In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology has profoundly impacted our daily lives and work. From machine translation to speech/image recognition and autonomous driving, the scope of AI applications continues to expand. Simultaneously recognized as a groundbreaking innovation comparable to computers and the internet, AI brings intelligent and transformative changes to socio-economic development. It has become a focal point of contemporary research, a crucial objective for IT enterprises, and a new arena for international competition. AI is gradually being applied in spatial information domains, significantly influencing GIS technological development and emerging as a key driver for future GIS advancements.
The impact of AI on GIS spans multiple dimensions. At the data level, the geospatial industry handles massive spatial datasets where AI technologies—particularly deep learning—enhance automation and accuracy in data processing, improving database construction and update efficiency. Technologically, AI-GIS integration significantly strengthens intelligent perception and analysis capabilities of spatial information, providing novel solutions for previously intractable problems. In industrial applications, AI technology combines with domain knowledge to enable automated and intelligent GIS solutions. Current technological developments demonstrate AI's enhancement of GIS capabilities in multiple directions: remote sensing image processing, spatial data processing, spatiotemporal prediction, trajectory analysis, spatial optimization, urban planning, geocoding, and new spatial analysis model development.
Machine Learning (ML), as an interdisciplinary field, focuses on enabling computer systems to simulate human learning behaviors—acquiring new knowledge/skills and reorganizing existing knowledge structures to continuously improve performance. As the core technology of contemporary AI, Machine Learning has seen rapid development in Deep Learning (DL), which constructs abstract high-level features through hierarchical combination of low-level features, enabling profound understanding of data patterns.
The relationship between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning is illustrated below:
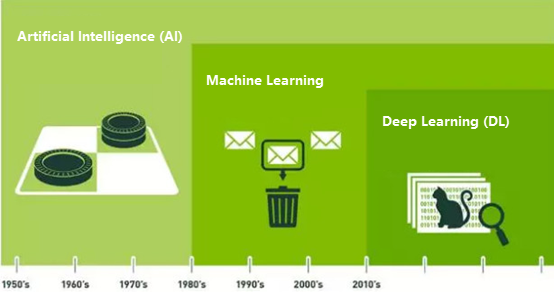
Artificial Intelligence represents machine-endowed human-like intelligence; Machine Learning serves as the implementation approach for AI; Deep Learning constitutes a specific Machine Learning technique. Thus, AI is the ultimate objective, Machine Learning provides the methodology, artificial neural networks represent an algorithmic approach within ML, and Deep Learning constitutes a specialized neural network technique. Deep Learning enables numerous Machine Learning applications and expands AI's capabilities.
In AI GIS, the integration of AI spatial analysis and processing models forms a crucial component of SuperMap's capabilities. Based on statistical foundations and rich spatial statistical operators, SuperMap incorporates Machine Learning and deep learning theories/algorithms to address geospatial challenges. It develops various AI GIS functions for spatial data processing, analysis, mining, and comprehensive modeling.
SuperMap integrates Machine Learning and Deep Learning technologies to deliver Imagery Analysis and Image Analysis functionalities. Imagery Analysis includes Model Training, Object Detection, Binary Classification, Multi-class Classification, and Scene Classification. Image Analysis encompasses Model Training and Image Classification.
This section includes the following:



