Overview
Location selection is a prerequisite for the success of a commercial or non-commercial establishment. Location-Allocation refers to the selection of the best or optimal location for one or more service facilities in a certain area, so that the facilities can provide services or goods to the demanders in the most economical and effective way. Location-Allocation is not only a location problem, but also needs to allocate the demand of the demand point to the corresponding facility service area.
Application example
- Retailers need to receive goods from different manufacturers every day to open new chain stores, and a large part of their budget is spent on transporting goods. Therefore, retailers need to consider the location of the original chain stores when choosing the location of the new chain stores, and at the same time ensure that the total transportation cost of all chain stores is the lowest. From the consumer's point of view, chain stores must be built within the Max Distance they are willing to travel. Based on the comprehensive consideration of the above factors, how many new chain stores should be opened and where should they be built.
- During the epidemic period, a large number of nucleic acid sampling points are needed. In order to facilitate citizens to receive nucleic acid testing nearby, it is necessary to build a 15-minute nucleic acid service circle based on Service Radius. For example, 240 nucleic acid sampling points need to be set up in a certain area, and the 15-minute service circle of all sampling points is required to cover the whole area. The existing communities, parks and other POIs can be used as the central points, and 240 expected central points can be set for analysis, so as to obtain the nucleic acid sampling sites.
Important Concepts Involved in Location-Allocation
- Location-Allocation Type
Least Center Mode: Analyst Result is required to allocate as many request points as possible to the resource supply center point within the maximum resistance range. This model is used in many areas, such as the problem of supermarket location, for example, retailers want to reduce the number of new supermarket chains, and when determining the route of school buses, the number of bus stops should be as small as possible. Analyst Result is required to meet the requirement of allocating as many request points as possible to the resource supply center point within the maximum resistance range.
Maximum Coverage Mode: Non-Least Center Mode. According to the set Analysis Parameters, the number of new addressing points is determined by the user. However, as many resource centers as possible should be allocated to the corresponding resource supply centers. This mode is applicable to the site selection of fire stations, police stations, hospitals and other service facilities.
- Resource supply center point: The resource supply center point is the facility point that provides resources and services, and corresponds to the network node. Each facility point has information such as the maximum resistance value, the Center Type, and the ID of the node where the center point is located in the network.
Maximum resistance value: It is used to limit the cost of the resource supply center. If the cost of the demand point to the resource supply center is greater than maximum resistance value, the demand point will be filtered out, that is, the resource supply center cannot serve the demand point.
Center Type: There are three types: Fix Center, Center, and Non-Center. Fix Center refers to the original and established service provision point, for example, the existing old chain store in the application case is Fix Center; Center refers to the candidate service provision point to be added, for example, the candidate position of the new chain store in the application case; Non-center is not considered in the analysis, and in practical problems, it is not allowed to establish service facilities or locations where other equipment and facilities already exist.
Resource Allocation Direction: When solving the location problem, it is necessary to consider the allocation direction of the resource center. There are two directions, Allocate from Center or not Allocate from Center.
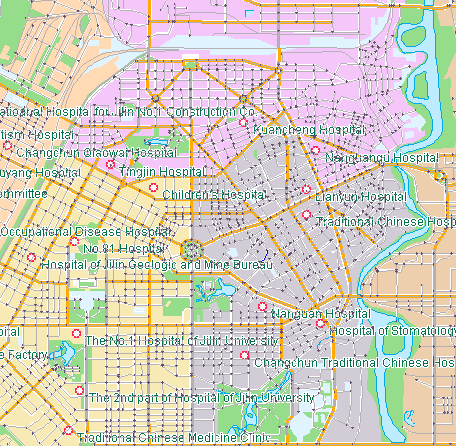
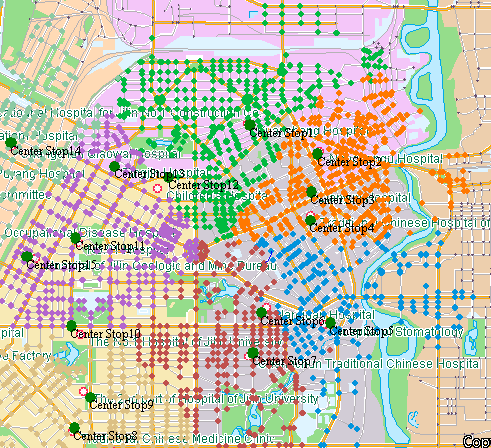
Example: There are 15 hospitals in a city, and the distribution is shown in the figure below. Now we want to choose 7 hospitals from these 15 hospitals as the centralized physical examination hospitals for the college entrance examination in the whole city, requiring as many areas as possible to facilitate the physical examination of candidates in each district. The 15 candidate hospitals (as shown in the left figure, the red symbols represent the 15 candidate hospitals) will select 7 best locations from these candidate hospitals as the physical examination hospitals. The physical examination hospital shall meet the following requirements: the time for the examinee to walk or take a bus to the physical examination hospital shall be controlled within 30 minutes. The Location-Allocation analysis will give the best location according to this condition, and circle the service area of each hospital (as shown in the right figure, the dots of different colors represent the best locations of the seven selected physical examination hospitals).
| 
|
| Schematic of Centre Point | Schematic diagram of the best Location-Allocation result |



