FME (Feature Manipulate Engine, abbreviated as FME)As a powerful spatial data conversion and processing system, it integrates over 320 spatial and non spatial data formats and contains rich data processing converters. SuperMap iDesktopX utilizes the flexible extension capability of processing automation to dock with FME, supporting the addition of FME Workbench workspaces (. fmw) to the toolbox, and connecting them with other tools in modeling to easily solve the problem of spatial data conversion.
Usage scenario
Conversion of CAD and GIS data: For example, the integration of real estate data, and the complex CAD graphic layers drawn in real estate field, FME tools can be used to achieve non-destructive conversion of the required data.
Data quality inspection: For example, in the processing of internal data in the three adjustments, FME tools can be used to check node density, irregular graphics, linear terrain width, adjacent patch attributes consistency but not merging, and attribute logic.
Instructions
- Set the installation path for FME-Desktop: Firstly, it is necessary to ensure that FME-Desktop is installed on this machine and relevant licenses are obtained (it is recommended to use versions 2020.2.5.1-b20828 and above, and only support 64-bit versions). There are two ways to set the FME installation path:
Set the FME-Desktop installation directory to the system variable path, and restart SuperMap iDesktopX;
In the FME group right-click menu of the SuperMap iDesktopX toolbox, set the FME-Desktop installation path for this machine. This method requires resetting the path every time the desktop is restarted in order to use the FME tool.
If 'Add FME Tool' is available in the right-click menu, it indicates that the path has been successfully set.
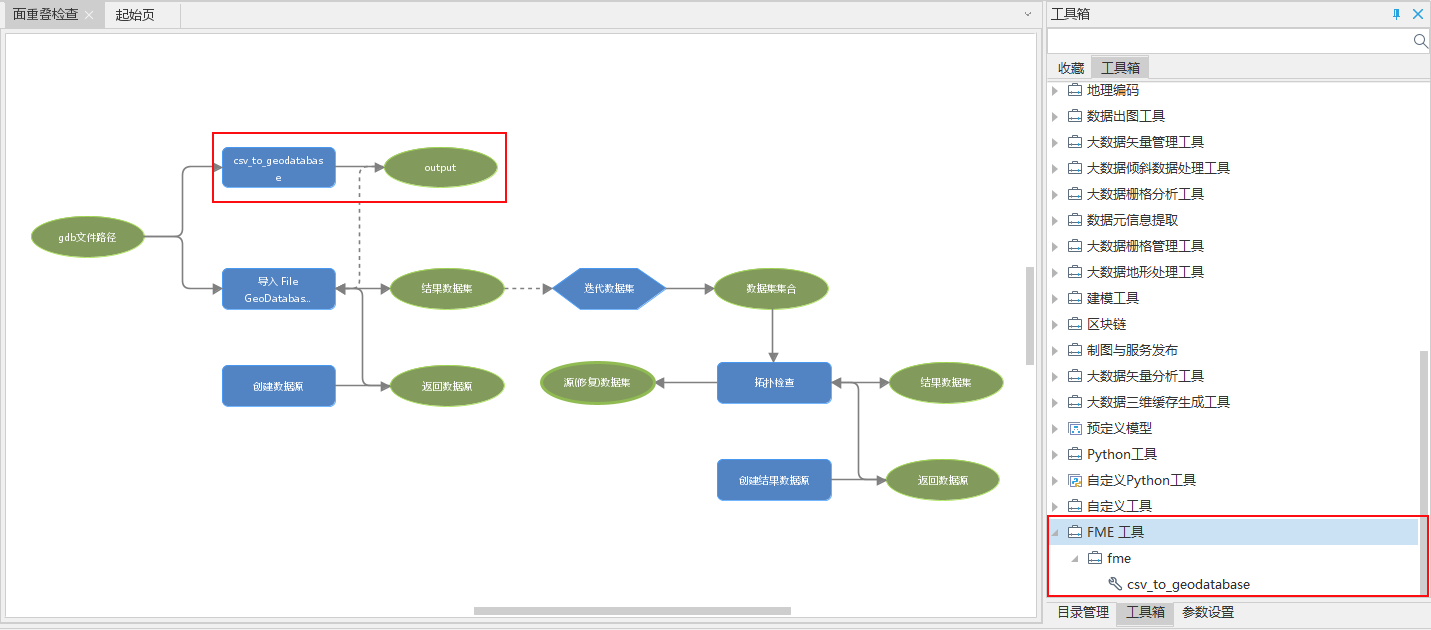
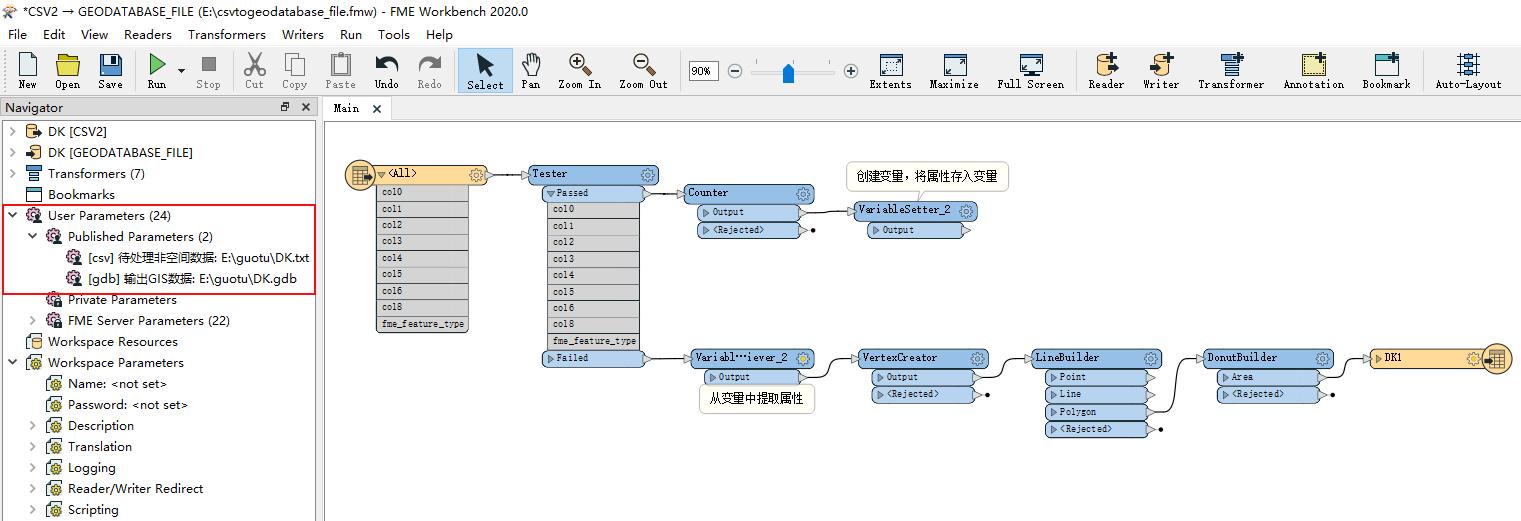
Create FME tools: Create data conversion processes and parameters that need to be published through the FME Workbench, facilitating tool connection and parameter filling in process automation modeling. After building the process of converting CSV data to GDB data as shown in the figure below, set the published parameters to "Import CSV Data Path" and "Export GDB Data Path". Finally, save the created workflow as a workspace (. fmw). It should be noted that at present, the docking FME tool only supports the English name and path. It is recommended that the published Parameter Name and the saved path and name of the workspace be in English.
Add/Remove FME Tools: In the FME group right-click menu, select Add/Remove FME Tools to add or remove tools from the toolbox. After adding the FME tool to the toolbox, the output values are all boolean values, with true indicating success and false indicating failure.
Using FME tools: Drag and drop the added tools onto the canvas to connect with other tools for use in modeling. In the overlap check model, the land surface data is a specific CSV format in the business, and existing tools cannot achieve data reading. Therefore, the added FME tools can be used to convert CSV data into GDB data. Firstly, drag the added "csv_to_geodatabase" tool onto the canvas, and since the output is a boolean value, connect the "Import File GeoDatabase Vector folder" as a prerequisite. Next, create a string type variable to store the file path, store the conversion results in the variable, and then connect the variable to the "Import File GeoDatabase Vector folder" to import the converted GDB file into the data source. Finally, iterate and expand the dataset.