The Manage Mosaic Data set includes Browse Footprint Attributes, Add Data, Reassign Path, Build Overview, Dataset check and optimization, Rebuild Bounds, Clear Data, Statistic Infomation, Export Data, Create Image Pyramid, etc.
Browse Mosaic Dataset Properties
Select the Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list, and right-click Browse Footprint Attributes to open the Mosaic Dataset attribute table, which is actually the attribute table of the contour line, in which each record corresponds to a contour object. Contents of main fields in the attribute table:
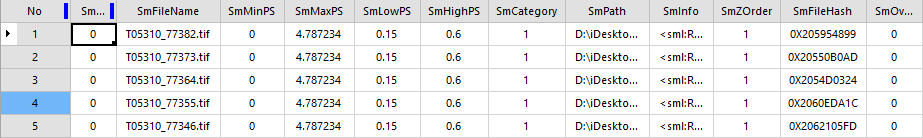 |
| Figure: Property table |
- SmFileName: File Name (excluding extension) added to all Original Images managed in Mosaic Dataset and Overview File Name (including extension).
- SmPath: The full path (absolute path) added to all the original Image Files managed in Mosaic Dataset and the full path of the overview file. These paths support the network share path. Therefore, the shared use of Mosaic Dataset can be achieved by editing this field.
- SmCategory: used to identify whether the currently displayed image within the image outline is the original Image Files or the overview. 1 indicates the original Image Files; 2 indicates the overview.
- SmMinPS and SmMaxPS: are obtained from LowPS/HighPS calculations. These two values are used to control the resolution of the grid used to create the dynamic mosaic image when the image is displayed. Generally, if there is no overview, the SmMinPS value is 0 and the SmMaxPS value is HighPS * 10. For example, if the multi-spectral band SmLowPS = 8m and SmHighPS = 16m, then SmMinPS = 0 and SmMaxPS = 160. The unit of SmMinPS/SmMaxPS is the map unit. If the map is a longitude and latitude coordinate system, the unit of value is degrees. If the map is a Projected Coordi Nate System, the unit of value is meters.
- SmLowPS and SmHighPS: Read from Raster Data to define the minimum and maximum resolution that Raster Data contains. The unit of the data value is different according to the Mosaic Dataset coordinate system. For the longitude and latitude coordinate system, the unit of the data value is degree; for the Projected Coordinate System, the unit of the data value is meter. For example, for the data of multi-spectral and panchromatic bands of Gaofen-1, the resolution of multi-spectral band of Gaofen-1 is 8 meters, and the resolution of panchromatic band is 2 meters. In the absence of pyramid, SmLowPS/SmHighPS values in the attribute table are equal. After Create Pyramid, the LowPS value is the base resolution, and the HighPS value represents the resolution of the top pyramid pixel. Therefore, for the multi-spectral band of Gaofen-1, the base resolution is 8m, and the top pyramid pixel resolution is 16m; for the panchromatic band, the base resolution is 2m, and the top pyramid pixel resolution is 16m.
- SmZOrder: The default value is 1. The user can modify the value of this field to control the Display Order of the image. The Display Order of the conventional image is displayed in the reverse order of SmID. Please refer to the Display Order settings for details.
Add Image
After completing the Build Mosaic Dataset, proceed to add.tif.tiff.imgImage Files to the current Mosaic Dataset.
Function Entry
Right-click Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list and select Change Mosaic Dataset-> Add Image to add new Image Files on the Add Mosaic Data dialog. In the toolbar area, the Add Image tool button is provided, which can be added in the form of single file, folder and folder list. After the Image file list is added, information such as the Image File Path is written to the Mosaic Dataset.
Create Image Pyramid
For Mosaic Dataset Create Image Pyramid, the purpose is to improve the display efficiency of a large number of Image Data. The program will construct a multi-layer pyramid for the Original Image according to certain rules, and display the pyramid image of the corresponding resolution at different scales. In addition, during Mosaic Dataset Build Overview, all images in Mosaic Dataset must be required to have pyramids to improve the speed of Data Browse.
