Basic Concept of Geographic Information System
GIS (Geographic Information System) is a system composed of computer software, hardware and different methods. The system is designed to support spatial Data Collection, management, processing, analysis, modeling and display. So as to address complex planning and management issues. The main difference between GIS and other information is that the information stored and processed by GIS is processed by Geocoding. Geographical location and Attributes related to the location become an important part of information retrieval. In GIS, the real world is represented as a series of geographical features and phenomena, which are composed of at least two parts: spatial Position Info and non-spatial Position Info.
A complete GIS is mainly composed of four parts: computer hardware system, computer software system, geographic data, system manager and operator. Its core part is the computer system. Spatial Data reflects the geographic content of GIS, while the manager and user decide the working mode and information expression mode of the system.
Basic functions of GIS
- Data Collection and Input: In the Data Processing system, the Source Data outside the system is transferred to the inside of the system, and the data is converted from the external format to the internal format that is convenient for the system to process.
- Edit Data and Update: Edit Data mainly includes graphic editing and attribute editing. Graphic editing mainly includes Topology creation, graphic editing, graphic decoration, map splicing, graphic transformation, projection transformation, error correction and other functions. Property editing is done primarily with Database Management. Data Update is to replace the corresponding data item or record in the data file or database with a new data item or record, which is realized by a series of operations such as deletion, modification and insertion.
- Data Save and Management: Spatial Data storage is the lowest and most basic technology in GIS. It directly affects the implementation efficiency of other high-level functions, thus affecting the performance of the entire GIS. Attribute Data Management can be managed by GIS software or commercial database software directly. Spatial Data Management is the core of GIS Data Management. All kinds of graphics or image information are stored in Spatial Data Database with strict logical structure.
- Spatial Query and Analysis: Spatial Query and analysis is the core of GIS, which mainly includes three aspects: data operation, data query and retrieval, and comprehensive data analysis. Through the Spatial Analysis function provided by GIS, users can draw important conclusions implicitly from the known Spatial Data, which is crucial for many application fields.
- Data display and output: It is the last process of GIS problem solving process to output the results of user query or data analysis in an appropriate form. Output format is usually of two types: display on a computer screen or output through a plotter. The technology in this aspect mainly includes: editing, graphic decoration, symbol making, picture legend generation, publishing and printing, etc.
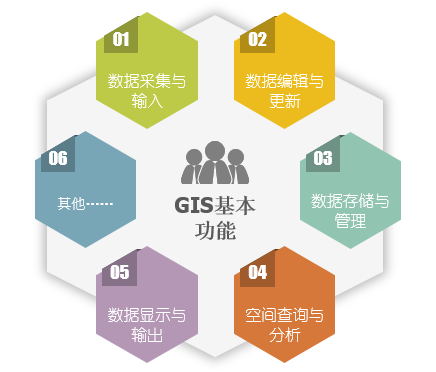 |
| Figure: Basic functions of GIS |
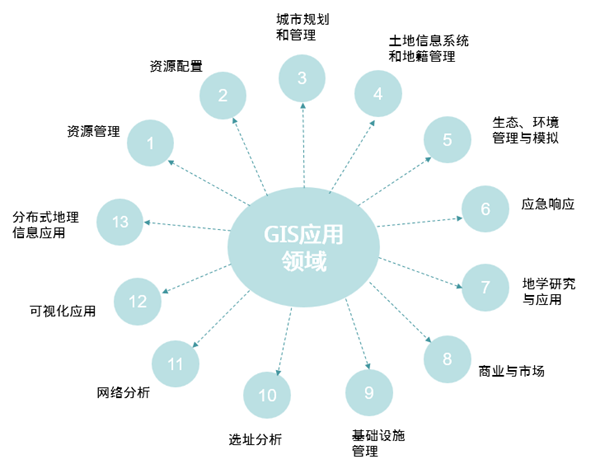
Application fields of GIS
Geographic Information System (GIS) has made great progress in recent years. It is mainly used in almost all fields, such as resource survey, environmental assessment, disaster prediction, land management, urban planning, communication, transportation, military public security, water conservancy and hydropower, public facility management, agriculture, forestry and animal husbandry, statistics, business and finance, etc.
- Resource management: It is mainly used in the field of agriculture and forestry to solve the problems of distribution, classification, statistics and mapping of various resources (such as land, forest, grassland, crops, etc.) in the field of agriculture and forestry.
- Resource allocation: Various public facilities in the city, material allocation in disaster relief and mitigation, energy security in the National Area, food supply and so on are all resource allocation issues. The goal of GIS in such applications is to ensure the most rational allocation of resources and maximize benefits. For example, in urban construction planning, how to ensure that schools, public facilities, sports venues, service facilities and so on can have the largest service coverage.
- Urban planning and management: Spatial planning is an important application field of GIS, and urban planning and management is the main content. For example, in large-scale urban infrastructure construction, how to ensure the proportion and rational distribution of green space.
- Land Information System and Cadastral Management: Land and cadastral management involves many contents, such as the change of land use nature, the change of plot outline, the change of cadastral ownership relationship, etc. With the help of GIS technology, these tasks can be completed efficiently and with high quality.
- Ecological and environmental management and simulation: regional ecological planning, environmental status assessment, environmental impact assessment, decision support for pollutant reduction and distribution, decision support for environment and regional sustainable development, management of environmental protection facilities, environmental planning, etc.
- Emergency response: to solve the problem of how to arrange the best evacuation route and equip the corresponding transportation and support facilities in the event of major natural or man-made disasters such as floods, wars and nuclear accidents.
- Geoscience Research and Application: Terrain analysis, watershed analysis, Land Use research, economic geography research, spatial decision support, Spatial Statistical Analysis, mapping, etc. Can be completed with the help of GIS tools.
- Business and market: The establishment of business facilities takes full account of its market potential. For example, if the establishment of large shopping malls does not take into account the distribution of other shopping malls, the distribution of residential areas around the area to be built and the number of people, it may not be able to achieve the expected market and service after completion. Sometimes even the variety and market positioning of shopping malls must be considered in combination with the population structure (age composition, gender composition, cultural level) and consumption level of the area to be built. The Spatial Analysis and database functions of GIS can solve these problems. In the process of real estate development and sales, GIS functions can also be used for decision-making and analysis.
- Infrastructure management: The ground and underground infrastructure of the city (telecommunications, tap water, road traffic, natural gas pipelines, sewage facilities, power facilities, etc.) are widely distributed in every corner of the city, and these facilities have obvious geographical reference characteristics. Their management, statistics and summary can be completed with the help of GIS, and the work efficiency can be greatly improved.
- Site selection analysis: According to the characteristics of regional geographical environment, comprehensively consider the factors such as resource allocation, market potential, traffic conditions, topographic features and environmental impact, and select the best location within the region. It is a typical application field of GIS, which fully reflects the Spatial Analysis function of GIS.
- Network Analysis: Establish the computer model of traffic network, Underground Pipelines network, etc., study the traffic flow, carry out Traffic Rules, deal with Underground Pipelines emergencies (pipe burst, circuit break) and other emergency treatment. Path optimization and vehicle navigation for police and medical rescue are also examples of GIS Network Analysis applications.
- Visualization application: Based on the digital terrain model, the three-dimensional visualization model of urban areas or large-scale construction projects and famous scenic spots is established to realize multi-angle browsing, which can be widely used in publicity, urban and regional planning, large-scale Project Management and simulation, tourism and other fields.
- Distributed geographic information application: With the development of network and Internet technology, the application type of geographic information system running in Intranet or Internet environment aims to realize distributed storage and information sharing of geographic information, as well as remote spatial navigation.