Chart Data conversion, display and publishing are closely related to the storage structure of S-57 Electronic Chart data. Next, the storage structure of Chart Data is introduced through the relationship between the feature object and the space object and the chart Topology.
Characteristic Object and Space Object
In the S-57 standard, entities in the real world are expressed in the form of sets of descriptive attributes and spatial attributes, and the sets of the two attributes are defined as characteristic objects and spatial objects. A feature object is an object that has a real-world entity other than Position Info. Feature objects contain descriptive attributes (Attributes that describe the kind, nature, characteristics, etc. Of the entity) but do not have any Geometric properties (such as information about the shape and location of real-world entities). Spatial object refers to the object with real world entity Position Info, which is mainly used to describe the spatial position characteristics of the entity. The feature object is located by its relationship with one or more space objects, and may not exist with reference to the space object, but each space object must refer to a feature object, as shown in the following figure:
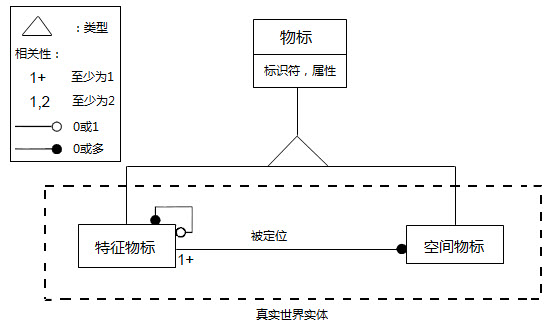 |
| Relationship between characteristic object and spatial object |
Chart Topology
In SuperMap iMaritimeEditor, the Chart Data model is based on the S-57 digital hydrographic data transmission standard, which defines the real-world entity as a combination of feature and spatial objects. That is to say, spatial objects (points, lines and surfaces) are used to express objects. Each object not only contains Attributes, but also expresses Spatial Info such as geometric shape and position. At the same time, it also stores the Topology information of space objects and charts.
S-57 classifies the description of the spatial characteristics of real-world entities into three types: vector, grid, and matrix. Among them, the vector space object is described, and its spatial relationship can be divided into four topological levels: no topology, chain node, planar graph and complete topology. The Topology of a chart describes the rules for how a feature object refers to a spatial object to determine its own Spatial Info. The SuperMap iMaritimeEditor uses the specified topology level for making ENC data: chain node topology, as shown in the following figure. In the topology level, the space object includes isolated nodes, connecting nodes and edges, and specifies that the point object refers to isolated nodes or connecting nodes, the linear object refers to the sequence of edges and connecting nodes, and the area object refers to the closed loop of edges starting and ending from the same connecting node. Three types of spatial objects and the reference information of the characteristic objects to the spatial objects are stored, so that the chain node Topology of the chart is established.
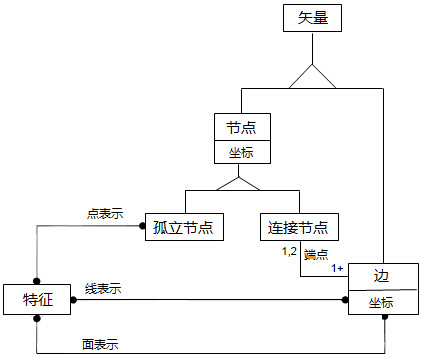 |
| Chain node model |
Chart Data Storage Structure
S-57 Electronic Chart adopts the data structure of link node topology and takes ISO/IEC 8211 as the encapsulation standard of its data structure, which is quite different from the hierarchical storage of GIS.
In Order to facilitate the data interaction between SuperMap data and S-57 file, the traditional GIS data hierarchical storage method is used, that is, the point, line, surface and attribute Dataset are used to store the characteristic object. The association relationship and the set relationship between the feature object objects and the reference relationship between the feature object objects and the space object objects are stored in an attribute table recording manner. However, because Chart Data contains a wealth of feature objects, based on the S-57 standard data model and the hierarchical storage structure of GIS data, a Dataset corresponds to a feature Object Type, resulting in a chart often contains hundreds or more Datasets, which is not easy to use. Therefore, Dataset Group is used to manage Chart Data. In this way, the efficient Spatial Database engine can ensure the correct storage of S-57 data and the republication of modified data.