Function Entry
Right-click Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list and select Optimize Mosaic Image Set-> Create Image Pyramid to open the Create Image Pyramid dialog.
Parameter Description: Set the parameters of the Create Image Pyramid, including Resampling Method, Encode Type, number of tasks, and whether to Use GDAL.
- Resampling Method: The program provides the following resampling methods:
- Nearest, take the nearest pixel value in the input Raster Dataset as the input value, and assign it to the corresponding pixel of the output Raster Dataset.
- Average, calculate the average of all valid values for resampling calculation.
- Gaussian Kernel, use the Gauss Kernel method for resampling, which is better for images with high contrast and obvious pattern boundaries.
- Average Complex Data, Average Magphase in a magphase space, a resampling method for an image in a complex data space.
- Bilinearity: Assign the Weighted Mean values of the 4 nearest pixel values in the input Raster Dataset to the corresponding pixels in the output Raster Dataset. The result of this method is smoother than Nearest, but it changes the original grid value.
- Cubic Convolution: Similar to Bilinear, the Weighted Mean values of the 16 nearest pixel values in the input Raster Dataset are assigned to the corresponding pixels in the output Raster Dataset. The processing result of this method is the clearest, and the boundary of Raster Data will be sharpened, but the amount of calculation is large and the processing time is long.
- Cubic Linearity: Cubic Linearity is based on the Akima interpolation algorithm. The Akima interpolation method requires interpolation between two measured points. In addition to the two measured values, the observed values of the four measured points adjacent to the two points are also used. That is, using Cubic Linearity to resample the pixel values in the input Raster Dataset, a total of six pixel values need to be considered. The algorithm takes into account the effect of the derivative value of the feature, so the whole interpolation curve is smooth and natural, and will not lead to the unnatural swing of the generated curve.
- Lanczos Sine Resampling: that Lanczos method use a convolution filter that move the origin of the convolution function to the center of each resample, and then multiplies and sums all the value in the input with the value of the convolution function at that location. The convolution function, also known as the Lanczos kernel, is based on the sinc (X) = sin (X * pi)/X function.
- Compression method: The program provides three Encode types: DEFLATE, JPEG and LZW, which can balance the relationship between the display quality of the pyramid and the occupied storage space according to the actual application needs. You can also select NONE to not compress the image. Please refer to the Grid Encode Type for specific instructions.
- Number of Tasks: Set the number of processes participating in the Create Pyramid to make the Create Image Pyramid more efficient.
- Use GDAL: Select the Use GDAL check box to use GDAL for optimization.
Delete Image Pyramid
Generally, images with a large amount of Import Data will Create Image Pyramid. When the Image Dataset is re-edited, the previously created Image Pyramid does not change. At this time, the previous Image Pyramid needs to be deleted and the Image Pyramid needs to be rebuilt.
Function Entry
Right-click the Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list and select Optimize Mosaic Image Set-> Delete Image Pyramid.
Manage Mosaic Dataset
In the Manage Mosaic Dataset, you can select an Image Dataset for which the Image Pyramid is not built with one click and set the Image Pyramid for it. You can also delete the selected Dataset and Export File List.
Function Entry
Right-click the Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list and select Change Mosaic Image Set-> Manage Mosaic Dataset.
Build Overview
In order to improve the display efficiency of Mosaic Dataset, only the mosaic contour is displayed at the default small scale, and the Original Image is not displayed.
Function Entry
Right-click Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list and select Optimize Mosaic Dataset-> Build Overview to open the Build Overview dialog.
Parameter Description: Set the maximum width, maximum height, sampling factor and Export Directory of the overview.
 |
| Figure: Comparison of Gland with No Value |
- Maximum Width and Height: Maximum width and height of the overview Image Files.
- Sampling factor: resolution ratio of two adjacent layer overviews.
- Export Directory: storage path of overview Image Files.
- Remove no-value gland: There may be black edges caused by the gland of the no-value area and the value area at the multi-scene image splicing. When creating the overview, you can specify the no-value value. After the Build Overview, you can get the correct gland area Display Effects.
The Mosaic Dataset Build Overview is to reconstruct a multi-layer pyramid for the Original Image according to a certain rule for display at a small scale. After the general view is constructed, Image Files will be generated under the general view Export Directory. In addition, in the attribute of the outline child Dataset, a profile related record is added, including information such as the file name and path of the profile Image Files, and the Image Files Resolution.
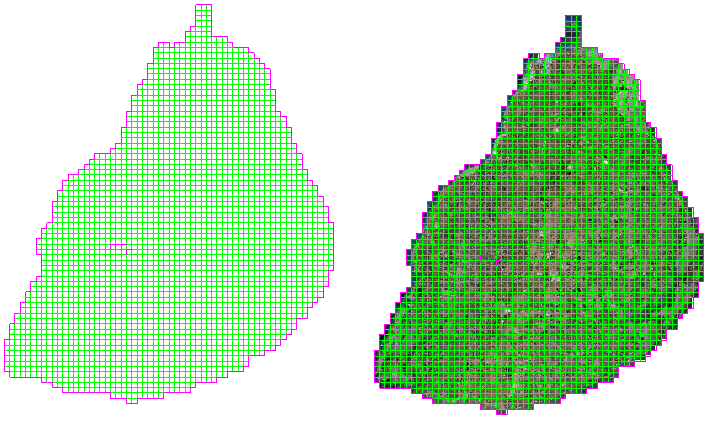 |
| Figure: Added profile view record in profile attribute table |
Note: After the Mosaic Dataset creates the overview view, the overview view cannot be seen when the Mosaic Dataset is zoomed to a very small scale. Because the display of the Mosaic Dataset overview is controlled by the SmMinPS/SmMaxPS field values, the Mosaic Dataset is not displayed when the resolution of the display grid is greater than SmMaxPS value.
If the user needs to view data at a very small scale due to large Layer Bounds and many mosaic images, the user can modify the values of the " SmMinPS and SmMaxPS" fields in the contour attribute table so that the SmMaxPS value is still greater than grid display resolution at a small scale.
Dataset check and optimization
Quickly check and optimize the data of Mosaic Dataset, such as whether it is block storage, Whether to create Image Pyramid, and whether Compression method is set.
Function Entry
Right-click Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list and select Optimize Mosaic Dataset-> Check and Optimize Data to open the Check and Optimize Data dialog. The table on the left side of the dialog shows the Current Data of the Mosaic Dataset.
Optimization Setting Parameter Description
- Block Storage and Compress: Select this check box to perform optimization processing for block storage and compression types. Save Image using Block Storage can improve the speed of loading and browsing Image Data and the Data Processing efficiency of Optimize Mosaic Dataset. The storage mode of
image is divided into scan line storage, strip storage and block storage. According to different storage modes, the reading mode is also different:
- Read
- with scan lines, the system reads one line at a time; Read
- in strips, and the system takes out N rows at a time according to the specified strip width N; Read
- by block storage, and the system takes out N blocks of data at a time according to the specified number of blocks N.
Take reading 2560 × 2560 images as an example:
- 2560 times are read
- in the scan line mode, and the size of data read at one time is 1 * 2560;
- In the form of stripe, the number of times to be read is 2560/N, and the size of data read at one time is 2560 × N. The larger N is, the more memory will be occupied, which will have a certain impact on the reading speed.
- In the way of block storage, the image is divided into 100 256 × 256 blocks. The system needs to read 100 times at most, and the size of the data read each time is 256 × 256, which shortens the Display Time and improves the reading efficiency. Compared with the above two methods, block storage is the optimal storage method.
