Buffer analysis (Buffer) is one of the fundamental spatial operations in GIS, which automatically builds a buffer zone around specified points, lines, or polygons according to given distances. For example, in environmental management, a certain width around polluted rivers is often delineated to represent contaminated areas; at airports, specific zones around the facility are typically designated as non-residential areas based on health requirements, etc.
Users can use the "Buffer" button or "Multiple Ring Buffer" button in the application to generate buffers of specified distances for one or multiple geometries.
Buffer analysis supports creating buffer zones for point datasets, line datasets, and region datasets. It can create buffer zones for all objects in an entire dataset or only for selected objects.
Single Buffer
| Type | Diagram | Description |
| Point Buffer Analysis | 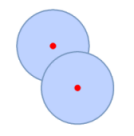 |
Creates buffers for point objects. For example, creating buffers for two radio transmitters can help analyze the coverage areas of their signals and overlapping coverage zones. |
| Line Buffer Analysis |  |
Creates buffers for line objects. For example, creating 20-meter buffers for adjacent streets scheduled for expansion can help identify buildings requiring demolition through combined queries. |
| Polygon Buffer Analysis | 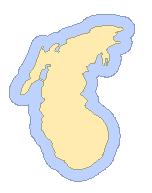 |
Creates buffers for polygon objects. For example, generating buffers around rivers or lakes helps analyze areas most prone to flooding. |
Multiple Ring Buffer
| Type | Diagram | Description |
| Point Multi-buffer Analysis | 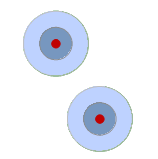 |
Creates multiple ring buffers for point objects. For example, analyzing the spread of pollution from a source at varying distances. |
| Line Multi-buffer Analysis | 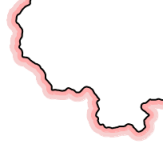 |
Creates multiple ring buffers for line objects. For example, generating unidirectional multiple buffers along national boundaries to create hachure effects. |
| Polygon Multi-buffer Analysis | 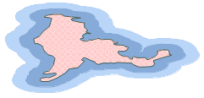 |
Creates multiple ring buffers for polygon objects. For example, performing 20 km and 50 km buffer analyses on a desert helps study sandstorm expansion patterns, providing references for desertification control. |
Related Topics



