Hydrological Analysis
Water is closely related to human life, so it is of great significance to study the origin, distribution, existence and movement of water. Hydrological Analysis is based on the Elevation Model (DEM) to establish the water system model, which is used to study the hydrological characteristics of the basin, simulate the surface hydrological process, and estimate the future surface hydrological conditions. Hydrological Analysis can help us analyze the scope of the flood, locate the source of surface runoff pollution, and predict the impact of landform changes on runoff. It is widely used in regional planning, agriculture and forestry, disaster prediction, Road Design and other industries and fields.
Basic concepts
When doing Hydrological Analysis based on dem grid, it is of great significance to understand the concepts related to watershed for the correct understanding and application of Hydrological Analysis. Use the following figure to help you understand the relevant concepts.
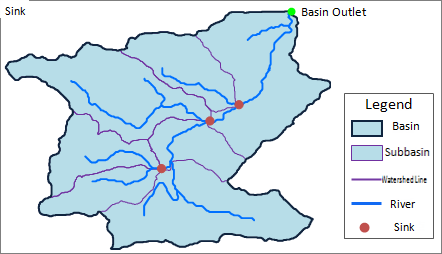 |
| Figure: Watershed Diagram |
Water system: refers to the water network system composed of water bodies with the same destination in a river basin. The water system is dominated by rivers, and can also include lakes, swamps, reservoirs and so on.
Drainage Basin: Each water system receives water supply from a part of the land area, which is the drainage basin of the water system, also known as the catchment area or drainage basin.
Sub-basin: The river system is composed of several river sections, each of which has its own basin, called a sub-basin. Larger basins can often be further divided into sub-basins.
Watershed: Also called watershed. An irregular curve formed by connecting the highest points of two adjacent drainage basins is the watershed line of two water systems. The water on both sides of the watershed flows into different watersheds. It can also be said that the area surrounded by the watershed is the watershed. In the real world, most of the watersheds are mountains or highlands, or they may be gently undulating plains or lakes.
Catchment: Outlet of water flow in a drainage basin. It is generally the lowest point on the watershed boundary.