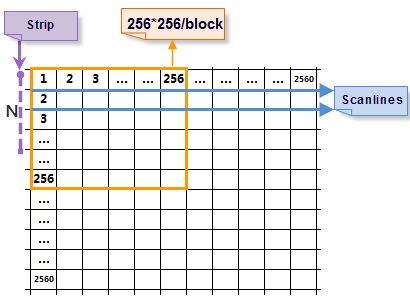
Image: 2560 × 2560 image - Compression Type: The program provides two Encode types, JPEG and LZW, which can be selected according to the actual application needs.
- Image Pyramid: Select the check box to Create Image Pyramid.
- Resampling Method: When the Image Pyramid check box is selected, the Resampling Method can be selected. Please refer to the Introduction to Resampling Method. For specific instructions.
- Use GDAL: Check this box to use GDAL for optimization.
- Number of tasks: Support the setting of starting multiple processes to perform optimization processing. The number of tasks needs to be set according to the configuration of the machine and the usage of the processes. The default is the number of processes available when the system is running divided by 2.
Reassign Image Path
If the Original ImageFile Position in the Mosaic Dataset is changed or the path for generating the overview view needs to be re-assigned, the File Position path can be changed through Reassign Path.
Function Entry
Right-click Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list, and select Change Mosaic Dataset-> Re-assign Image Path to open the Re-assign Image Path dialog box. There is already a path to the file in the File List in the Change Mosaic Dataset of the dialog.
 Caution:
Caution: When you Reassign Image Data set path, it must be a full path.
Clear Data
Function Entry
Right-click Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list and select Clear Data to open the Clear Data dialog.
You can select Remove all records from moscia dataset, including overviews. Delete All data. You can also select Only Delete Overviews to delete the created overview from the Dataset.
Rebuild Bounds
When the data in Mosaic Dataset changes, for example, some images are deleted, new images are added, and Clip Bounds exist in the image, click this function to Mosaic DatasetRebuild Bounds. For the application of Rebuild Bounds, see Image Map Configuration-Rebuild Layer Bounds.
Function Entry
Right-click Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list, and select Change Mosaic Dataset-> Re-scope to open the Re-scope dialog box.
Parameter Description
The Rebuild Bounds dialog box provides three range update options: Rebuild Footprint, Rebuild Boundary, and Rebuild Clip Bound. Users can select one or more ranges to update.
- Rebuild Footprint: Select this check box to rebuild the Mosaic Dataset outline range.
- Rebuild Boundary: Select the check box to rebuild the boundary range of the image. Rebuild Bounds can be set in three ways: Auto calculation of boundary bounds., Select Dataset Bounds, and Custom Bounds.
- Auto calculation of boundary bounds.: The system is based on the Image DataAuto calculation of boundary bounds.
- Select Dataset Bounds: Rebuild Bounds through Region Dataset in Select Datasource.
- Custom Bounds: Determine Scope of update by Draw Bounds and Select Object. Click the Drop-down Button on the right side to select the border Scope of update in two ways: Draw Bounds "and Select Object".
 Caution:
Caution: Because the creation of the overview also uses the crop area of the image, if you rebuild Clip Bounds, you can consider whether to rebuild the overview based on the display needs of the overview.
Compute Statistic Data
The Compute Statistic Data is Data Preparation for Show Settings and different Stretch methods of Mosaic Dataset. Statistical mosaic data information is required to set Stretch method. If there is no Statistic Infomation, when setting Mosaic Dataset to display Stretch method, The system will pop up a prompt box to prompt Statistical mosaic data information.
Function Entry
Right-click Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list, and select Change Mosaic Dataset-> Compute Statistic Data. The program will count the maximum, minimum, mean, standard deviation, variance and other information of the images in Mosaic Dataset one by one. Each image generates a separate Statistic Infomation file (*.xml) in the folder where the image is stored. The File Name is the same as the Image File Name.
Export Data
Function Entry
Right-click Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list and select Export Data to open the Export Mosaic Data dialog.
Parameter description: The program provides two export methods: Export File and Export File List. Users can select an export form according to their needs. Both export methods support setting the following parameters:
- Select Range: You can set the range of Export File or file list. By selecting Whole Map, Current Windows, Custom Bounds (Select Object or Draw Rectangle), and by copying and pasting the coordinate values of the existing range. It should be noted that Draw Bounds must ensure that Mosaic Dataset is in the map open state. Select Object requires a face Dataset Select object in the current Map to be available.
- Parameter Settings: The program provides two export types: Export Attached File and Export Overview. You can select one or both. That is, when the Export File mode is selected, the Image Data and overview data in Bounds Settings will be exported. If Export File List is selected, the File List of Image Data and the File List of Overview in Bounds Settings will be exported.
- Result Data: Set Export Directory for Export Data.
Balance Mosaic Dataset Colors
The Balance Mosaic Dataset Colors specifies a standard image as the Target Dataset to guide the color balance, and the Mosaic Dataset will be color-corrected according to the standard image, so that the images can be displayed seamlessly.
Function Entry
Right-click the Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list and select Change Mosaic Dataset-> Balance Mosaic Dataset Colors.
In the Balance Mosaic Dataset Colors dialog, set the following parameter information:
- Standard image path: Set the path information of the standard image.
- Color balancing method: Select a method for changing the color of an image. The Histogram Method and the Homing Method are available. The Histogram Method is to correct the color of Mosaic Dataset according to the histogram information of the standard image; the Homogenization Method is to correct the color of Mosaic Dataset by setting the variance expansion coefficient and Brightness coefficient.
- Variance expansion coefficient: it can be set when the uniform method is selected. When the Brightness coefficient is constant, if the variance is equal to 1, the image contrast effect is constant and consistent with the contrast effect of the Reference image; if the variance is less than 1, the contrast of the Result image decreases with the decrease of the variance value.
- Brightness coefficient: can be set when the dodging method is selected. When the variance expansion coefficient is constant, if the pixel mean value of Reference Image is greater than pixel mean value of Original Image, the Brightness coefficient is larger. The higher the brightness of the Result image is; if the average value of the pixels of the Reference image is less than that of the Original image, the higher the Brightness coefficient is, the lower the brightness of the Result image is.
Clear Color Balance
Clear Color Balance removes the set flat Mosaic Dataset color and restores the original color of the Mosaic Dataset.
Function Entry
Right-click the Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list and select Change Mosaic Dataset-> Clear Color Balance.
Create Histogram
For Mosaic Dataset Create Histogram, it can reflect the data characteristics of Mosaic Dataset and determine the Stretch Display effect of Dataset. The histogram is created for All File in Mosaic Dataset. If part of the image contains the histogram and part of the image does not contain the histogram, a prompt dialog box will pop up when using the Create Histo gram, "Part of the image already contains the histogram, Rebuild?"? " ? Select Yes to Create Histo gram all images, overwriting the original contents; select No to Create Histo gram only images without histograms.
There is no access to view the histogram.
Function Entry
Right-click the Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list and select Optimize Mosaic Dataset-> Create Histo gram.
Rebuild Spatial Index
In the Spatial Index Manager dialog box, you can view, create, and modify the Spatial Index of a Dataset.
Function Entry
Right-click the Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list and select Optimize Mosaic Dataset-> Rebuild Spa tial Index.
Crop Display Range
Crop Display Range is used to set the Visible Bounds of the current Map:, Select Objects, Draw Rectangle, Draw Circle and Draw Polygon Show Settings are provided. You can also delete the Crop Display Range with the Clear button. Please refer to the Crop the display image for specific operation.
Function Entry
Right-click the Mosaic Dataset in the Datasource list and select Change Mosaic Dataset-> Crop Display Range.
Related topics



