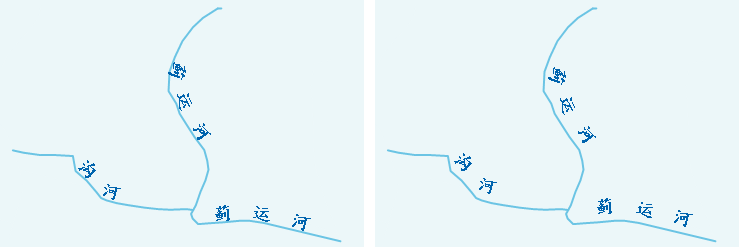
Figure: Setting Label Alongline Offset - Set Repeated Labeling
When line objects are too long, users can control the number of labels displayed on line objects using "Alongline Period Spacing" and "Fix Repeat Interval" to make thematic maps more intuitive. This function is located in the Advanced tab of the Uniform Label Thematic Map window.
Set the distance between two labels (i.e., from the start of the previous label text to the start of the next label text) in the text box to the right of "Alongline Period Spacing" to control the number of labels on the line object. This function only takes effect when "Fix Repeat Interval" is checked.
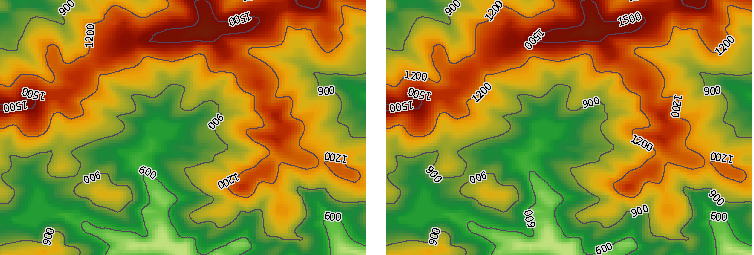
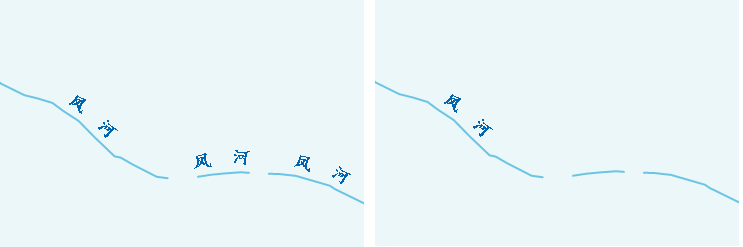
"Remove Duplicate Labels" is used to control the duplicate display function of compound labels. Users can use this function to control the display method of labels for line objects with multiple sub-objects. When the "Remove Duplicate Labels" checkbox is not checked, every sub-object within the line object is labeled. When checked, only sub-objects with larger lengths within the visible range are labeled. It is checked by default in the system.
As shown in the figure below, the left image shows the display effects without "Remove Duplicate Labels" checked. The line object contains three sub-objects, each labeled. The right image shows the display effects with "Remove Duplicate Labels" checked. After obtaining the length of each sub-object within the visible range, the system labels the sub-object with the larger length (i.e., the left sub-object), and does not label the others.