Feature Description
Under biased sampling conditions, this method calculates association coefficients between every two samples using existing data or covariates (i.e., ratios between samples and population, or between sample means and population means) to achieve unbiased estimation of population means from biased samples.
(Biased sampling: In statistical research, parameter estimation relies on samples drawn from a population. If samples are randomly selected (e.g., lottery-style), the estimated parameters accurately reflect population characteristics and are theoretically unbiased. However, most real-world sampling occurs within researcher-defined scopes and rules, leading to potential selection bias. Non-random samples may result in biased parameter estimates that fail to represent true population distributions.)
When sufficient historical data or prior information exists to measure each sample's ratio relative to the target population (total or mean), and when covariance between paired samples within the population can be calculated, this model significantly improves estimation accuracy. The B-Shade model leverages geospatial horizontal correlations and vertical correlations between samples and regional populations, widely applied in biased-sample statistical inference. Even with biased samples, it delivers unbiased optimal estimates for regional populations.
Feature Entry
- Spatial Statistics Tab -> Spatial Sampling and Statistical Inference -> Bshade Sampling.
- Toolbox->Spatial Statistics->Spatial Sampling and Statistical Inference-> Bshade Sampling.
Parameter Description
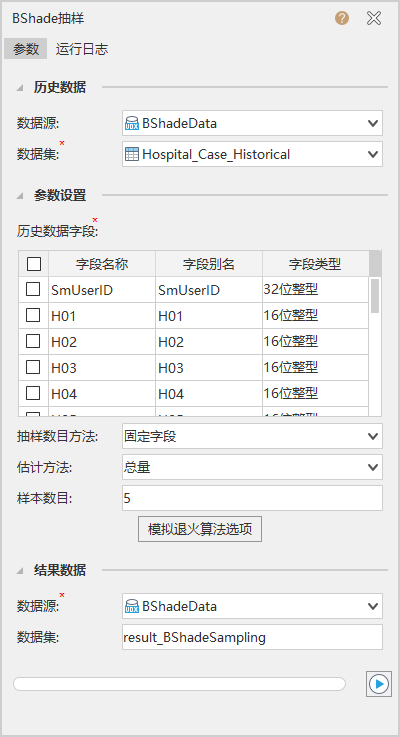
Historical data fields: Select specified fields from the historical dataset. In the case below, 19 fields representing last year's data from hospitals are selected.
Sampling quantity method: Choose between fixed field or extent field.
Estimation method: BShade estimation method. Total method (sample-to-population ratio) or mean method (sample mean-to-population mean ratio).
Sample quantity: Number of samples to extract.
Simulated Annealing Algorithm Options: A general optimization algorithm inspired by physical annealing processes. Starts at high initial temperature, combines probabilistic state transitions with gradual cooling to find global optima, escaping local optima with controlled probability. Parameters include initial temperature, minimum temperature, minimum energy, annealing rate, maximum rejections/attempts/successes, and maximum combinations (default values provided).
- Historical Data: Specified historical dataset and its datasource. In the case below, this represents last year's disease incidence data from 19 hospitals.
- Parameters:
- Fixed field: Selects a fixed number of samples with minimal estimation variance. In the case below, sample quantity is set to 5, indicating 5 hospitals with minimal estimation differences are selected as optimal samples.
- Extent field: Generates all possible sample selections and corresponding estimation variances based on upper/lower limits and step size. Allows balancing between minimal sample size (cost reduction) and minimal estimation variance (higher accuracy).
- Result Data: Set result dataset and its datasource.
- Click the "Execute" button to run the analysis. Upon completion, the output window will indicate success or failure.
Application Case
A region requires daily disease incidence rates for a specific month. Collecting data from all hospitals is time-consuming. Using last year's data from 19 hospitals as reference, Bshade Sampling selects 5 hospitals with minimal estimation variance. Their current-year incidence data is then used for predictive analysis.
- Case data: Download Bshade Sampling case data (requires extraction). Key dataset: Hospital_Case_Historical (historical incidence data from regional hospitals).
- Parameters: Open BShadeData.udbx and configure parameters as shown below. This case uses extent field sampling to generate multiple sample groups based on upper/lower limits and step size.
- Result interpretation: Extent field analysis produces multiple sample groups. The final selection (5 hospitals) is used for BShade Prediction. Result data visualization:



